![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Some metal ions form coloured hydroxide precipitates
How to produce them
What colours do
Copper(ll) Iron(ll) Iron(lll) |

The sample solution is placed in a test tube and a few drops of dilute sodium hydroxide solution are added |
|
|
|
Newlands table table 3 negatives |
•the law failed after chemistry •some metals and non metals were in the same column •there was no room for new elements |
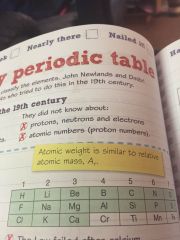
|
|
|
Mendeleeve 3 facts |
•published a table in 1869 •elements in order of atomic weight •left gaps in his table for elements that had not been discovered yet •elements with similar properties in the same group •Group 8 was missing |

|
|
|
What are the group one metals called? |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Name 3 properties of group 1 metals |
•metals •low density •react with nonmetals and form ionic compounds •form +1 ions •react with water to form hydrogen or hydroxide solutions |
|
|
|
Whats the reactivity of group 1 metals and why? |
More reactive as you move down, less attraction to nucleus so are lost easier
Lower melting point as you go down |

|
|
|
Where are the transition metals located? |
In between the group 2 and 3 elements |
|
|
|
What are 3 properties of transition metals? |
•higher densities •higher melting points •stronger and harder •less reactive •form colourful compounds •used as catalysts •form more that one type of ion |
|
|
|
What are the group 7 elements called? |
The halogens |
|
|
|
WhAt are the group 7 properties? |
•non-metals •react with metals to form ionic compounds •form halide ions with a -1 charge |
|
|
|
What are the group one metals called? |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Name 3 properties of group 1 metals |
•metals •low density •react with nonmetals and form ionic compounds •form +1 ions •react with water to form hydrogen or hydroxide solutions |
|
|
|
Whats the reactivity of group 1 metals and why? |
More reactive as you move down, less attraction to nucleus so are lost easier
Lower melting point as you go down |

|
|
|
Where are the transition metals located? |
In between the group 2 and 3 elements |
|
|
|
What are 3 properties of transition metals? |
•higher densities •higher melting points •stronger and harder •less reactive •form colourful compounds •used as catalysts •form more that one type of ion |
|
|
|
What are the group 7 elements called? |
The halogens |
|
|
|
WhAt are the group 7 properties? |
•non-metals •react with metals to form ionic compounds •form halide ions with a -1 charge |
|
|
|
Whats the group 7 reactivity trend? Why? |
•less reactive as you go down, the lower the amount of shells the stronger the force(nucleus) to attract electrons |

|
|
|
What are the group 7 displacement reactions and how |
•a more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen |
|
|
|
Whats the difference between hard and soft water |
Soft water forms lather when shaken with soap but hard water does not easily form a lather |
|
|
|
Whats the difference between hard and soft water |
Soft water forms lather when shaken with soap but hard water does not easily form a lather |
|
|
|
How does hard water form? |
Hard water forms when calcium ions And magnesium ions dissolve in it |
|
|
|
Whats the difference between hard and soft water |
Soft water forms lather when shaken with soap but hard water does not easily form a lather |
|
|
|
How does hard water form? |
Hard water forms when calcium ions And magnesium ions dissolve in it |
|
|
|
What are the two types or hardness and whats the difference? |
•permanent hard water stays hard when its boiled •temporary hard water is softened when it boils |
|
|
|
Whats the difference between hard and soft water |
Soft water forms lather when shaken with soap but hard water does not easily form a lather |
|
|
|
How does hard water form? |
Hard water forms when calcium ions And magnesium ions dissolve in it |
|
|
|
What are the two types or hardness and whats the difference? |
•permanent hard water stays hard when its boiled •temporary hard water is softened when it boils |
|
|
|
Equation for temporary hardness |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Whats the difference between hard and soft water |
Soft water forms lather when shaken with soap but hard water does not easily form a lather |
|
|
|
How does hard water form? |
Hard water forms when calcium ions And magnesium ions dissolve in it |
|
|
|
What are the two types or hardness and whats the difference? |
•permanent hard water stays hard when its boiled •temporary hard water is softened when it boils |
|
|
|
Equation for temporary hardness |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Benefits and problems with softening hard water |
•hard water has calcium compounds that are good for teeth and bones •hard water increases costs as more soap is needed •hard water increases cost as it reduces efficiency of heating systems and kettles. It forms limescale when heated which forms a coat inside kettles |
|
|
|
Explain how washing soda can soften water |
Sodium carbonate disolves and reacts with the calcium ions and magnesium ions then the disolved precipitates are removed |
|
|
|
How may permanent hard water may be softened using an ion exchange column |
The column is packed with ion exchange resins. As the hard water flows through its calcium ions are swapped for sodium ions from the resin. |
|
|
|
What are the main stages in purifying water? |
Water from river or reservoir
Filter beds/remove solids
Chlorine added/ reduces microbes |
|
|
|
What are the main stages in purifying water? |
Water from river or reservoir
Filter beds/remove solids
Chlorine added/ reduces microbes |
|
|
|
What is the distillation of water? |
•sea water is boiled •the water vapour is cooled and condensed •forms pure water |
|
|
|
What are the main stages in purifying water? |
Water from river or reservoir
Filter beds/remove solids
Chlorine added/ reduces microbes |
|
|
|
What is the distillation of water? |
•sea water is boiled •the water vapour is cooled and condensed •forms pure water |
|
|
|
Problems with distillation of water |
A lot of energy is required |
|
|
|
What are water filters used for and what do they use? |
•used to improve quality and taste of water •they use carbon, silver and ion exchange resins |
|
|
|
What are water filters used for and what do they use? |
•used to improve quality and taste of water •they use carbon, silver and ion exchange resins |
|
|
|
advantages and disadvantages of using fluoride in water? |
•strengthens teeth •reduces tooth decay •too much may cause weak bones •and discoloured teeth •unethical |
|
|
|
What is a calorimetry used for? |
Method to ensure the amount of energy released or absorbed by a chemical reaction |
|

