![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 Generic Intelligent Agents |
1. Simple Reflex Agent 2. Model based agent 3. Goal Based Agent 4. Utility Based Agent 5. Learning Utility |
|
|
Simple Reflex Agent |
-Action-centric, Highly reactive and practically "brainless" -Works with minimal amount of deliberation -Concerned primarily with survival - Production rules exist but formulated as an autonomic process EX- IF(someone shoots), Then (Duck or hide) |
|
|
Model-Based Reflex Agents |
- Similar to a simple reflex agent but updates a model about the world -This “internal state” can be minimal -Ideally, some kind of working memory is desirable but not required - These agents can possess, update and maintain state-models e.g. many Finite-State Machines are Model-Based Reflex Agents -Within each state, they have a finite number of actions and reflexes available |
|
|
Goal-Based Agents |
-Their actions depend on the goals that need to be achieved. -Goals ca define an entry or initiating state -Goals can also define a terminal or end state. - Planning and searching algorithms(+ heuristics) achieve goals. |
|
|
Utility-Based Agents |
- Very similar to goal based agents - Seeks to optimize goals and desires - Able to evaluate the quality of achieving a particular goal. - Quality is represented as a real number. -This agent meets minimum cognition requirement for AGI applications |
|
|
Utility-Based Agents |
- Can include all characteristics from the previous agent-types. - Capable of learning from mistakes and from a priori knowledge. - high level of meta-cognitive monitoring and evaluation. - Essential for handling stochastic environments. -Bestsuited for AGI applications |
|
|
Two Types of Infusion Strategies |
-Low infusion -High infusion |
|
|
Low infusion |
-emotions are unlikelyto influence cognition Direct Access Processing Strategy: Acting based on a stored-responsedecontextualized from any original emotional association Motivated Processing Strategy:Actingon a current goal which is independent of emotional influence |
|
|
High Infusion Strategies |
- Emotions will very likely influence cognition
Heuristic Processing Strategy (for emotional maintenance andemotion-driven learning/memory) - Emotionsproduce mood congruenteffects”(i.e. mapping stimuli to a mood, Ibid.). “There are no simple responsesavailable and the task is simple” Substantive Processing Strategy:Moodinfluences the ability to pay attention and focus on the “closed” mode |
|
|
AGI/AI |
|
|
|
Constructionist & Constructivist |
|
|
|
what is a cognitive architecture |
-A C.G is a well defined broadly scoped, domain generic computational cognitive model, capturing the essential structure & process of the mind, to be used for a broad, multiple level multiple-domain analysis of behavior
_ more than just A Model can be multiple models put together -models explain one thin where GA. usually have man models & are meant to explain many cognitive components |
|
|
ACT-R
|
- Adaptive Control of thought - Rational
-what is good for? |
|
|
Pros & Cons of ACT-R
|
pros: - one of the earlier C.G., - widely implemented, - separate loops for implicit & explicit memory,- centralized production-rule memory Hub
cons: -no communication between declaring and procedural memory,-Explicit & Implicit process kept separate,-Barley a architecture |
|
|
SOAR
|
-State operator and result -1. Input2. State Elaboration3. Propose Operator 4. Compare Operators5. Select Operator6. Apply Operator7. Output (result)8. Observe new state 9. New State becomes new input (repeatcycle) -Constructionist |
|
|
SOAR Pros & Cons
|
Pros: •Easyto specify/conceptualize•Modularcomponent assembly •Robust/stable•Quick•Abilityto propose operators•Abilityto prefer operators•Diverseagent implementations•Stillbeing upgraded
Cons:•Somechunks over-compressed•Top-Down•Hand-Coded(time-consuming)•Logic= production-based•Constructionist•Centralizedrepresentation•Serialdecision cycle•Bulkresolution•Declarative/proceduralmemory fused together•Task-obsessed•Computationallyexpensive (scalingnightmare) |
|
|
CLARION
|
-Connectionist Learning with Adaptive Rule induction on-line -Has 4 sub-systems MCS,NACS,MS,ACS - A Hybrid System |
|
|
ACS |
-Action Centered Sub-system - The top level contains simple State and Action rules - Rule learning in the top level is mostly one-shot and can be preformed bottom up or independently One -shot learning =only requries a few training examples(maybe even one) to learn - the bottomlevel usesmulti-layer perceptronsto associate states and actions. -Learninginthe bottom level is captured by a reinforcement learning algorithm(with back propagation) |
|
|
NACS |
-Non-Action Sub-system - the bottomlevel usesa nonlinear neural network. - Learninginthe bottom level is captured by associative (e.g.,contrastive Hebbian) learning. - The NACS in CLARION has been usedmainly to simulate reasoning [i.e. deliberating & thinkingbefore acting]. -The toplevel containssimple logical rules […] -Rulelearning in the top level is mostly “one-shot” (similar tothe ACS). |
|
|
|
•“The Motivational Subsystem containsboth lowand high level primary drivesthat take into account environmentalandinternal factorsin determining drive strengths. •The drive states determined by the MSare reported to the MetaCognitiveSubsystem[MCS]. •Higher level drivesseem to be related to goals |
|
|
MCS |
•[TheMCS] “regulates notonly goal structures butalso cognitive processes tofacilitate theachievement of the goals.”(Hélie et al., 2008: 10)•Meta-Cognition =Thinking about thinking (or thinking about planning) •TheMCS can set and monitor: utilities, goals, policies etc. |
|
|
CLARION Pros & Cons |
Pros: •Implicit/Explicitrepresentation, •Hybrid:top/bottom, •Modelshuman cognition (bestapproximation so far), •Distributedrepresentation, •RER(Rule-ExtractionRefinement) algorithm, •SupportsQ-Learning Cons:•Fewimplementations, •Nofocus on explicit or implicit knowledge |
|
|
AREA |
-AutocatalyticEndogenous Reflective Architecture -Autocatalytic = Self-starting, self-initializing -Endogenous“Self-maintained originates from itself” -[self]-ReflectiveLooksback on its own processes and semantic evolution - Is a constructivist approach |
|
|
Bootstrapping |
Building, creating or thinking aboutsomething from verylittle, orvirtually no resources or priorknowledge |
|
|
AREA PROs and CONs |
PROS: •Implicit/Explicitrepresentation•Bottom-up•Recursiveself-improvement•Bootstrapping•Atomicresolution•Uniformfine-grained representation•Forward/Backwardchaining CONS:•Fewimplementations•Manualcustomization (too atomic)•Nonmodular•Validityquestioned (by some)•RequiresReplicode (its own language) |
|
|
GOLEM |
-A cognitive meta-architecture - Goal-OrientedLearning Meta-Architecture |
|
|
GOLEM’scomponents |
HistoricalRepository =database storing the past history of Ss internalstates and actions, as well asinformation about the environmentduring Sspast • OperatingProgram =the program that S is governing its actionsby, at a given point in time • Predictor= program that estimates, given a candidate operatingprogramP and a possible future world W, the odds of P leading to W •Memory Manager program = program that decides when to storenew observations and actions in theHistorical Repository, and whichones to delete in order to do so;potentially it may be given somehard-wired constraints to follow,such as ‘never forget human history,or the previous century of yourlife.’•Tester =hard-wired program that estimates the quality of a candidatePredictor, using a simple backtestingmethodologyNZp |
|
|
All C.G.
|
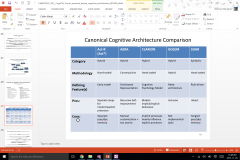
|

