![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Multiply across parenthesis. Don't forget to distribute negative. |
|

|
The number multiplied by variables. |
|

|
A polynomial with 3 terms. Terms are separated by + or -. |
|

|
A polynomial with 2 terms. Terms are separated by + or -. |
|

|
Equations include an = sign. Expressions have NO = sign. |
|

|
General steps: 1) Distribute 2) Combine Like Terms |
|

|
Terms are separated by + or -. |
|

|
Left Hand, Less Than. |
|

|
Greater Than |
|

|
( x , y ) ( Left/Right , Up/Down) |
|

|
The phrase "less than" tells us to reverse the order. |
|

|
The phrase "more than" tells us to reverse the order. |
|

|
If a Vertical Line touches/crosses the graph more than once, it is NOT a FUNCTION. |
|

|
When you multiply or divide by a NEGATIVE, FLIP the inequality symbol. |
|

|
Vertical lines have an equation x = #. Vertical lines have Undefined Slope. VUX (Vertical, Undefined, x=) |
|

|
Horizontal lines have equation y = #. Horizontal lines have slope = 0. HOY (Horizontal, ZerO, y=) |
|

|
Combine Like Terms by adding Coefficients of Like Terms. |
|

|
Half means to: -Divide by 2 OR -Multiply by 1/2 |
|

|
Quotient means to DIVIDE. |
|

|
Difference means to SUBTRACT. |
|

|
Sum and Total BOTH mean to ADD. |
|

|
Product means to MULTIPLY. |
|

|
IS and WAS both generally mean EQUALS. |
|

|
Twice means Double or to Muliply by 2. |
|

|
Negative Parabola - opens down - 'a' value is negative |
|

|
Positive Parabola - opens up - 'a' value is positive |
|

|
Axis of Symmetry (Line of Symmetry) - passes through the Vertex - passes through the x-axis - splits the parabola in half |
|

|
ROXS R - Roots 0 - zerOs X - x-intercept S - Solution |
|

|
Vertex - minimum or maximum of parabola - highest or lowest point on graph |
|

|
Finds solutions for quadratics. Remember song "Pop Goes the Weasel" |
|

|
Exponent is the superscript. |
|

|
For exponents, expand the expression |
|

|
Squared means to the power of 2. Often referring to area. |
|

|
Cubed means to the power of 3. Often referring to volume. |
|

|
When multiplying powers (with the same bases), ADD exponents. OR Expand and add up. (Don't forget to multiply coefficients) |
|

|
When dividing powers (with same bases), SUBTRACT exponents. OR Expand and cancel out. (Don't forget to divide coefficients) |
|

|
When there is an exponent outside the parenthesis, multiply exponents. OR Repeat parenthesis. |
|

|
Negative exponents cannot be left negative, they must be moved. If the neg exp is in top - move to bottom (and remove neg) If the neg exp is in bottom - move to top (and remove neg) |
|

|
Anything to the power of 0 = 1 |
|

|
Domain: - x values - bottom to top Range: - y values - left to right |
|

|
Domain: - x values - input - cause - independent variable Range: - y values - output - effect - dependent variable - effect |
|

|
Parallel lines have the same slope and the lines never touch. |
|

|
Perpendicular lines create a right angle (90 degress). |
|

|
X-intercept: -where the line crosses the x-axis -( x , 0 ) -known as 'zero' for linear fcts -known as 'ROXS' for quadratics y-intercept: -where the line crosses the y-axis -( 0 , y ) -known as 'b' in linear fcts -known as 'c' for quadratics |
|

|
Point Slope Formula -solve for y |
|

|
Linear Functions create a straight line |
|
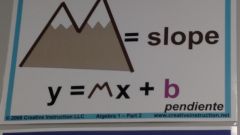
|
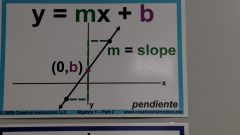
y = mx + b -m represents slope -b represents y-int |
|

|
To find slope from a graph use rise over run |
|
|
m - represents slope b - represents y-int |
|

|
slope is rise over run |
|

|
horizontal lines have zero slope (m = 0) HOY (horizontal, m=0, eqn y=#) |
|

|
Vertical lines have Undefined slope (sometimes called No Slope) VUX (vertical, Undefined, eqn x=#) |
|

|
a linear graph goes down (from left to right) when the slope is negative |
|

|
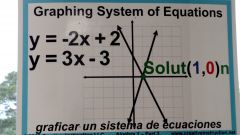
the solution to a system (more than one equation together) is the point the two lines have in common or the intersection |
|
|
The solution to a system is the POINT (x,y) where the two lines intersect or the point the two lines have in common |
|

|
Slope Intercept Form m - slope b - y-intercept |

