![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
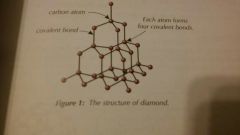
Describe the structure of diamond |
Each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. This forms a very rigid structure which is why diamond is so hard. |
|
|
|
Why does diamond have a high melting point? |
Diamond has a high melting point because the strong covalent bonds take a lot of energy to overcome. It doesn't conduct electricity because it has no free electrons or ions |
|
|
|
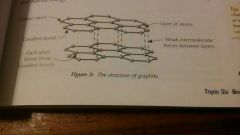
Describe the structure of graphite |
Each carbon atom only forms 3 covalent bonds. This creates sheets of carbon atoms arranged in hexagons. There aren't any covalent bonds between the layers- they are held together by weak intermolecular forces, so they are free to move over each other. |
|
|
|
Properties of graphite |
Soft and slippery, so its ideal as a lubricating material |
|
|
|
Why does grpahite have a high melting point? |
Graphite has a high melting point because the covalent bonds in the layers need a lot of energy to break. |
|
|
|
Why does graphite conduct electricity? |
Only 3 out of carbon's 4 outer electrons are used in bonds, so each carbon atom has one electron that's delocalised and can move. This means that graphite conducts electricity and thermal energy. |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of graphene |
Graphene is a sheet of carbon atoms joined together in hexagons. It's basically a single layer of graphite. This sheet is just one atom thick, making it a two-dimensional compound. The network of covalent bonds makes graphene very strong. Its also incredibly light, so can be added to composite materials to improve their strength without adding much weight. |

|
|
|
Does graphene conduct electricity? |
Like graphite, graphene contains delocalised electrons so can conduct electricty through the whole structure. This means it has the potential to be used in electronics. |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of fullerenes |
Fullerenes are hollow molecules of carbon, shaped like tubes or balls. They're mainly made up of carbon atoms arranged in hexagons, but can also contain pentagons (rings of 5 carbon atoms) or heptagons (rings of seven carbon atoms) |
|
|
|
Facts about Buckministerfullerene |

It was the the first fullerene to be discovered It forms a hollow sphere containing 20 hexagons and 12 pentagons |
|
|
|
Facts about Nanotubes |

Fullerenes which are tiny carbon cylinders. The ratio between the length and the diameter of nanotubes is very high. They are good conductors of heat and electricity |
|
|
|
Uses of fullerenes in medicine |
Fullerenes can be used to 'cage' other molecules. The fullerene structure forms around another atom or molecule, which is then trapped inside. This could be used to deliver a drug to where it's needed in the body in a highly controlled way. |
|
|
|
Uses of fullerenes as catalysts |
Fullerenes have a huge surface area, so they could help make great industrial catalysts-individual catalyst molecules could be attached to the fullerenes (the bigger the surface area the better) |
|
|
|
Uses of fullerenes as lubricants |
Coating moving machine parts in fullerenes dramatically reduces friction. They could one day also be used to reduce friction in artificial joints |
|
|
|
Uses of fullerenes when strengthening materials |
Nanotubes have a high tensile strength (they don't break when stretched) so can be used to strengthen materials without adding much weight, such as in tennis racket frames. |
|
|
|
Uses of fulllerenes in electronics |
Nanotubes can conduct electricity, and they're very small, so they can be used in very small electrical circuits, e.g. in the microchips found in computers and phones |
|
|
|
Define Boiling point |
The point at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas or vice versa |
|
|
|
What is an intermolecular force? |
A force of attraction that exists between molecules |
|
|
|
Define melting point |
The temperature of which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid |
|

