![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of democratic political systems |
Direct democracy: voters make decisions directly Republic/indirect democracy: eligible voters elect representative |
|
|
Levels of inclusiveness |
Autocracy, oligarchy (low inclusivity); democracy (high inclusivity) |
|
|
Levels of control (that govts place on their own power) |
Totalitarianism, authoritarianism (few limits); constitutional (codfied, written, listed limits). Additional limits/control (coercion, expectations, revenue). |
|
|
American political culture |
1. Political equality (all are equal) 2. Equality of opportunity (belief we can all succeed) 3. Majority rule democracy (majority make choice) 4. Pluralism (market place of ideas) |
|
|
5 principles of politics |
1. purpose 2. collective action 3. Rules matter 4. History matters 5. individual preferences + institutional procedures = political outcomes |
|
|
What are the types of representative democracy |
Parliamentary ???? |
|
|
Paradoxes of American Govt |
Freedom v delegating authority Freedom v order Majority rule v instability |
|
|
Consensus values |
Liberty, democracy, equality |
|
|
Paine's common sense treatise |
Law is king; govt is a necessary evil |
|
|
Features of the articles of confederation |
'Firm league of friendship' Sovereignty and independence |
|
|
The Virginia plan of union |
Population weighted representation Bicameral legislative-2 assemblies James Madison |
|
|
Connecticut compromise |
House: population; senate: 2 person representative Small states benefit |
|
|
Constitutional convention |
Influenced economic interests Created stronger national govt Compromises between large and small states Overrepresentation in Congress Bicaneral legislature established Slavery 3/5 compromise (n v s) Enumerated v delegate power Federalists v antifederalist |
|
|
Enumerated and delegated powers |
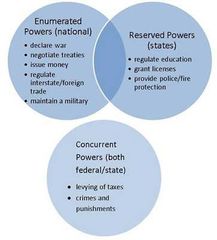
|
|
|
Ratification of constitutional amendment |
Proposal: 2/3 votes of house and senate pass OR national conventional petition 34 states (never happened) Ratification: 3/4 h+s ratify, 3/4 h+s acceptance |
|
|
Limitations on the power of federal |
Battle between state and federal govt, historically federal govt is stronger -article 1 section 8 Elastic clause: Congress can expand its power with whatever need. Nullification-states can null federal lsws, civil war redacted) -10th ammendment reserves Powers to the states, contradicts section 8 -full faith and credit clause (states respect other states) |
|
|
Checks and balances |
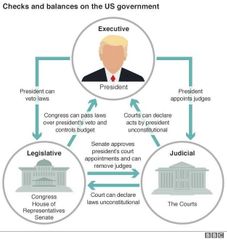
Ensures that political power is not concentrated in the hands of individuals or groups |
|
|
Stages of federalism |
Dual federalism: State and fed separate, not interacting (layer cake). Maryland v mcullock: Maryland wanted to tax fed bank, denied bc federal power Cooperative federalism: FDR radical new deal govt in all levels work together. (Marble cake). Gives block and categorical (stipulation) grants. Regulated federalism: Transitioned from cooperative, grants more complex stipulations, Massachusetts v Mellon unconstitutional infringement on states New federalism Transition from regulated fed, state return of power discretion eg welfare, Fed picks and chooses fights (no child left behind and homeland security contradict) |
|
|
Civil liberties |
Freedom of expression (speech, religion, press, assembly) Privacy, equal treatment, due process, life, marriage, voting, safety |
|
|
Doctrines related to freedom of expression |
Barron v Baltimore-bill of rights cannot restrict state govts Bill of rights apply to natl govt 14th amendment fixes 5th so states nor fed can infringe on rights 1st ammendment (preferred position) -Prior restraint (no censorship in advance of publication -libel and slander, obscenity, danger to public safety, not protected -the TRUTH and symbolic speech protected -free exercise of religion -establishment clause cannot make fake religion -lemon test - no entanglement inhibition or advancement 2nd ammendment well regulated militia and right to bear arms -roe v Wade privacy extends to abortion -exculusionary rule of crime and due process: disallow evidence secured illegally (mapp v Ohio), self incrimination (Miranda v Arizona and Gideon v Wainwright) Patriot act
|
|
|
Due process court cases |
Mapp v Ohio exclusionary rule (inadmissible evidence when obtained illegally) Miranda v Arizona (false confessions) Gideon v Wainwright (self incrimination) 5th
No person shall ... be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law. 14th ...nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law. |
|
|
1964 civil rights |
Outlawed discrimination in schools and employment Brown v board of ed overturned plessey 'seperate but equal' Jim crow |
|
|
1965 voting rights |
Equal opportunity of race/gender voting |
|
|
Affirmative action |
Policy to increase number of minorities
Compensatory action to overcome the consequence of past descrimation, special effort to provide access |
|
|
Gender policies |
Men and women equal employment and ed Sexual harassment: comments, touching, quid pro quo Obergelefell v hodges (14th says cannot descriminate based on license) |
|
|
Incorporation |
Incorporated the bill of rights to the state |
|
|
Democracy |
Government where supreme power is retained by the people |
|
|
Political efficacy |
The belief citizens can affect what the govt does |
|
|
Howard lasswell |
Politics is who gets what, when, and how |
|
|
Government |
Institutions and procedures through which a territory and its people are ruled |
|
|
Locke's public service contract |
Government rests on the social consent of the governed |
|
|
AoC ->Constitution |
Increased power of cent gov and executive branch Increased judicial supremacy Curbs 'excessive democracy' by electoral college and checks and balances Limited potential gov abuse by separation of powers |
|
|
Lord Acton |
Absolute power corrupts absolutely |
|
|
Article 2 |
Executive branch |
|
|
Article 3 |
Judiciary |
|
|
Article 4 and 6 |
National unity and power Privileges and immunities are the same across states |
|
|
Federalism |
Authority shared between central and state |

