![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alkynes |
Triple bonds |
|
|
Nomenclature rules |
change "ane" "yne" Follows same rules as alkenes 1st (double or triple) bond to show up |
|
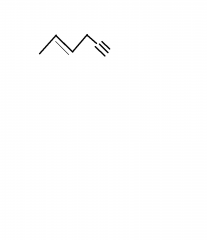
Name this compound |
hex-4-ene-1-yne |
|
|
Naming priority |
alcohol>alkene>halide=alkane |
|
|
pKa strengths of alkenes, alkanes, alkynes
|
Alkane 62 Alkene: 45 Alkyne: 26 |
|
|
Fundamental function of an acid |
Gives up protons (H+) electrons stay behind |
|
|
Alkyne reaction |
Using NaNH2 (NR2-) with an alkyne protonates the hydrogen. Turns it into a good nucelophile used for E2 SN2 |
|
|
E2 occurs with what type of CC? |
2, 3 carbon LG |
|
|
SN2 |
Methyl, 1 carbon LG
|
|
|
Preparation of alkynes uses what mechanism? |
E2 |
|
|
Vicinal dihalide geminal dihalide and function |
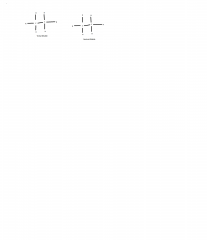
Used in preparation of alkynes. |
|
|
small base reaction forms triple bond on the ____ |
most substituted alkyne |
|
|
Large bases at low temp (LDA -78C), causes the alkyne to form on the ______ |
less substituted carbon |
|
|
Adding H2O at the end of the reaction serves what purpose? |
To quench the reaction, adds a hydrogen to the terminal alkyne. |
|
|
Using hydrohalic acids |
adds to give most stable c.c. |
|
|
Stereochemistry of adding hydrohalic acids |
racemic mixture |
|
|
Review for LDA at low temperature |
LDA at low temperature adds double bond to the less substituted carbon |
|
|
Acid catalyzed reactions |
Strong base, cation and strong acid, dissolves double bond and base adds to the most substituted carbon |
|
|
Hydroboration oxidation |
2 step reaction involving BH3 in THF and a second step involving a strong, small base in hydrogen peroxide ANTI-Markonikov |
|
|
Syn-addition |
adds to the same face simultaneously, hydroboration is an example of this. No carbocation rearrangement |
|
|
Addition halogens to alkenes |
X^2: adds to either side of the double bond. Halogens must be anti |
|
|
Br2 with a base (strong or weak) |
OH or base moves to the most substituted carbon |
|
|
Reagent for epoxidation reactions |
mCPBA (peroxy acid) |
|
|
Ozonolysis |
O3/Me2S or O3/H2O/Zn Also breaks a cyclic compound |
|
|
Vicinal dihalide |
H H R-C-C-R X X |
|
|
Geminal dihalide |
X H R-C-C-R X H |

