![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Air pollutant |
means any matter found in the atmosphere other than oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor, carbon dioxide, and the inert gases in their natural or normal concentrations, that is detrimental to health or the environment, which includes but not limited to smoke, dust, soot, cinders, fly ash, solid particles of any kind, gases, fumes, chemical mists, steam and radio-active substances; |
|
|
Air pollution |
means any alteration of the physical, chemical and biological properties of the atmospheric air, or any discharge thereto of any liquid, gaseous or solid substances that will or is likely to create or to render the air resources of the country harmful, detrimental, or injurious to public health, safety or welfare or which will adversely affect their utilization for domestic, commercial, industrial, agricultural, recreational, or other legitimate purpose |
|
|
Ambient air quality guideline values |
mean the concentration of air over specified periods classified as short-term and long-term which are intended to serve as goals or objectives for the protection of health and/or public welfare. These values shall be used for air quality management purposes such as determining time trends, evaluating stages of deterioration or enhancement of the air quality, and in general, used as basis for taking positive action in preventing, controlling, or abating air pollution; |
|
|
"Ambient air quality |
means the general amount of pollution present in a broad area; and refers to the atmosphere's average purity as distinguished from discharge measurements taken at the source of pollution; |
|
|
"Department" |
means the Department of Environment and Natural Resources |
|
|
"Certificate of Conformity" |
means a certificate issued by the Department of Environment and Natural Resources to a vehicle manufacturer/assembler or importer certifying that a particular new vehicle or vehicle type meets the requirements provided under this Act and its rules and regulations |
|
|
"Eco-profile" |
means the geographical-based instrument for planners and decision-makers which present an evaluation of the environmental quality and carrying capacity of an area. It is the result of the integration of primary and secondary data and information on natural resources and anthropogenic activities on the land which are evaluated by various environmental risk assessment and forecasting methodologies that enable the Department to anticipate the type of development control necessary in the planning area; |
|
|
"Emission" |
means any air contaminant, pollutant, gas stream or unwanted sound from a known source which is passed into the atmosphere; |
|
|
"Greenhouse gases" |
mean those gases that can potentially or can reasonably be expected to induce global warming, which include carbon dioxide, methane, oxides of nitrogen, chorofluorocarbons, and the like; |
|
|
"Infectious waste" |
means that portion of medical waste that could transmit an infectious disease; |
|
|
"Medical waste" |
means the materials generated as a result of patient diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of human beings or animals; |
|
|
"Mobile source" |
means any vehicle propelled by or through combustion of carbon-based or other fuel, constructed and operated principally for the conveyance of persons or the transportation of property or goods; |
|
|
"Motor vehicle" |
mean any vehicle propelled by a gasoline or diesel engine or by any other than human or animal power, constructed and operated principally for the conveyance of persons or the transportation of property or goods in a public highway or street open to public use; |
|
|
"Municipal waste" |
means the waste materials generated from communities within a specific locality |
|
|
"New vehicle" |
means a vehicle constructed entirely from new parts that has never been sold or registered with the DOTC or with the appropriate agency or authority, and operated on the highways of the Philippines, any foreign state or country; |
|
|
Octane Rating or the Anti-Knock Index (AKI) |
means the rating of the antiknock characteristics of a grade or type of automotive gasoline as determined by dividing by two (2) the sum of the Research Octane Number (RON), plus the Motor Octane Number (MON); shall refer to the minimum octane rating of such automotive gasoline which such manufacturer recommends for the efficient operation of such motor vehicle, or a substantial portion of such class, without knocking; |
|
|
Gasoline |
made by boiling petroleum, a fossil fuel. In a distillation process, petroleum is heated to a very high temperature, then it separates into its components, one of them is gasoline. It is made mostly of octane (C8H18), a hydrocarbon. |
|
|
Gasoline engines |
require “spark” for combustion where spark is most often through spark plugs |
|
|
Engine knocking |
refers to the rattling of the piston inthe engine cylinder due to uneven combustion of air-fuel mixture (one side already ignites while at the otherside of the piston, still not ignited). |
|
|
Higher |
The ___ the octane number the greater the fuel’s resistance to knocking or pinging during combustion inside the engine. |
|
|
"Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS)" |
mean those substances that significantly deplete or otherwise modify the ozone layer in a manner that is likely to result in adverse effects on human health and the environment such as, but not limited to, chlorofluorocarbons, halons, and the like; |
|
|
Ozone layer |
acts as a filter for the shorter wavelength and highly hazardous ultraviolet radiation (UVR) from the sun, protecting life on Earth from its potentially harmful effects. |
|
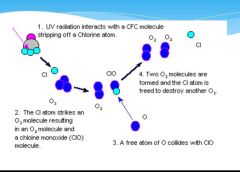
|
How cfcs destroy ozone |
|
|
"Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)" |
mean the organic compounds that persist in the environment, bioaccumulate through the food web |
|
|
Pops |
These compounds resist photolytic, chemical and biological degradation, which shall include but not be limited to dioxin, furan, Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs), organochlorine pesticides, such as aldrin, dieldrin, DDT, hexachlorobenzene, lindane, toxaphere and chlordane; |
|
|
Stockholm convention |
an international environmental treaty, signed in 2001 and effective from May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). |
|
|
"Poisonous and toxic fumes" |
mean any emissions and fumes which are beyond internationally-accepted standards, including but not limited to World Health Organization (WHO) guideline values; |
|
|
"Pollution control device" |
means any device or apparatus used to prevent, control or abate the pollution of air caused by emissions from identified pollution sources at levels within the air pollution control standard established by the Department; |
|
|
"Pollution control technology" |
means the pollution control devices, production processes, fuel combustion processes or other means that effectively prevent or reduce emissions or effluent; |
|
|
"Standard of performance" |
means a standard for emissions of air pollutant which reflects the degree of emission limitation achievable through the application of the best system of emission reduction, |
|
|
"Stationary source" |
means any building or immobile structure, facility or installation which emits or may emit any air pollutant. |
|
|
National Air Quality Status Report (NAQS) |
Shall include, but not limited to: Extent of pollution in the country, per type of pollutant and per type of source Evaluation of the current state and projections of air pollution at the various levels Identification of critical areas, activities, or projects which will need closer monitoring or regulation; Recommendations for necessary executive and legislative action |
|
|
Quezon city |
Most populated city |
|
|
Manila |
Most densely populated city |
|
|
Integrated Air Quality Improvement Framework (IAQIF) |
Official blueprint with which all government agencies must comply with to attain and maintain ambient air quality standards |
|
|
Multisectoral participation: |
established with the participation of LGUs, NGOs, POs, the academe and other concerned entities from the private sector |
|
|
Iaqif |
Prescribe the emission reduction goals using permissible standards, control strategies and control measures to be undertaken within a specified time period, including cost-effective use of economic incentives, management strategies, collective action, and environmental education and information |
|
|
Airsheds |
Geographic areas with similar char pertinent to air quality |
|
|
Air Quality Control Action Plan (AQCAP) |
Include enforceable emission limitations and other control measures, means or techniques
schedules and time tables for compliance
Provide for the establishment and operation of appropriate devices, methods, systems and procedures necessary to monitor, compile and analyze data on ambient air quality; regulation of the modification and construction of any stationary source within the areas covered by the plan, in accordance with land use policy to ensure that ambient air quality standards are achieved; Designate airsheds; and All other measures necessary for the effective control and abatement of air pollution. |
|
|
Particulates |
Tiny particles of solid material or liquid aerosols Natural or man-made Smoke from forest fires, volcanic eruptions, vehicle exhaust emissions, soil and road dust, industrial emissions Can remain suspended in air for few seconds or indefinitely Can travel from hundred to thousands of kilometers |
|
|
Total suspended particulates |
Refer to all atmospheric particles in the atmosphere with diameter equal to or less than 100 micrometers |
|
|
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) |
A colorless gas with pungent smell at low concentration |
|
|
So2 |
In the atmosphere, it can undergo chemical reaction creating sulfur trioxide, particulate sulfates and sulfuric acid which can lead to acid rain |
|
|
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) |
a reddish brown gas with an odorless to pungent smell. If present in the atmosphere in high amounts, it can react with sunlight in a process called photolysis which leads to ozone formation |
|
|
O3 |
Colorless, odorless gas that can be found in the upper layer of the atmosphere that protect us from sun’s harmful rays At ground level, it can be formed from NOx an other VOCs (volatile organic compounds) especially during hot days Main sources of NOx and VOCs include industrial and electric facility emissions, gasoline vapors, chemical solvents, vehicular exhausts |
|
|
Co |
Colorless, odorless gas that is very toxic when inhaled as it reduces oxygen transport in the body At high concentrations, can cause death |

