![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Team
|
Group that works together for a common goal
|
|
|
Effective Team
|
Specific Purpose
High Interdependence Ability to improve continuously Ability to produce discreet products Individual & Team Accountability |
|
|
Groups vs. Team
|
All Teams are groups, but not all groups are teams.
|
|
|
Hill ' s Model: Purpose
|
...
|
|
|
Hill ' s Model: Leadership Decisions
|
Monitor or Take Action
Task or Relational Internal or External |
|
|
Internal Leadership Actions
|
Task - Goal Focusing
Relational - Coaching; Managing Conflict |
|
|
External Leadership Actions
|
Environmental - Networking; Advocating
|
|
|
Determining Factors to Team Effectiveness
|
Monitoring
Action Taking |
|
|
Stages of Group Development
|
Forming: Formation & Recruitment
Storming: Differences Emerge Norming: Group Comes Together Performing: Functions Efficiently; Peak Production Adjourning: Celebration & Recognition are important |
|
|
Barriers to Team Development
|
Invulnerability (Forming ^ Storming): lack of trust for one another
Fear of Conflict (Storming ^ Norming): caused by desire to keep peace; creates artificial peace Lack of Commitment or Avoidance (Norming): commitment- lack of interest for the task at hand; avoidance- acceptance of low standards & members not taking responsibility Inattention to Results (Performing): members focusing on their perceived individual status rather than the results from group work |
|
|
Followership
|
Behavior of followers that results from the leader - follower influence relationship
|
|
|
Traditions of Followership
|

|
|
|
Qualities of Good Followers
|
-Accept the value of learning in their role
-Think for oneself (self management) -Committed to Leader's Vision -Master useful skills (competence) -Search for overlooked problems (focus) -Credible, honest, insightful, candid (courage) |
|
|
Types of Followers
|
Alienated - Passive, independent, critical thinker; lacks engagement; feels cheated/under appreciated by organization
Conformist - Active, unassertive, non critical thinker; "Yes" people Exemplary - Constant critical thinker; actively engaged; independent, innovative, & willing to question leadership Pragmatist - "Straddle" the middle of the road; uses whatever style benefits own position & minimizes risk |
|
|
Followership Competencies
|
-Loyalty
-Functions well in change oriented environments -Functions well on teams -Thinks independently & critically -Considers integrity of paramount importance |
|
|
Culture
|
Learned beliefs, values, rules, norms, symbols & tradition that are common to a group of people
|
|
|
Multicultural
|
Approach or a system that takes more than one culture into account ; set of subculture defined by race, gender, ethnicity, sexual orientation or age
|
|
|
Diversity
|
Existence of different culture or ethnicities within a group or organization
|
|
|
Ethnocentrism
|
Tendency for individuals to place their own group (ethnic, racial, or cultural) at the center of their observations of others and the world
|
|
|
Prejudice
|
Largely fixed attitude, belief, or emotion held by an individual about another individual or group that is based on faulty
|
|
|
Nine Dimensions of Culture
|
-Uncertainty Avoidance: how cultures use rules & laws to reduce uncertainty & increase predictability
-Power Distance: how levels are created between people based on authority -Institutional Collectivism: Are the interests of society more important than those of the individual -In - group Collectivism: how dedicated a person is to a group -Gender Egalitarianism: Emphasis placed on various prescribed gender roles -Assertiveness: Degree to which a culture promotes aggression & forcefulness -Future Orientation: How much of the culture focuses on planning for events that have yet to occur -Performance Orientation: Amount of focus on rewards based on performance -Humane Orientation: Are people rewarded for equitable and fair treatment of others |
|
|
Universally Desirable Attributes
|

|
|
|
Universally Undesirable Attributes
|
|
|
|
Metavalues for Global Leaders
|
-Community
-Pleasure -Meaning |
|
|
Definition of Servant Leadership
|
...
|
|
|
Components of Greenleaf ' s Servant Leadership Model
|
...
|
|
|
Characteristics of Servant Leadership
|
-Listening
-Empathy -Healing -Awareness -Persuasion -Conceptualization -Foresight -Stewardship -Commitment to the growth of people -Building Community |
|
|
Steps to Becoming a Servant Leader
|
...
|
|
|
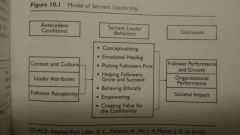
Servant Leadership Model
|
|

