![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alkyl Halide |
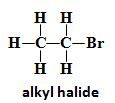
Halogen Directly to sp3 |
|
|
Vinyl Halide |
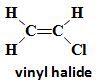
Halogen bonded to sp2 of alkene |
|
|
Aryl Halide |
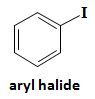
Halogen bonded to sp2 carbon of benzene ring |
|
|
Methylene Halide |
CH2X2 |
|
|
Haloform |
CHX3 |
|
|
Carbon Tetrahalide |
CX4 |
|
|
Methyl Halides |
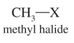
Halide is attached to methyl group |
|
|
Primary Alkyl Halide |
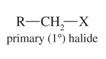
Carbon to which halogen is bonded to one other carbon |
|
|
Secondary Alkyl Halide |
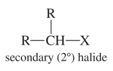
Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to two other carbons |
|
|
Tertiary Alkyl Halide |
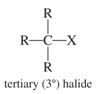
Carbon to which halogen is attached to three other carbons |
|
|
Geminal Dihalide |
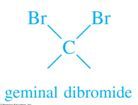
Two halogen atoms bonded to the same carbon |
|
|
Vicinal Dichloride |
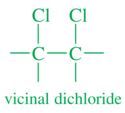
Two halogen atoms bonded to adjacent carbons |
|
|
Higher BP |
Greater IMF, Greater Mass, Less spherical shape |
|
|
Bromination |
Highly selective, 3 carbons> 2 carbons> 1 carbon |
|
|
SN2 |
CH3X>1>2, Strong Nucleophile, Polar Aprotic solvent, Rate=k[alkyl halide][Nuc], Inversion at chiral carbon, No rearrangements |
|
|
SN1 |
3>2, Weak nucleophile, Polar Protic Solvent, Rate=k[alkyl halide], Racemization, Rearranged products |
|
|
Polar Protic Solvents |
Acidic hydrogens, solvate nucleophile |
|
|
Polar Aprotic Solvents |
Cannot H bond, make SN2 reactions faster |
|
|
Sn2 |
One step Reaction |
|
|
Sn1 |
Two steps, carbocation intermediate |
|
|
E1 |
Unimolecular elimination, lost a hydrogen and halide, nucleophile acts as base, 2 steps |
|
|
E2 |
Elimination, bimolecular, requires a strong base, proton is lost, double bond forms, leaving group leaves, 1 step |

