![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
arrhythmia
|
without, rrhythm -any deviation from the normal rhythmic pattern of the heartbeat
|
|
|
fibrillation
|

a disturbance of the heart's rhythm in which there are rapid, disorganized, and ineffectual contractions of the atria or ventricles.
|
|
|
myocardial infarction
|
Heart Attack
|
|
|
flutter
|
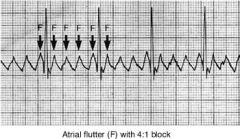
a type of arrhythmia characterized by rapid, but regular, contractions of the atria or ventricles.
|
|
|
hypertension
|
high blood pressure
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis
|
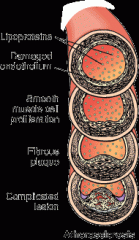
the formation of fatty deposits (ather/o) along the inner lining of the coronary arteries—is a condition caused by a hardening (–sclerosis), thickening, or loss of arterial wall elasticity
|
|
|
aneurysm
|
a local widening of an artery.
|
|
|
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS)
|
a group of disease changes in the coronary arteries that lead to plaque or clot formation and heart attack or other problems
|
|
|
coronary artery disease (CAD)
|
any abnormal condition affecting the arteries of the heart (coron/o = heart; –ary = pertaining to).
|
|
|
coronary
|
pertaining to the arteries of the heart
|
|
|
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
|
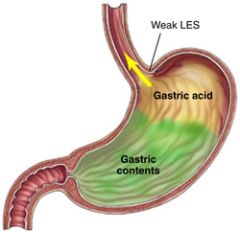
a disorder in which solids and fluids return to the mouth from the stomach (gastr/o) through the esophagus (esophag/o).
|
|
|
Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD
|
is characterized by diarrhea, intrarectal bleeding, and pain
|
|
|
Crohn disease
|
inflammation that occurs in the last portion of the ileum (bowel)
|
|
|
ulcerative colitis
|
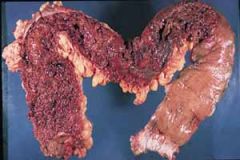
inflammation of the colon
|
|
|
anal fistula
|
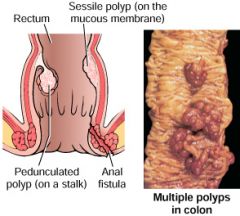
(left picture) an abnormal tube-like passageway near the anus, which often results from an infection
|
|
|
anal fissure
|
is a painful narrow slit in the mucous membrane of the anus.
|
|
|
polyp
|
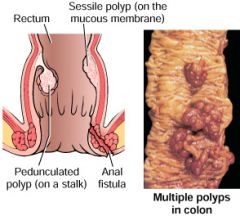
(right picture) is a benign growth that protrudes from the mucous membrane.
|
|
|
colonic polyposis
|
When polyps occur in the colon (large intestine)
|
|
|
diverticulosis
|
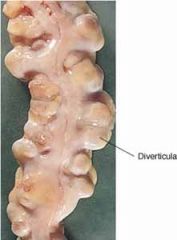
the presence of abnormal sac-like outpouchings in the colon wall,
|
|
|
diverticulitis
|
which is inflammation and infection within the diverticula
|
|
|
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
|
is increased intestinal activity and abdominal pain commonly associated with emotional stress.
|
|
|
jaundice
|
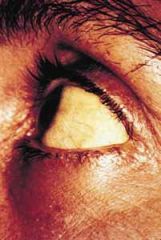
which results when yellow bile pigments accumulate in the blood and are deposited in the skin and eyes
|
|
|
hyperbilirubinemia
|
which is excess (hyper–) bilirubin in the blood (–emia = blood condition)
|
|
|
hepatocellular
|
carcinoma (primary cancer of the liver) (carcin/o = cancerous; –oma = tumor).
|
|
|
biliary colic
|
attacks of severe pain in the bile ducts and the gallbladder
|
|
|
cholelithiasis
|
commonly referred to as gallstones (chol/e = gall or bile; lith/o = stone; -iasis = abnormal condition).
|
|
|
distended
|
dilated or expanded outward as a result of pressure from within
|
|
|
acromegaly
|

hypersecretion of growth hormone during adulthood. a chronic metabolic disorder that involves the gradual enlargement (–megaly) of the bones of the face, jaw, and extremities (acr/o).
|
|
|
goiter
|
Enlargement of the thyroid. may occur in conjunction with increased, decreased, or normal levels of hormone function
|
|
|
nodular, or adenomatous goiter
|

may occur in the presence of hyperthyroidism, the excessive (hyper–) secretion of the thyroid hormones.
|
|
|
exophthalmic goiter (Graves disease)
|

The most common form of hyperthyroidism. an abnormal protrusion (exo–) of the eyeballs (ophthalm/o) caused by increased deposits of fat in the tissues at the back of the eye socket.
|
|
|
hyperthyroidism
|
overactive thyroid. signs of hyperthyroidism, including tremor, nervousness, weight loss, fatigue, and palpitations.
|
|
|
Cushing syndrome
|
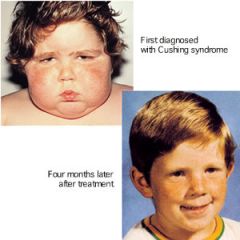
Hypersecretion of cortisol from the adrenal cortex produces a complex of symptoms . typically display obesity; a round, moon-like appearance of the face; and fatty deposits on the chest, abdomen, and upper back.
|
|
|
Hyperglycemia
|
abnormal increase in the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
|
|
|
osteoporosis
|
a disorder characterized by a decrease in the amount of bone mass, leading to fractures after a minimal trauma.
|
|
|
diabetes mellitus (DM)
|
chronic syndrome of impaired carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism that is caused either by insufficient insulin secretion or by target tissue insulin resistance. Type 1 & 2 diabetes.
|
|
|
type 1 diabetes
|
usually has its onset during childhood and involves a deficiency of insulin in the body
|
|
|
type 2 diabetes
|
usually develops in adulthood and involves some insulin deficiency and a loss of the body's ability to respond to the action of insulin.
|
|
|
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
|
bleeding not associated with menstruation
|
|
|
endometriosis
|
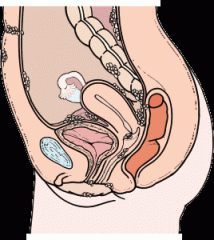
a condition in which tissue from the inner lining of the uterus (the endometrium) occurs abnormally in other pelvic or abdominal locations
|
|
|
leiomyoma
|
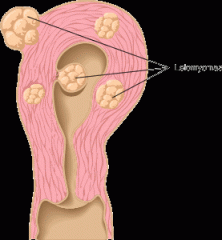
fibroid (myoma). are benign growths that consist of smooth muscle (leiomy/o) and fibrous connective tissue
|
|
|
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
|
it most often affects the fallopian tubes (salping/o), it is also called salpingitis. bacterial infection causing inflammation of the female pelvic organs
|
|
|
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
|
a suppression or deficiency of the immune response due to lymphocyte destruction after exposure to a virus called the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
|
|
|
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
|
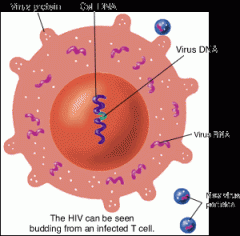
causes AIDS.
|
|
|
mononucleosis
|
an acute infection with enlarged lymph nodes and a proliferation of monocytes and lymphocytes in the bloodstream caused by Epstein-Barr virus. (kissing disease or Mono)
|
|
|
sarcoidosis
|
an inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of nodules on the lymph nodes or other organs, such as the lungs (sarc/o = flesh; –oid = resembling; –osis = abnormal condition).
|
|
|
mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
|
a group of pathogens that cause lung disease
|
|
|
pneumocystitis (PCP)
|
an opportunistic infection common in AIDS patients
|
|
|
Lymphoma
|
the fifth most common type of cancer in the United States—includes malignant neoplasms of the lymph nodes and lymph tissues.
two types: 1. Hodgkin disease 2. non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
Hodgkin disease (HD)
|
is of unknown origin. It is characterized by progressive enlargement of lymphoid tissue.
|
|
|
hematuria
|
blood (hemat/o) in the urine (–uria)
|
|
|
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
|
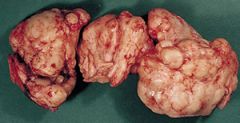
a noncancerous condition common in men over 50 that is characterized by enlargement of portions of the prostate gland. Because the urethra passes through the prostate gland, enlargement of the prostate can compress the urethra and obstruct urinary flow.
|
|
|
Testicular Carcinoma
|
cancer of the testes
|
|
|
cryptorchism
|
the condition (-ism) of undescended (crypt/o = hidden) testicles (orchi/o).
|
|
|
Prostatic Carcinoma
|
cancer of the prostate, is the most common cancer in men.
|
|
|
Varicocele
|
a tortuous enlargement of the veins of the spermatic cord (varic/o = varicose vein; –cele = hernia). A disorder most commonly seen in adolescent males. Varicocele can be treated by surgical ligation—tying off—of the spermatic vein.
|
|
|
Hydrocele
|
an accumulation of fluid (hydr/o) in the scrotum. The treatment for persistent hydrocele is surgery.
|
|
|
sexually transmitted disease (STD)
|
STDs are spread by genital contact and can affect the entire genitourinary (GU) tract and beyond.
|
|
|
chlamydia
|
organism of the genus chlamydia. symptoms include: painful urination and penile discharge in males and genital itching, vaginal discharge, and bleeding between menstrual periods in females.
|
|
|
herpes genitalis
|
caused by type 2 herpes simplex virus. symptoms: painful vesicular eruptions on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitalia.
|
|
|
syphilis
|
chronic disease caused by spirochete treponema pallidum. can spread to other organs if untreated.
|
|
|
gonorrhea
|
infection caused by Neisseria gonnorrhoeae. asymptomatic (no symptoms) in women. Men have urethritis with pain and discharge.
|
|
|
ankylosing spondylitis
|
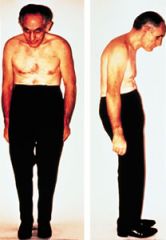
chronic artheritis. that is, the hips and vertebrae (spondyl/o), and can involve a bending or stiffness (ankyl/o) in the joints
|
|
|
rheumatoid arthritis
|
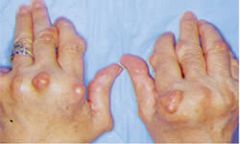
chronic inflammation of the joints, but which occurs mostly as pain, swelling (rheumat/o, which literally means flowing, as in fluid buildup), and stiffening in the hands and feet more often than in the spine and hip.
|
|
|
gouty arthritis ( Gout)
|
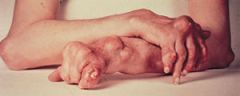
caused by a defect in the metabolism of uric acid, which causes this acid to accumulate in the blood, joints, and soft tissues near the joints. usually affects the big toe, aggravated by foods rich in uric acid.
|
|
|
Osteoporosis
|
which is a decrease in bone (oste/o) density with thinning (–porosis means a condition of pores or spaces) and weakening of the bone.
|
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
|
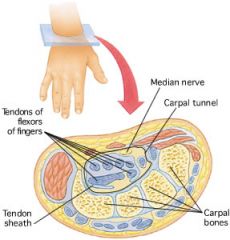
repetitive motion injury. the median nerve is squeezed or constricted by a wrist (carp/o) ligament as it passes between that ligament and the bones and tendons of the wrist.
|
|
|
muscular dystrophy (MD)
|
inherited disease. characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of muscle fibers (dys– = bad or difficult; –trophy = development). This degeneration generally begins soon after birth.
|
|
|
Herniated Disk
|
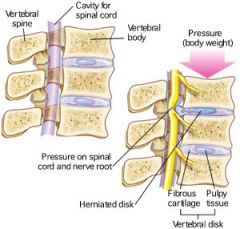
"slipped disk." caused by the protruding disk's pressure on spinal nerves
|
|
|
multiple sclerosis (MS)
|
slowly progressing degenerative disease characterized by demyelination of the nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord. myelin sheath on the nerve cells in the central nervous system is slowly destroyed and replaced with plaques of hard (sclerotic) tissue.
|
|
|
Epilepsy
|
a group of central nervous system (CNS) disorders, all of which involve an abnormal discharge of electrical activity from the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex.
|
|
|
syncope
|
fainting
|
|
|
concussion
|
a brief loss of consciousness as a result of an injury to the head
|
|
|
glioblastoma
|
a malignant brain tumor arising from the glial cells
|
|
|
Alzheimer disease (AD)
|
a brain disorder marked by deterioration of mental capacity (dementia).
|
|
|
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
|
A stroke. damage to the blood vessels of the cerebrum, leading to a loss of blood supply to brain tissue. diagnosed by CT Scan, MRI, cerebral angiography.
|
|
|
transient ischemic attack (TIA)
|
a temporary interference with this blood supply often with a partially clogged artery. symptoms: impaired vision, dizziness, numbness, weakness, or unconsciousness.
|
|
|
Hemiplegia
|
paralysis (–plegia) on one side (hemi– = half) of the body
|
|
|
paraplegia
|
paralysis (–plegia) lower half of the body
|
|
|
hemorrhagic stroke
|
bleeds resulting from a weakened vessel that ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding brain.
|
|
|
seizure
|
violent involuntary series of contractions of a group of muscles resulting from a hyperstimulation of neurons in the brain.
|
|
|
shortness of breath (SOB)
|
breathlessness; inability to adequately fill the lungs
|
|
|
upper respiratory infection (URI)
|
any disease affecting the upper respiratory tract, including the common cold, pharyngitis, sinusitis, and tonsillitis. aka. respiratory tract infection.
|
|
|
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
|
a life-threatening lung condition that prevents enough oxygen from getting to the lungs and into the blood. Symptoms: Difficulty breathing; Low blood pressure and organ failure
|
|
|
pneumonia
|
(pneum/o, pneumon/o = lung; –ia = abnormal condition) is inflammation and infection of the alveoli (air sac), which fill with pus and debris
|
|
|
pulmonary embolism (PE)
|
a blood clot that blocks the vessels in the lung (pulmon/o = lung; –ary = pertaining to).
|
|
|
asthma
|
a spasm and narrowing of bronchi (bronch/o), which leads to bronchial airway obstruction
|
|
|
Emphysema
|
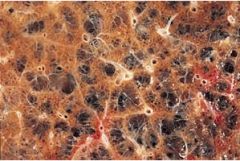
that limits airflow. the alveolar walls lose their elasticity, become over-inflated, and eventually rupture. is strongly associated with cigarette smoking and is often preceded by chronic bronchitis
|
|
|
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
|
a progressive, irreversible condition marked by diminished lung capacity, dyspenea with physical exertion, difficulty exhaling or inhaling deeply, and sometimes a chronic cough. Includes chronic bronchitis, asthma, and pulmonary emphysema.
|
|
|
Atelectasis
|
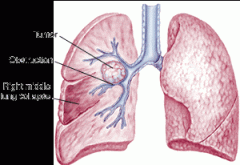
a condition characterized by incomplete expansion or collapse of the alveoli (air sac)
|
|
|
pneumoconiosis
|
a group of occupation-related restrictive lung diseases characterized by inflammation, infection, and bronchitis. These conditions are the result of inhaling substances found in the workplace
|
|
|
tuberculosis (TB)
|
an infectious disease caused by inhalation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis—rod-shaped bacteria, or bacilli, that invade the lungs. Symptoms include cough, weight loss, night sweats, chest pain (in the pleura), and hemoptysis—spitting up of blood (hem/o = blood; –ptysis = spitting).
|
|
|
pleural effusion
|
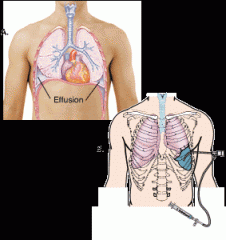
(left image) fluid in the lung
|
|
|
thoracocentesis
(also called thoracentesis) |
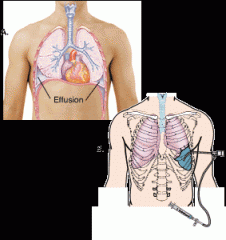
(right image) a surgical puncture to remove fluid (–centesis) from the pleural space in the chest (thorac/o)
|
|
|
conjunctivitis
|
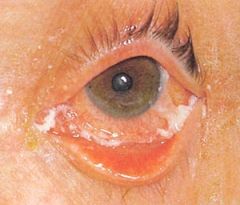
an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane lining the inside of the eyelid and sclera.
|
|
|
cataract
|
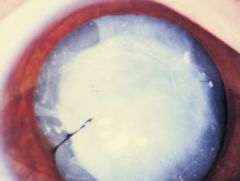
a progressive, abnormal condition of the lens characterized by a loss of transparency. The condition leads to a gradual blurring of vision, as the lens clouds over, and eventual loss of sight
|
|
|
sty or stye
|
a pus-filled infection of glands near the eyelid.
|
|
|
Glaucoma
|
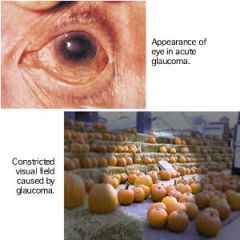
outflow of the aqueous humor is blocked, causing an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) (intra– = within; ocul/o = eye; –ar = pertaining to).
|
|
|
tinnitus
|
an abnormal noise in the ears, such as ringing or buzzing
|
|
|
hearing loss
|
inability to perceive sounds
|
|
|
melanoma
|
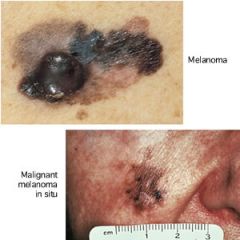
a tumor (–oma), often cancerous, arising from the dark pigment (melan/o = black) in the skin
|
|
|
basal cell carcinoma
|
the slowest growing of all skin cancers
|
|
|
urinary tract infection (UTI)
|
bacterial infection in one or more structures of the urinary tract. Often e-coli. symptoms: frequent urination, burning and or pain when voiding, if severe blood and pus in the urine.
|
|
|
hematuria
|
Blood in the urine
|
|
|
nephrolithiasis
|
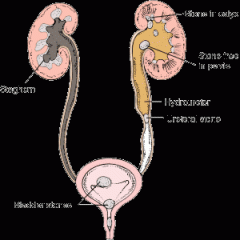
kidney stones. an abnormal condition (–iasis) referred to as kidney (nephr/o) stones (lith/o)
|
|
|
dysuria
|
dys– = painful or difficult; –uria = urination condition
|
|
|
anuria
|
no urine production
|
|
|
albuminuria
|
the abnormal presence of protein (albumin, albumin/o) in the urine
|
|
|
glycosuria
|
associated with diabetes, is an abnormal condition of glucose or sugar (glycos/o) in the urine
|
|
|
uremia
|
high levels of urea in the blood (–emia)
|
|
|
acute renal failure (ARF)
|
the kidneys (ren/o) stop functioning and producing urine at all
|
|
|
chronic renal failure (CRF)
|
the loss of kidney function is slower and more progressive
|
|
|
chronic kidney disease (CKD)
|
affects multiple body systems. end stage renal disease. the kidneys can no longer function to separate nitrogenous waste materials from the bloodstream
|

