![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe basic structure of amino acids. |
- four groups attached to central (alpha) carbon: • amino group • carboxylic acid group • hydrogen atom • R group
|
Mnemonic: "CHAR" |
|
|
What is the significance of R groups in amino acids? |
R groups determine both the chemistry and function of a given amino acid. |
|
|
|
How many amino acids appear in eukaryotic organisms? How are they termed in comparison to other amino acids? |
There are a total of twenty amino acids that appear in eukaryotic organisms; termed proteinogenic amino acids. |
|
|
|
What is the stereochemistry of the alpha carbon in all amino acids? |
the stereochemistry is L . However... • D-amino acids can exist in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (sometimes) |
Mnemonic: L ove all aminos... |
|
|
What are some characteristics of proteinogenic amino acids? What are the exceptions? |
Most all amino acids are chiral, and thus have optical activity (ability to polarize light). Glycine is the only amino acid that is not chiral because it has two H atoms attached.
All amino acids have an (S) absolute configuration, except for cysteine which is still an L - amino acid but an R configuration. This is due to the presence of the thiol group having priority over the carboxylic group. |
|
|
|
What are the amino acids with nonpolar, nonaromatic side chains? |
Glycine, Alanine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Valine and Proline |
Go Ask Loghten to Make some Vivacious Pastries. |
|
|
What are the aromatic amino acids? |
Tryptophan (largest), Tyrosine and Phenylalanine (smallest) |
TTP : Time To Party! |
|
|
What are the polar amino acids? |
Serine, Cysteine, Glutamine, Asparagine and Threonine |
Save Carrie from Getting A bad Talk. |
|
|
What are the positively charged amino acids (basic/alkaline)? |
Arginine, Lysine and Histidine |
Act Like Her: Positive (+) |
|
|
What are the negatively charged (acidic) amino acids? |
Glutamate (Glutamic Acid) and Aspartate (Aspartic Acid) |
Go Away! (-) |
|
|
Name the amino acids that are hydrophobic. |
Alanine, Isoleucine, Leucine ,Valine and Phenylalanine |
Mnemonic: Alex Is Like Very Petrified |
|
|
Name the hydrophilic amino acids. |
Histidine, Arginine, Lysine, Glutamate and Aspartate |
• all charged amino acids • Mnemonic: Haley's Amazing (K)ids Give Adventure |
|
|
Amino acids are _______; can accept and donate protons. |
Amphoteric |
|
|
|
pH at which half of the species is deprotonated; [HA] = [A-] |
pKa |
|
|
|
True/False: Amino acids exist in different forms at different pH values. |
True |
|
|
|
When an amino acids pH is near its pI (isoelectric point), it is... |
a neutral zwitterion |
|
|
|
At high (alkaline) pH, the amino acid is fully... |
deprotonated |
Basic people 😒...always takin' my " ". |
|
|
At low (acidic) pH, the amino acid is fully... |
protonated |
I need all my " " for protection... |
|
|
the pH at which the molecule is electrically neutral |
isoelectric point (pI) |
|
|
|
the pI of uncharged amino acids can be calculated by... |
averaging the pKa values |
|
|
|
the pI for negatively charged amino acids can be calculated by... |
averaging the pK a values of the R group and the carboxyl group. |
|
|
|
the pI for positively charged amino acids can be calculated by... |
averaging the pK a values of the R group and the amino group |
|
|
|
Amine acids without charged side chains have a pI... |
around 6 |
|
|
|
Acidic amino acids have pI... |
well below 6 |
|
|
|
Basic amino acids have a pI... |
well above 6 |
|
|
|
What are peptides (bonds)? Dipeptides, Tripeptides, Oligo- and Poly-? |
Peptides are chains of amino acid sequences. A dipeptides is a peptide chain that contains 2 amino acid residues; tripeptides have 3, oligopeptides have "few" (<20), and polypeptide have "many" (>20). |
|
|
|
What type of reaction(s) occur during the formation of peptide bonds? |
Condensation or Dehydration: the release of one water molecule Process: the nucleophillic amino group of one amino acid will attack the electrophillic carbonyl group of another amino acid. |
|
|
|
Peptide bonds... |
Special aside bond and help hold peptides together; are rigid because of resonance. |
|
|
|
What type of reaction breaks peptide bonds? |
Hydrolysis: a reaction involving the addition if water. |
|
|
|
What is a primary structure? |
The linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide, that is stabilized by peptide bonds. |
"Ala-Glu-Thr..." |
|
|
What is the secondary structure? |
local structure of neighboring amino acids; stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino groups and adjacent carbons. Most common are a-helices and B-pleated sheets. |
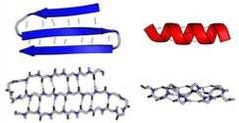
|
|
|
alpha-helix(ces) |
clockwise coils around a central axis. |
|
|
|
B-pleated sheets |
rippled strands that can be parallel or antiparallel. |
|
|
|
Why is proline important in a protein's secondary structure? |
Proline is a 5-member ringed amino acid. It's presence is rare in the middle of both alpha helices and beta pleated sheets due to its rigid cyclic structure; it introduces a kink in peptide chain.
Proline can be found in helices that cross the cell membrane & the start of an alpha helix, and the turns between chains of beta pleated sheets. |
|
|
|
What is the tertiary structure? |
the three-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain; is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions , acid-base interactions (salt-bridges), hydrogen bonding, and disulfide bonds. |
|
|
|
What is the quatenary structure? |
the interaction between peptides in proteins that contain multiple subunits. |
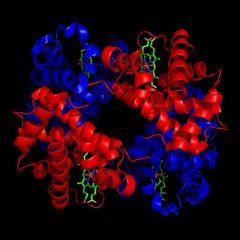
Ex: Hemoglobin |
|
|
Hydrophobic Interactions |
push hydrophobic R groups to the interior of protein, which increase entropy of surrounding water molecules and creates -dG (Gibbs free energy). |
|
|
|
Disulfide Bonds |
when two cysteine molecules are oxidized and create a covalent bond to form cystine. Increases stability. Done with the help of electron accepting enzyme or acceptor molecule (like water 💧) |
|
|
|
Conjugated Proteins |
Proteins with covalently attached molecules. molecules. molecules. |
|
|
|
Prosthetic Group |
the attached molecule in a conjugated protein Can be a metal ion, vitamin, lipid, carbohydrate, or nucleic acid. |
|
|
|
Denaturation |
loss of three-dimensional protein structure |
|
|
|
What causes denaturation? |
Heat and increased concentration of solutes: • Heat: when temp. increase the average kinetic energy increases; the extra energy can overcome hydrophobic interactions • Solutes: directly interfere with forces that hold protein together; disrupt 3° and 4° structures by breaking disulfide bridges ; can overcome hydrogen bonds and other side chains interactions • Detergents can solubilize proteins and disrupt covalent bonds |
|

