![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
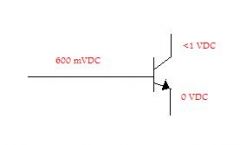
What state is this transistor in?
|
Saturation
|
|
|
A transistor with input current on the Emitter and output current on the Collector uses which gain relationship?
|
ALPHA
|
|
|
A transistor with input current on the Base and output current on the Collector uses which gain relationship?
|
BETA
|
|
|
A transistor with input current on the Base and output current on the Emitter uses which gain relationship?
|
GAMMA
|
|
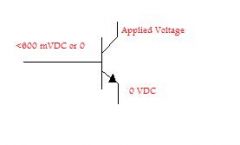
What state is the transistor in?
|
Cut-Off
|
|
|
Common Amplifier with high current gain?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
If the impedance of both the source and the load are exactly matched, it is known as ___________ __________?
|
Impedance Matching
|
|
|
When determining the static values of common emitter divide the amplifier into two of these?
|
Voltage Dividers
|
|
|
This Amplifier's input is applied to the base and the output is found on the collector?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Collector is also known as_____________ _________?
|
Emitter Follower
|
|
|
This Common Amplfier has an output of 180 degree phase shift from it's input?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
The common base amplifier is also used as this type of amplifier in high frequency applications?
|
Buffer
|
|
|
Common amp with input on emitter and output on the collector?
|
Common Base
|
|
|
Current relationship with collector over emitter?
|
ALPHA
|
|
|
Current relationship with emitter over base?
|
GAMMA
|
|
|
What component can be added to the emitter leg to decrease gain?
|
Swamping resistor
|
|
|
Current gain is figured by the________ over ________?
|
Output over Input
|
|
|
This is a linear representation of the current relationship in a transistor and determines where the quiescent point of operation is?
|
Load Line
|
|
|
Which class of amplifiers has a quiescent current that is exactly half of its saturation value therfore maintaining an out put that never reaches cut-off or saturation?
|
Class A
|
|
|
How true the output signal is compared to the input signal is known as ______________?
|
Fidelity
|
|
|
Which class of amplifier has a base bias less than cut-off?
|
Class C
|
|
|
Which class of amplifier has a base bias that is the same as cut-off?
|
Class B
|
|
|
Which class of amplifier has a base bias that is slightly higher than cut-off?
|
Class AB
|
|
|
Which biasing circuitry is primarily used as a switch either enabling or disabling a signal?
|
Fixed
|
|
|
Which Biasing circuitry maintains a constant output throughout rapid signal variations and is the most common?
|
Combination
|
|
|
Which type of biasing is used for amplification, is very stable but uses two power supplies?
|
Emitter Bias.
|
|
|
Which type of biasing is used for amplification, is best for heat dissipation?
|
Self Bias
|
|
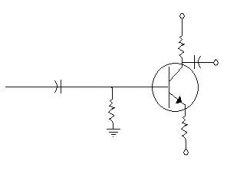
Which Biasing type is this?
|
Emitter Bias
|
|
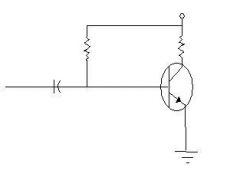
Which biasing is this?
|
Fixed
|
|
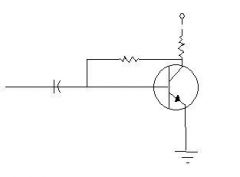
Which biasing is this?
|
Self Biasing
|
|
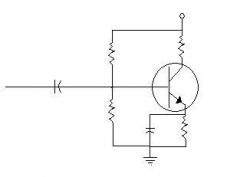
What type of biasing is this?
|
Combination Biasing
|
|
|
Common Amp with High Voltage gain?
|
Common Base
|
|
|
Common Amp with High input impedance?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
Common Amp with medium power gain?
|
Common Base and Common Collector
|
|
|
Common Amp with low current gain?
|
Common Base
|
|
|
Common Amp with low input impedance?
|
Common Base
|
|
|
Common Amp with high power gain?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Amp with medium voltage gain?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Amp with medium input impedance?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Amp with medium output impedance?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Amp with medium current gain?
|
Common Emitter
|
|
|
Common Amp with high current gain?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
Common Amp with high input impedance?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
Common Amp with low voltage gain?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
Common Amp with high output impedance?
|
Common Base
|
|
|
Common Collector uses this gain relationship?
|
GAMMA
|
|
|
Common Base uses this gain relationship?
|
ALPHA
|
|
|
Common Emitter uses this gain relationship?
|
BETA
|
|
|
When a transistor is not properly biased and is not conducting current, it is said to be in ___________ condition?
|
Cut-Off
|
|
|
This is the term for a voltage potential applied to the base that is more than or equal to the knee voltage, enables the forward biasing from the base emitter?
|
Transistor Base
|
|
|
This part of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is heavily doped so that it can pass a large quantity of current carriers?
|
Emitter
|
|
|
This part of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is very thin and lightly doped so that it will pas most of the electrons?
|
Base
|
|
|
This part of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is moderately doped but is the largest in area so that it can dissipate the heat developed by electron flow?
|
Collector
|
|
|
Creating a larger signal is known as?
|
Amplification
|
|
|
Transistors are said to be controlled by _________?
|
Current
|
|
|
The two types of transistors?
|
Field-Effect Transistor (FET) and Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
|
|
|
When a transistor is properly conducting and considered to be in a static state is known as________?
|
Quiescence
|
|
|
The amount by which an electrical signal is increased or decreased?
|
Gain
|
|
|
The number of electrons on the valence shell of a semiconductor?
|
4
|
|
|
Solid state devices are used for?
|
Rectification (AC to DC w/ Diodes)
Amplification Oscillation Timing Switching Sensing |
|
|
The two types of current flow are?
|
Electron flow (- to +)
Hole Flow/ conventional flow (+ to-) |
|
|
The two most common semiconductors?
|
Silicon Si
Germainium Ge |
|
|
On an analog meter a diode will show a relationship of ________ to ________ from reverse to forward bias?
|
10 to 1
|
|
|
The two types of Bipolar Junction Transistors are?
|
Positive Negative Positive (PNP arrow pointed in)
Negative Positive Negative (NPN arrow not pointed in) |
|
|
In schematics what letter stands for a transistor?
|
Q
|
|
|
On BJT controlling current is on the____________?
|
Base
|
|
|
On BJT controled current is on the____________?
|
Collector
|
|
|
An NPN transistor needs what to operate?
|
Transistor Base Voltage
Base-Emitter Forward Bias Collector Current |
|
|
When an transistor has base voltage, base-emitter forward bias, and collector current it is said to be in __________ state?
|
Quiescence
|
|
|
What is the current relationship for the DC biasing current?
|
Emitter=100%
Collector=95%-98% Base=2%-5% |
|
|
Impedance matching device used to match a low impedance load?
|
Common Collector
|
|
|
When frequency is too low _______ reduces gain?
|
Capacitor
|
|
|
When frequency is too high _______ reduces gain
|
Transistor
|
|
|
_________ amps are special amps that use two transistors biased class B to accurately transfer the input power to the load with the best efficiency.
|
Push Pull
|
|
|
Charecteristics of a push pull amp ?
|
Low Distortion
Low output Impedance High current gain High Effeciency |
|
|
The common emitter configuration of the push-pull amplifier utilizes the advantages of what impedance matching components
|
Transformers
|
|
|
Both transistors of a push-pull are biased at ________
|
Cut-off
|
|
|
The design of the push-pull amplifiers eliminates _________ to a minimum?
|
Cross-over Distortion
|
|
|
Common collector push pull amplifiers are also known as_________.
|
Complimentary symmetry
|
|
|
Complimentary symmetry push-pull amplifiers' transistors are_______?
|
1 pnp
1 npn |
|
|
Common emitter push-pull amplifiers' transistors are _________?
|
2pnp or 2npn
|
|
|
What do coupling caps do in an amplifier circuit?
|
Allow AC to pass and block DC
|
|
|
If gain is unknown of a cascade amplifier it is assumed to be__________?
|
10
|
|
|
________ can cause a change in quiescence values and amplification.
|
Loading
|
|
|
T/F
The output of one amplifier providing the input to another amplifier is called cascade? |
True
|
|
|
__ ______ is the most common method of coupling, is inexpensive.
|
RC Coupling
|
|
|
What are the two major concerns of a high gain amplifier?
|
Stability and predictability.
|
|
|
The transistor and its associated components in a cascade amplifier are known as ___________?
|
stage
|
|
|
What are the four types of coupling methods used for multistage amplifiers
|
RC, LC, Transformer, Direct
|
|
|
Which coupling method has superior impedance mathching and is used for isolation?
|
Transformer
|
|
|
Low frequency coupling method is?
|
Direct
|
|
|
Many voltage regulators in today's fast evolving electronics world have become _________
|
Integrated (Zener and transistor)
|
|
|
Name the different circuits of a power supply, explain the waveform and give the primary component.
|
Input= AC wave/AC wave, Transfomer
Rectifier= AC wave/Pulsating DC, Diode Filter= Pulsating DC/Ripple DC Capacitor/Inductor Regulator=Ripple DC/Smooth DC Zener Diode, Transistor Protection=Smooth DC/Smooth DC Fuse or Circuit Breaker. |
|
|
It is often an adantage to use a ____________ in a regulator circuit to handle higher current restrictions an linear operation to maintain a more constant output voltage.
|
Transistor
|
|
|
___________ provide control of output voltage.
|
Zener Diode
|
|
|
____________ circuit maintains a contant outputvoltage within certain pre-defined limits.
|
Regulator
|
|
|
The regulator circuit elimnate voltage ____________ caused by input or load.
|
Variation
|
|
|
List the four charecteristics of a zener diode.
|
Semi conductor material
Work in reverse bias Used as regulators Provide control for output voltage |
|
|
What is different about R1 in a Voltage Regulator and Current Regulator?
|
Voltage Regulator R1 in Parrellel
Current Regulator R1 in Series |
|
|
A circuit that prevents further damage to the external circuit and prevents damage to the power supply is know as a ____________.
|
Current Limiter
|
|
|
A__________ is a signal device that uses two transistor.
|
Darlington Pair
|
|
|
In a darlington pair, the difference in _________ between the base and emitter is 1.2.
|
Voltage
|
|
|
The final collector current through a darlington pair to equal to a factor of ________.
|
beta squared
|
|
|
When _____________ occurs, regulation is lost because it is impossible to hold both voltage and current constant under changing load conditions.
|
Fold-Back
|
|
|
Any sigle transistor or darlington pair that is conected in series to the load so all the current must go throught it is know as a _______________.
|
Pass Transistor.
|
|
|
The first resistor in current regulator is in________ and is used as a _________ resistor.
|
Series, Sensing
|
|
|
What are the four troubleshooting groups on card 97? What order do you check them?
|
Darlington Pair 1st
Differential Amp 2nd Reference Regulator 3rd Out Volt. Divider 4th |

