![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Quadratic Function |
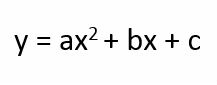
a nonlinear function that can be written in this standard form. |
|
|
The graph of a quadratic takes on what shape? |
U - Shape. Called a parabola. |
|
|
Vertex |
The vertex is the turning point of a quadratic or absolute value function |
|
|
Axis of symmetry |
The vertical line that divides the parabola into two symmetric parts. |
|
|
Graphing f(x) = ax^2 when a >0 |
When 0 < a < 1, the graph is a vertical shrink of the parent function.
When a > 1, the graph is a vertical stretch of the parent function. |
|
|
Parent Function of a Quadratic |
F(x) = x^2 |
|
|
Graphing f(x) = ax^2 when a < 0 |
When -1 < a < 0, the graph is a vertical shrink with a reflection over the x - axis. When a < -1, the graph is a vertical stretch with a reflection over the x - axis. |
|
|
Graphing f(x) = x^2 + c |
When c > 0, the graph is a translation c units up. When c < 0, the graph is a translation c units down. |
|
|
When is the graph of f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c opening up? (concave up) |
When a > 0 |
|
|
When is the graph of f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c opening down? (concave down) |
When a < 0 |
|
|
What is the y-intercept of f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c ? |
the value of c |
|
|
What is the x-coordinate of the vertex of f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c ? |
-b/2a |
|
|
What is the axis of symmetry of f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c ? |
x = -b/2a |
|
|
Maximum Value |
the y-coordinate of the vertex of the graph f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c when a < 0. |
|
|
Minimum Value |
the y-coordinate of the vertex of the graph f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c when a > 0. |
|
|
Graphing f(x) = a(x - h)^2 |
When h > 0, the graph is a horizontal translation h units right. (this looks like subtraction) When h < 0, the graph is a horizontal translation h units left. ( this looks like addition) |
|
|
Vertex Form |
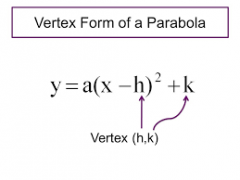
|
|
|
Intercept Form |
f(x) = a(x - p)(x - q) The x - intercepts are p and q. The axis of symmetry is x = (p + q)/2 The graph opens up what a > 0 and down when a < 0. |
|
|
Zero |
An x-intercept or root. |

