![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
series |
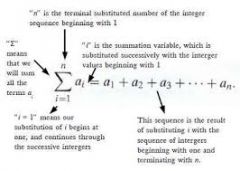
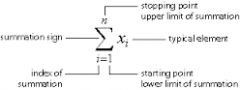
the sum of the terms of a sequence |
|
|
|
finite series |
a series with defined first and last terms |
|
|
|
infinite series |
a series that continues indefinitely |
|
|
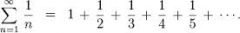
|
harmonic series |
divergent infinite series named for the concept of overtones in music |
|
|
divergent series |
an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a finite limit. |
|
|
|
convergent series |
a series that is not divergent, meaning that the sequence of the partial sums of the series approach a limit under certain conditions. |
|
|
|
sequence |
string separated by commas |
|
|
|
analysis |
the study of limits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
trivial factor |
the number itself and one. |
|
|
|
proper factor |
all factors that are not the number itself or one. |
|
|
|
prime number |
a number with no proper factors |
|
|
|
Eucllid's proof of the infinitude of primes |
Suppose N is prime. Form the number (1 x 2 x 3 x ... x N)+1. This number doesn't divide exactly by any number from 1 to N; there is always remainder 1. So either it has no proper factors-and therefore is itself a prime larger than N-or its smallest proper factor is some number larger than N. |
|
|
|
argument |
the specific input of a function, also called the independent variable. |
|
|
|
function value |
the result associated to a value of its argument (also called variable of the function). |
|
|
|
function |
the application of some rule or procedure to an argument and its output. |
|
|
|
domain |
the set of argument values for which the function is defined. |
|

