![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Relationship between mass and energy
|
Einstein:
E=mc^2 matter is frozen energy |
|
|
Modern Conservation Law
|
sum total of mass and energy is conserved
|
|
|
How much energy can a tiny mass of sun produce?
|
LOTS OF ENERGY, the sun can remain hot and unchanging for billions of years
|
|
|
How does the conversion of mass to energy occur?
|
1. spontaneously, energy released in the radioactive breakdown of naturally occurring elements like Uranium
|
|
|
Another way of conversion of mass to energy?
|
happens in great effectiveness due to simply because it is HOT there, allows serious of
THERMONUCLEAR REACTIONS |
|
|
How is helium produced in the sun?
|
hydrogen atoms are fused together to make helium, a lump of helium less massive than four hydrogens that were joined together, and the loss in mass appears in energy
|
|
|
HYDROGEN --> HELIUM, cannot happen unless very hot environment? why?
|
hydrogen nuclei, which are protons, repel each other since have same positive electrical charge, PROTONS WILL ONLY FUSE TOGETHER IF THEY CAN BE MADE TO RACE ABOUT AT HIGH SPPED AND SLAM INTO ONE ANOTHER, once they get very close, then another force takes over
|
|
|
Where were the heavier elements created?
|
in stars
|
|
|
Why is the sun SO stable?
|
squeezing makes it hotter in the middle, which increases the sustaining pressure, it also increases the thermonuclear reactions, which releases more energy
|
|
|
Why are the thermonuclear reactions taking place between the nuclei?
|
since the material in the centre of the sun is completely ionized plasma (hot gas where the electrons are stripped off)
|
|
|
What happens in fission?
|
-a big nucleus breaks into two or more smaller pieces
-the sum of the masses of the pieces is less than the original, with the difference showing up in the form of energy |
|
|
What happens in fusion?
|
-two or more small lumps are merged together to form a heavier nucleus
-the new lumps weighs less than the sum of the small pieces, and energy is released |
|
|
Binding energy curve
|
critical point: shape
steepness @ low-atomic number end tell us that merging little pieces (hydrogen to for helium) you get out ALOT of energy -breaking a lump, like uranium into smaller pieces yields less energy but still a lot (atomic bomb) |
|
|
fission occurs...
|
-stay neutron hits the uranium nucleus and makes it unstable
uranium breaks into two big nuclei (Krypton and Barium) and releases two or more neutrons, then sparks another fission |
|
|
What happens if uranium atoms are close together?
|
CHAIN REACTION, release LOTS of energy
|
|
|
What happens if TOO many uraniums in close proximity (more than the critical mass)?
|
reaction is uncontrollable and you have an atomic bomb
|
|
|
Do hydrogen bombs rely on chain reactions?
|
NO.
you have to have ultra-hot material, with colossal release of energy |
|
|
What is the difference between atomic and hydrogen bomb?
|
atomic: accumulate the fuel into a lump that exceeds the critical mass
hydrogen: fuel needs to be heated to millions of degrees before the reaction will start, in fact, the "fuse" in hydrogen bomb is a atomic bomb |
|
|
FUSION products vs. FISSION products?
|
fusion: essentially limitless energy and not produce dirty waste products
fission: dirty waste products since hard to confine gas which is temperature of millions of degrees |
|
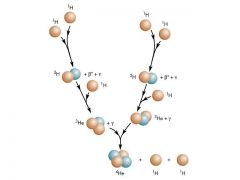
pp/ proton-proton cycle
|
cycle produces positrons ("ant-matter") and neutrinos
|
|
|
What are positrons?
|
carry off positive charge of two of the original protons
-positrons short lived -promptly run into electrons and annihilate completely, forming gamma rays (radiant energy) |
|
|
What are the medical application of positrons?
|
PET (positron emission tomography)
-created by decay of trace elements of radioactive elements introduced into the body |
|
|
Law of the Conservation of Mass and Energy
|
if mass vanishes, an exactly equivalent amount of energy must appear
|
|
|
How much percentage does the sun convert it's mass to energy?
|
less than one percent
|
|
|
How do we know the relative abundance of hydrogen atoms?
|
1. spectrum of the sun
2. composition of things like comets and meteorites 3. composition of the planets Jupiter and Saturn 4. relative abundances of at least the heavier element from moon rocks and earth rocks 5. spectra of other stars and gas clouds |
|
|
Ratio of lithium to hydrogen atoms?
|
10^10 hydrogen atoms for one lithium atom
|
|
|
What elements are rare?
|
heavier elements
|
|
|
"odd-even" effect
|
-carbon is abundant (6) and oxygen (8) BUT nitrogen (7) is less abundant
can be explained: as a consequence of nuclear reaction in stars |
|
|
Where in the sun is the energy generated by nuclear reactions most?
|
91% of energy generated by nuclear reactions occurs within the innermost twenty percent of the sun's radius
|
|
|
How does the energy in the innermost core diffuse out?
|
radiative transport: photons make their way through the material, without the material itself moving much)
|
|
|
How does the energy in outermost parts of the sun diffuse out?
|
convective transport: large churning motions in the material itself, just as in a pot boiling soup
|
|
|
What sort of radiation (light) does it emit?
|
sun emits yellow (visible) light because of its high temperature, whereas your much cooler human body emits infrared radiation
|
|
|
What happens if energy is put into the material? (heat it)
|
1. moderate temperatures: breaking of the inter-atomic or intermolecular bonds , still held together but not in a rigid structured way
2. @500K: molecules and atoms can escape liquids so that the particles are now moving freely as a gas 3. @5000K: temperatures like that at the sun, many atoms are therefore ionized, free moving charged particles typically motions of charged particles give rise to magnetic fields called plasma |
|
|
@ 10million K, where is this temperature found?
|
CORE OF A STAR
all atoms are completely ionized: all electrons are torn off from positively charged nuclei by virtue of vigorous collisions -thermonuclear reactions can take place and a new source of energy can be tapped, the energy source of the stars |
|
|
What is a deuterium?
|
"HEAVY WATER", a hydrogen with an extra neutron
|
|
|
Sun's energy-generation going..
|
keeps a little bit to sustain itself against continuing gravitational contraction
|
|
|
what happens in an atomic bomb
|
1.-lump of fuel, one nuclei spontaneously fissions and large amounts of energy released +couple of neutrons
2. new neutrons individually run into yet another uranium nucleus, chain reaction 3.moderators that control speed of the neutrons to not explode 4.if want explosion, fissionable material which exceeds the so-called critical mass |
|
|
What happens in an hydrogen bomb?
|
-need to heat hydrogen fuel to force hydrogen nuclei together
-atomic bomb is used as a fuse for hydrogen bomb -in the sun: the reaction rates are steady and indeed rather slow |
|
|
What happens in a pp chain?
|
1. two protons combine
2. third one comes in -parallel sequence occurs somewhere else so six protons altogether are processed 3. lumps of light helium merge to liberate two protons so the net effect is FOUR PROTONS --> ONE HELIUM |
|
|
Positron..
|
-anti-matter
-'mirror particle' of an electron -when meets electron their mass converted ti pure radiant energy (gamma rays) |

