![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
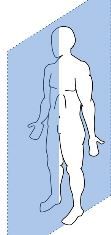
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts
|
Saggital (Median) Plane |
|
|
A saggital plane that lies exactly in the midline.
|
Midsaggital Plane |
|
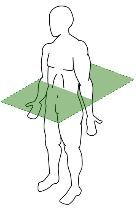
A plane that runs horizontally from right to left, dividing body into superior and inferior parts.
|
Transverse (horizontal) Plane |
|
|
All other sagittal planes, offset from the midline.
|
Parasagittal Plane |
|
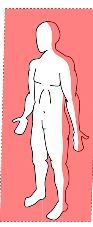
A vertical plane at a right angle to the midsagittal plane which divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
|
Frontal (coronal) Plane
|
|
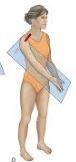
A slanted or at an angle plane?
|
Oblique Plane |
|
|
What is the anatomical position?
|
-Subject standing erect & facing forward -upper extremities at sides w/palms of hands facing forward -Feet flat on floor w/toes pointing forward |
|
|
Position term for: Toward the head end or above?
|
Superior (cranial) |
|
|
Position term for: Away from the head end or toward the lower part of structure.
|
Inferior (Caudal) |
|
|
Position term for: Toward or at the front of the body? |
Anterior (Ventral)
|
|
|
Position term for: Toward or at the back of the body? |
Posterior (Dorsal) |
|
|
Position term for: Toward or at the midline of body, on the inner side of.
|
Medial |
|
|
Position term for: Away from the midline of the body, on the outer side of. |
Lateral |
|
|
Position term for: Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
|
Proximal |
|
|
Position term for: Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
|
Distal |
|
|
Position term for: Toward or at the body surface?
|
Superficial |
|
|
Position term for: away from the body surface, more internal
|
Deep |
|
|
Body cavity that contains the brain?
|
Cranial Cavity |
|
|
Body cavity that contains the spinal cord
|
Vertebral Cavity |
|
|
Muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities?
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
What body cavity is enclosed by the ribs, sternum, and vertebral column?
|
Thoracic Cavity |
|
|
What body cavity contains the heart?
|
Pericardial Cavity |
|
|
What body cavity contains the lungs? |
Pleural Cavity |
|
|
What is the central area within the thoracic cavity?
|
Mediastinum |
|
|
What body cavity contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities?
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity |
|
|
What body cavity is between the diaphragm and the brim of the pelvis?
|
Abdominal Cavity |
|
|
What body cavity contains the reproductive organs and urinary bladder?
|
Pelvic Cavity |
|
|
What body cavity contains the cranial cavity and spinal column?
|
Posterior (Dorsal) body cavity |
|
|
What body cavity consists of the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity?
|
Anterior (Ventral) body cavity
|
|
|
What is the study of "to cut apart"?
|
Anatomy |
|
|
What is the study of the function of the body structures?
|
Physiology |
|
|
What is the study of microscopic structures of the tissues?
|
Histology |
|
|
What is the study of the structure and function of cells?
|
Cytology |
|
|
What is gross anatomy?
|
Anatomy that is visible to naked eye
|
|
|
What is systemic anatomy?
|
Gross Anatomy that is by organ systems |
|
|
What is regional anatomy?
|
Gross Anatomy that is by body regions |
|
|
A process that is used o find answer to question about the world around us?
|
Scientific Method |
|
|
What are the steps to scientific method?
|
2: Question 3: Hypothesis 4: Prediction 5: Experiment 6: Conclusion |
|
|
What biological level of organization is all body systems functioning interdependently in a single living human?
|
Organism |
|
|
What biological level of organization is two or more organs whose separate function are integrated in the performance of a specific task?
|
Organ systems |
|
|
What biological level of organization is two or more tissue types that work together to perform specific, complex functions? |
Organs |
|
|
What biological level of organization is a group of similar cells with a common function?
|
Tissues |
|
|
What are the 4 different tissues?
|
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous tissue |
|
|
What biological level of organization that is the smallest living structures?
|
Cells |
|
|
What biological level of organization is membranous sacs or other compartments that separate different metabolic reactions inside the cell?
|
Organelles |
|
|
What biological level of organization is a unit of two or more atoms of the same or different elements bonded together. example is proteins
|
Macromolecules |
|
|
Name three organs of the Integumentary System?
|
Skin, hair & sweat glands |
|
|
Name two functions of the integumentary system?
|
Provides a physical barrier and prevents water loss
|
|
|
Name 3 organs of the Skeletal System?
|
Bones, Cartilage, Ligaments |
|
|
Name 2 functions of the Skeletal system?
|
Provides supporting framework and site for muscle attachment
|
|
|
Name 3 organs of the Muscular System?
|
skeletal, cardiac, smooth muscles |
|
|
Name 2 functions of the Muscular System?
|
Produces body movement and holds your abdominal organs in place |
|
|
Name 3 organs of Nervous System?
|
Brain, Spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
|
|
|
Name 2 functions of the Nervous System?
|
Memory and motor commands to muscles
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of the Endocrine System?
|
Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid gland |
|
|
What are 2 functions of the Endocrine System? |
Regulate body homeostasis and reproductive functions
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of the Cardiovascular System?
|
Heart, artery, & veins |
|
|
What are 2 functions of the Cardiovascular System? |
Heart pumps blood in one-directions through system and generates pressure to drive blood through blood vessels
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of Lymphatic System?
|
Thymus, spleen and tonsils |
|
|
What are 2 functions of Lymphatic System?
|
Carries interstitial fluid back to the bloodstream and generates an immune response
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of the Respiratory System?
|
Lungs, pharynx, trachea |
|
|
What is 2 functions of the Respiratory System?
|
Pulmonary ventilation and sound production |
|
|
What are 3 organs of the Digestive System?
|
stomach, small and large intestine |
|
|
What is 2 functions of the Digestive System?
|
Mechanically and chemically digest food
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of the Urinary System?
|
kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra |
|
|
What are 2 functions of the Urinary System?
|
Filters the blood and excrete urine |
|
|
What are 3 organs of the male Reproductive System?
|
Testes, prostate gland, penis
|
|
|
What are 2 functions of the male Reproductive System?
|
To produce sperm and sex hormones
|
|
|
What are 3 organs of the female Reproductive System?
|
Ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes |
|
|
What are 2 functions of the female Reproductive System?
|
To produce eggs and produce sex hormones |
|
|
What are the five parts to the human body plan?
|
2. Dorsal, hollow nerve cord 3. Segmented 4. Tube within a tube construction, cavities 5. Bilaterally symmetrical |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Esophagus?
|
Mediastinum |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Trachea?
|
Mediastinum |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Heart? |
Pericardial Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Stomach? |
Abdominal Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Uterus?
|
Pelvic Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Colon?
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Liver? |
Abdominal Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Kidneys? |
Abdominal Cavity
|
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Urinary Bladder? |
Pelvic Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Spleen?
|
Abdominal Cavity
|
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Adrenal Glands?
|
Abdominal Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Pancreas?
|
Abdominal Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Lungs? |
Pleural Cavity |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Brain?
|
Cranial Cavity
|
|
|
The human head is ____ to the neck.
|
Superior |
|
|
The elbow is ____ to the wrist.
|
Proximal
|
|
|
The neck is ____ to the head. |
inferior |
|
|
The eye is ______ to the nose |
superior & lateral
|
|
|
The mouth is _____ to the ear |
inferior & medial & anterior |
|
|
What is the specific body cavity for Thymus?
|
Mediastinum |
|
|
The fingers are ___ to the wrist
|
distal |
|
|
The stomach is ___ to the spine
|
anterior |
|
|
The heart is ___ to the stomach |
superior |
|
|
The upper arm is ___ to the forearm?
|
proximal |
|
|
The bridge of the nose is ___ to the left eye
|
medial |
|
|
The eye is ___ to the nose?
|
lateral |
|
|
The neck is ____ to the shoulder
|
medial |
|
|
The shoulder blades are ___ to the ribs
|
posterior |
|
|
The ankle is ___ to the knee
|
distal |
|
|
The sternum is ___ to the spine
|
anterior |
|
|
The kidneys are ___ to the small intestine |
posterior |
|
|
The thyroid gland is ___ to the thymus gland
|
superior |
|
|
The heart is ___ to the arms
|
medial |
|
|
The lungs are ___ to the rib cage
|
deep |
|
|
The skin is ___ to the skeleton
|
superficial |
|
|
The skin is ___ to the muscles
|
superficial |
|
|
|
|

