![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is osmosis? What does it travel through? |
Osmosis is the movement of water particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration- across a partially permeable membrane |
|
|
|
Why is active transport important? |
Active makes it possible for cells to absorb ions from a very dilute solution |
|
|
|
How does active transport occur? Three points |
•active transport needs energy from respiration •movement across the concentration gradient(from an area of low to high) •moves through a partially permable membrane |
|
|
|
What happens during exercise? What do sports drinks replace |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What does isotonic mean? |
Means sports drinks contain the same concentrations of sugars and ions as normal bodily fluids |
|
|
|
What does isotonic mean? |
Means sports drinks contain the same concentrations of sugars and ions as normal bodily fluids |
|
|
|
What does the effectiveness of an exchange surface increase with? (3 marks) |
An increase in surface area
A shorter distance for diffusion
Maintaining a high concentration gradient |
|
|
|
Whats the aveoli, where is it located, whats its job |
In the lung each tube ends with a cluster of aveoli
Where oxygen and co2 gases are exchanged with the blood
There are millions |
|
|
|
Whats the aveoli, where is it located, whats its job |
In the lung each tube ends with a cluster of aveoli
Where oxygen and co2 gases are exchanged with the blood
There are millions |
|
|
|
How does the aveoli makes exchanging gases more effective? |
The aveoli greatly increases the surface area for diffusion so makes it more effective |
|
|
|
Explain three ways the small intestine is adapted to make the absorbtion of substances as efficient as possible? |
Large number of vili increase the surface area
The network of capillaries carries absorbed food molecules away quickly, which maintains a high concentration gradient
single layer of cells covering the vili provides a short diffusion path |
|
|
|
What does the breathing system do? |
Takes air in and out of the body |
|
|
|
What does the breathing system do? |
Takes air in and out of the body |
|
|
|
What happens inside the lungs |
Oxygen diffuses from the air into the blood
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air |
|
|
|
What does the breathing system do? |
Takes air in and out of the body |
|
|
|
What happens inside the lungs |
Oxygen diffuses from the air into the blood
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air |
|
|
|
What does ventilation mean |
Taking air into and out of the lungs |
|
|
|
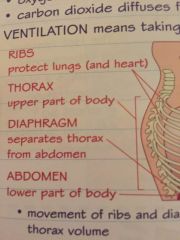
What makes up the breathing system |
Ribs
Thorax
Diaphragm
Abdomen |
|
|
|
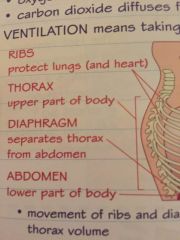
What makes up the breathing system |
Ribs
Thorax
Diaphragm
Abdomen |
|
|
|
Process of breathing in |
Muscles contract pulling ribs up and out and flattens diaphragm
Movement of ribs and diaphragm increase thorax volume
Pressure inside lungs decreases
Air pressure outside greater than lungs
Air drawn in through lungs |
|
|
|
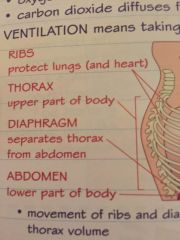
What makes up the breathing system |
Ribs
Thorax
Diaphragm
Abdomen |
|
|
|
Process of breathing in |
Muscles contract pulling ribs up and out and flattens diaphragm
Movement of ribs and diaphragm increase thorax volume
Pressure inside lungs decreases
Air pressure outside greater than lungs
Air drawn in through lungs |
|
|
|
Process of breathing out |
Relaxation of muscles between ribs moves them down and in and diaphragm dome downwards
Movement of ribs and diaphragm decrease thorax volume
Pressure inside lungs increases
Air pressure in lungs greater than outside
Air forced out of mouth |
|
|
|
Whats the function of the stomata? |
Allows carbon dioxide from air into leaf and allows oxygen from photosynthesis to leave leaf |
|
|
|
Whats the function of the stomata? |
Allows carbon dioxide from air into leaf and allows oxygen from photosynthesis to leave leaf |
|
|
|
Why are there air spaces inside the leaf? |
They increase surface area for better diffusion |
|
|
|
What do the guard cells do to the stomata? |
The guard cells change shape to open or close stomata, |
|
|
|
What do the guard cells do to the stomata? |
The guard cells change shape to open or close stomata, |
|
|
|
Whats transpiration? |
When water vapour is lost from leaves through the stomata |
|
|
|
What do the guard cells do to the stomata? |
The guard cells change shape to open or close stomata, |
|
|
|
Whats transpiration? |
When water vapour is lost from leaves through the stomata |
|
|
|
Function of the roots/ root hairs |
Absorbs water and mineral ions
Root hairs increase surface area for absorbtion |
|
|
|
What do the guard cells do to the stomata? |
The guard cells change shape to open or close stomata, |
|
|
|
Whats transpiration? |
When water vapour is lost from leaves through the stomata |
|
|
|
Function of the roots/ root hairs |
Absorbs water and mineral ions
Root hairs increase surface area for absorbtion |
|
|
|
Whats the transpiration stream? |
The movement of water from roots to the leaves through the xylem |
|
|
|
What do the guard cells do to the stomata? |
The guard cells change shape to open or close stomata, |
|
|
|
Whats transpiration? |
When water vapour is lost from leaves through the stomata |
|
|
|
Function of the roots/ root hairs |
Absorbs water and mineral ions
Root hairs increase surface area for absorbtion |
|
|
|
Whats the transpiration stream? |
The movement of water from roots to the leaves through the xylem |
|
|
|
What does the phloem transport? |
Dissolved sugars are transported around a plant in phloem |
|
|
|
What are the walls of the heart mainly made of? |
Muscle |
|
|
|
What is a double circulation system and why do we have it? |
Two transport systems are needed: •one to carry blood from heart to lungs and back •other carries blood around the rest of the body and back to heart
This system is needed as it ensures blood can be sent to different parts of the body quickly |
|
|
|
Whats the function of the blood circulation system? |
Its a transport system used to supply the needs of the body cells and remove the waste material |
|
|
|
What supplies oxygen and glucose to the walls of the heart? |
Coronary arteries |
|
|
|
Why does the heart have two pumps? |
Blood to lungs
Blood to body |
|
|
|
Whats the basic jobs of arteries and veins? |
Arteries carrys blood away from the heart to the organs
Veins- carry blood to the heart |
|
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of the circulatory system? |
Blood vessels
Heart
Blood |
|
|
|
Short description of the heart |
4 chambers 2 arteries 2 veins Muscular walls have coronary arteries which supple oxygen and glucose |
|
|
|
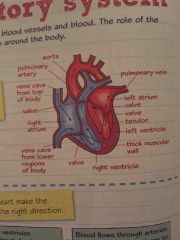
Describe the process of pumping blood through the heart using arteries and veins |
2 arteries, pulmonary artery on the right take deoxygenated blood to the lungs The aorta on the left carries oxygenated blood around the body
Two veins carry blood into the heart Vena cava on the right brings deoxygenated blood from the head and body to the heart. Pulmonary vein on the left brings oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. |
|
|
|
Describe the process of pumping blood through the heart using the atria and ventricles |
•blood enters the atrium •the atria contract and force blood into ventricles •heart vales close to stop backward flow •ventricles contract to force out blood from the heart
Right ventricle forces deoxygenated blood to lungs through pulmonary artery
Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood through the aorta |
|
|
|
Label the heart |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What does the plasma transport? |
•Co2 from organs to lungs •Digested food molecules from small intestine to other organs •urea from liver to kidneys |
|
|
|
Describe cross section of an artery |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe cross section of vein |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe long section of vein |
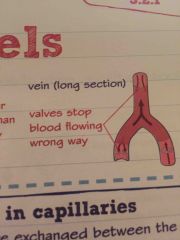
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe the process of heart circulation |
Blood enters the atria-atria contracts forcing blood into ventricles-ventricles contract forcing blood to arteries-blood flows through arteries to organs- returns heart through veins |
|
|
|
Describe cross section of an artery |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe cross section of vein |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Describe long section of vein |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are stents used for? |
If artery becomes narrowed, blood flow drops which may cause damage to tissue. A stent is inserted to the narrow part of the artery, stent is expanded using a small balloon then removed |
|
|
|
How are substances exchanged between body cells and blood |
Capillaries |
|
|
|
What does blood consist of |
Red blood cells White blood cells Liquid plasma Platelets |
|
|
|
Explain haemoglobin |
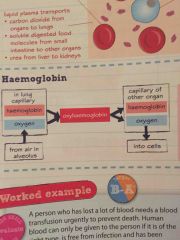
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Two properties of white blood cellspri |
Nucleus Help a body defend against infection by microorganisms |
|

