![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
267 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many kjs are in a kcal?
|
4.18 kj
|
|
|
What does water intake depend on?
|
Species
Diet Temperature Work |
|
|
How does diet affect water intake?
|
Dry diet - less water intake
Dogs make up for this by drinking more water; cats have less total water intake |
|
|
What is gross energy?
|
The total amount of energy contained within a feed
|
|
|
What is digestible energy?
|
Gross energy - energy lost in faeces
|
|
|
What is metabolisable energy?
|
Digestible energy - energy lost in urine and combustible gases
|
|
|
Which energy term is used in small animal nutrition?
|
Metabolisable energy
|
|
|
Which classes of nutrients contribute to energy and thus can be used to work out the metabolisable energy of a food?
|
Carbohydrates
Fats Proteins |
|
|
What does metabolisable energy depend on?
|
Composition of the diet
Efficiency of the digestive system |
|
|
What is the energy density of a food?
|
The amount of metabolisable energy in kcal/weight (usually gram) of a dry weight of food
|
|
|
What is the usual energy density of pet food?
|
3.5 - 4.0 kcal/gram
|
|
|
What could happen if an animal eats a very energy dense food?
|
They may be deficient in other nutrients that need to be in balance with the increased kcal.
|
|
|
What could happen if an animal eats a low energy dense food?
|
They may not receive the energy required to fulfil its energy needs
|
|
|
What is the maintenance requirement of an animal?
|
The energy required to maintain a dog or cat at its optimal weight
|
|
|
What is the basal energy requirement?
|
The energy needed for a healthy, resting animal in the post-absorptive phase in a thermoneutral environment
|
|
|
What is the resting energy requirement?
|
The BER plus the energy required for the assimilation of food and recovery from physical activity
Usually about 10% greater than BER |
|
|
What is the formula for the resting energy requirement in cats and dogs?
|
70 x (current body weight)^0.75
Or linear formula for animals between 2 and 30kg: 70 x (current body weight x 30) |
|
|
What is the maintenance energy requirement in relation to RER?
|
Energy required by an animal with a moderately active life at home
Canine MER = 1.8 X RER Feline MER = 1.4 X RER |
|
|
How much dry matter does a dry pet food contain?
|
90-94%
|
|
|
What are the benefits of dry pet food?
|
Easy to store and feed
Usually most economical type of food Chewing may prevent plaque and tartar accumulation on the pet's teeth May be fed free choice if animal has no weight control problem |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of dry pet food?
|
Low quality dry foods may have:
Low palatability Low digestibility Low nutrient availability |
|
|
How much moisture do canned foods contain?
|
75-85%
|
|
|
What are the advantages of canned foods?
|
May be more palatable
Fewer preservatives (as sterile until can opened) |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of canned foods?
|
More expensive
Does not prevent plaque/tartar Difficult to feed free choice May only be complementary to diet (may not be complete and balanced) |
|
|
What are disadvantages of a homemade pet diet?
|
May not contain all nutrients needed; may result in deficiencies in calcium, fatty acids etc.
Raw food diets are more likely to contain bacteria e.g. toxoplasma, campylobacter, clostridium, salmonella etc. May be a health risk to children etc. |
|
|
What are food additives added for?
|
Colour, texture, palatability, stability or resistance to spoilage
|
|
|
What are types of preservatives?
|
Antioxidants, antimicrobials, food colour preservatives
|
|
|
Which types of nutrients are susceptible to oxidative destruction?
|
Animal fats, vegetable oils, fat-soluble vitamins
|
|
|
What does rancidity result in?
|
Offensive odour/flavour
Changes in colour/texture Loss of lipid and nutritional value |
|
|
Give an example of a natural colouring agent and examples of synthetic colouring agents
|
Carotene;
Azo dyes Nonazo dyes |
|
|
Give examples of additives used to preserve colour
|
Ascorbate
Nitrites Bisulphates |
|
|
Give examples of emulsifying agents
|
Gums, glycerides, glycerin and modified starch
|
|
|
How can pet foods be tested for adequacy?
|
Computer analysis
Laboratory (chemical) analysis Feeding trials |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of computer analysis?
|
Picks up large errors in formulation
Assumes that food in diet and database contain the same nutrients |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of laboratory analysis?
|
More accurate
More costly Doesn't take into account: interactions between nutrients, digestibility, acceptability, digestibility, availability of nutrients, toxicities Doesn't analyse individual minerals, vitamins and amino acids |
|
|
How are feeding trials evaluated?
|
Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO)
|
|
|
What is the best form of evaluation of a diet?
|
Feeding trials, esp. if long term
|
|
|
What are the two parts of a pet food label?
|
Principal display panel
Statutory/information panel |
|
|
What does the principal display panel contain?
|
Brand name
Product name Statement of intent Net weight Bursts/flags Product picture/slogan |
|
|
What does the statutory/information panel contain?
|
Ingredient statement
Typical/guaranteed analysis Product description Feeding guidelines Nutrient declaration Additives declaration Manufacturer/distributor name and address |
|
|
At what percentage of moisture must the water content be listed?
|
Over 14%
|
|
|
How do you convert a protein value of 20% in an as fed food to its value in a dry matter basis if the percent of moisture in the feed is 10%?
|
Take 10% from 100% = 90%
20%/90% = 22.2% protein on a dry matter basis |
|
|
What are the 5 vital assessments?
|
Temperature, pulse, respiration, pain assessment, nutritional assessment
|
|
|
What is involved in the nutritional assessment?
|
Diet specific factors, animal specific factors, feeding management, environmental factors
|
|
|
What are the 2 parts of a nutritional assessment?
|
Screening evaluation and extended evaluation
|
|
|
What forms part of the screening evaluation?
|
Every visit - diet history, body weight, body condition score, muscle condition score and evaluation of the coat
|
|
|
What body condition scoring is used with dogs and cats?
|
5 or 9 scale
3/5 or 4 or 5/9 for dogs 3/5 or 5/9 for cats |
|
|
Where would you palpate for scoring muscle mass?
|
Over the skull, scapula, spine and pelvis
|
|
|
What are the life stages recognised by nutritionists?
|
Maintenance, growth, reproduction, work
|
|
|
What should diets for growth contain more of?
|
Energy, protein, calcium and phosphorus
|
|
|
What could incorrect ratios of calcium and phosphorus lead to?
|
Skeletal problems
|
|
|
When are puppies introduced to different types of food?
|
3 weeks - gruel consistence weaning formula
4-6 weeks - Canned food/moistened dry food 7-8 weeks - weaned |
|
|
When are kittens introduced to different types of food?
|
4 weeks - canned food
7-8 weeks - weaned |
|
|
When does most of foetal growth occur in dogs?
|
3-4 weeks
|
|
|
When does most of foetal growth occur in dogs?
|
Throughout pregnancy
|
|
|
When should the dam's food intake be increased?
|
6th week of gestation - 10% increase per week
|
|
|
When should the queen's food intake be increased?
|
From time of conception
|
|
|
What may an inadequate diet cause in dog/cat gestation?
|
Loss of condition in dam/queen
Diarrhoea in dam/queen Poor performance in puppies/kittens |
|
|
What are the energy requirements of a ***** during lactation?
|
1.5x during week 1
2x during week 2 3x from week 3 to weaning |
|
|
What are the energy requirements of a queen during lactation?
|
2-4 times
|
|
|
Name types of work dogs
|
Guide, cattle/sheep, sledge, racing, guard, rescue, agility, hunting
|
|
|
How much more energy do cattle/sheep dogs require compared to dogs at maintenance level?
|
3-4 times
|
|
|
How much more energy do agility dogs require?
|
2-3 times
|
|
|
How much of the calorie intake by working dogs should be protein?
|
At least 24%
|
|
|
What percentage of older dogs are a) overweight and b) underweight?
|
a) 25-35%
b)20% |
|
|
How much less energy do dogs over 8 require compared to 1 yr old dogs?
|
20% less
|
|
|
What is the reduction in energy requirements of older dogs caused by?
|
1/3 caused by decreased lean body mass
2/3 caused by decreased activity |
|
|
What is the MER of older cats like compared to dogs?
|
Does not decrease as much as dogs (due to lower reduction in lean body mass and less of a decrease in physical activity as dogs)
|
|
|
How does protein/fat/carbohydrate digestion change in older cats?
|
Protein digestion - decreases linearly
Fat digestion - varies among cats Carbohydrate - stays the same |
|
|
What are the effects of this on an older cat's diet?
|
May require more food or food with higher digestibility
|
|
|
What percentage of dogs and cats are overweight?
|
Dogs - 24-34%
Cats - 25% to 40% |
|
|
What is the definition of obesity?
|
Excess body weight of 20%
|
|
|
What factors influence the risk of dogs/cats to obesity?
|
Metabolic rate and satiety feedback mechanisms
Activity level Food intake Diet composition and palatability Environment and lifestyle |
|
|
Why is fasting an inappropriate form of weight loss?
|
Fasting leads to loss of muscle mass. Decrease in metabolic rate which stays low when return to feeding (therefore easier to gain weight than before)
|
|
|
Why do cats have higher blood glucose after eating a high-carbohydrate meal compared to a high-protein meal?
|
They do not have hepatic glucokinase -> less hepatic storage of glycogen -> higher blood glucose
Also limited amylase produced from feline pancreas |
|
|
How much of a feed (in dry matter) needs to be protein for cats and dogs?
|
Cats:
30% kittens 26% adults Dogs: 28% puppies 22% adults |
|
|
How much of total protein should be meat protein?
|
19% at least
|
|
|
Why do cats have a dietary requirement for taurine?
|
They have a limited ability to synthesise taurine from methionine and cystine
Are obligate users of taurine for bile acid conjugation |
|
|
When might taurine deficiency occur in cats?
|
Cats fed dog food
Insufficient meat protein Poor quality commercial diets Low quality protein e.g. offal |
|
|
What does taurine deficiency cause?
|
Reproductive problems
Retinal blindness Dilated cardiomyopathy |
|
|
Which essential amino acid is required by all mammals?
|
Omega-6 linoleic acid
|
|
|
Which amino acid is required by cats?
|
Arachadonic acid
|
|
|
What might an insufficiency in arachadonic acid cause?
|
Reproductive problems
Poor platelet aggregation |
|
|
Why do cats require vitamin A in their diets?
|
They cannot convert beta-carotene to vitamin A
|
|
|
What might a vitamin A deficiency result in?
|
Night blindness, reduced fertility, poor coat condition, impaired growth, abnormal bone structure, increased risk of respiratory disease
|
|
|
What are signs of vitamin A toxicity?
|
Pain and stiffness in the neck, lethargy, reduced grooming, gingivitis, lameness, depression, irritability, bony exostoses
|
|
|
What increases the requirement for vitamin E in cats?
|
Diet high in polyunsaturated fats
|
|
|
What can a deficiency in vitamin E, caused by diet too high in polyunsaturated fats compared to antioxidant, cause?
|
Body fat peroxidation
Pansteatitis, anorexia, pain, fever, nodules under the skin |
|
|
How many times more B vitamins do cats require than dogs?
|
2-3 times
|
|
|
What destroys thiamin?
|
Thiamin - B vitamin
Overcooking Fish Sulphites |
|
|
What does a deficiency in thiamin cause?
|
Ataxia, blindness, ventroflexion of the neck
|
|
|
Do cats and dogs require vitamin D in their diet?
|
Yes, they cannot obtain it from sunlight
|
|
|
Why do cats require vitamin B niacin?
|
They cannot convert tryptophan to niacin (B vitamin)
|
|
|
What is the dominance hierarchy in cats like?
|
No dominance hierarchy - sometimes matriarchal
|
|
|
What is the return to emotional homeostasis like in cats?
|
Slow return
|
|
|
Do cats show submissive signals?
|
NO
|
|
|
What is the primary reason for cats scratching?
|
Marking territory
(Shortening claws) |
|
|
What is eyesight like in cats?
|
Excellent
|
|
|
What is the purpose of cats "spraying"?
|
Due to stress response
Other cats Attention seeking Sexual ;) |
|
|
What is urination dependent on?
|
Substrate and location
Familiarity |
|
|
What is middening?
|
Cat marking his territory by defaecating in prominent areas
|
|
|
What may cause inappropriate toileting in cats?
|
Use of cleaning product
Stress SMells Noises Novelty etc. |
|
|
What is the difference between wolf and dog aggression?
|
Wolf - last resort
Dog - not always |
|
|
When is the sensitive socialisation and learning phase in puppies?
|
3-12 weeks
Should experience all of pleasure, apprehension, frustration, anxiety |
|
|
What could lack of exposure to mild negative stimuli lead to?
|
Lack of coping mechanisms learnt by exposure -> excessive negative emotions
|
|
|
What is swayback, white muscle disease and pining in sheep?
|
Swayback - Cu deficiency in mid to late preggers ewews
White muscle disease - Se/Vit E Pining - Co/vit B12 |
|
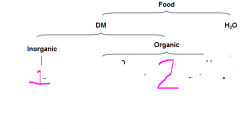
What is contained in the organic and inorganic parts of food?
|
Organic - carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, organic acids, vitamins
Inorganic - minerals |
|
|
What is an ether extract used to measure in a feed?
|
Lipid content
|
|
|
How do you calculate crude protein of a feed?
|
Assumes food contains 16% N
Calculate N content of food and then x by 6.25 |
|
|
How is the organic matter of a feed calculated?
|
DM - ash
|
|
|
What does the neutral detergent fibre contain?
|
NDF - cell wall materials - lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose (not pectins)
|
|
|
What does the acid detergent fibre contain?
|
ADF - cell wall materials - lignin and cellulose
|
|
|
What is a structural and non-structural CHO?
|
Structural - in cell wall
Non-structural - storage |
|
|
What is the microbial degradation of plant cell walls variable on?
|
Plant species
Stage of growth Cell wall composition Type of cell wall constituents |
|
|
What else is found in plant cell walls except for polysaccharides?
|
Proteins
Water Phenolics (e.g. lignin) Minerals |
|
|
How is lignin correlated to digestibility?
|
Inversely correlated
|
|
|
How does the lignin content change as plants mature?
|
Lignin content increases
Mature plants, hay, straw |
|
|
How does structural CHO content change as plants mature?
|
Increases, decreases nutritive value
|
|
|
Give 2 examples of non-structural CHOs in plants
|
Fructan
Starch |
|
|
What is fructan and where is it stored in a plant?
|
Primarily stem
Polymer of fructose |
|
|
What is the water-soluble CHO fraction? (WSC fraction)
|
Fructan + simple sugars (glucose, fructose, sucrose)
|
|
|
Which factors affect CHO storage in plants?
|
Genetics
Plant part Stage of growth Time of day Environment Season |
|
|
What is the non-CHO content of plants like in early spring/late spring and summer?
|
Early spring - increased growth thus decreased non-CHOs
Late spring/summer - increased non-CHOs |
|
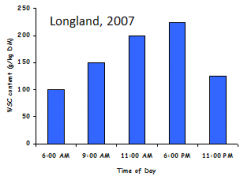
What does this graph show?
|
Peak non-CHOs in late afternoon
|
|

lol remember this
|
low temp, more non-cho
low water, more non-cho |
|
|
What does starch content vary with?
|
Plant species
40-70% dry matter in cereal grains 5% in legumes |
|

What do these statistics represent?
|
How much of animals' diets are grass
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of grassland?
|
Natural (16 million acres)
Cultivated - permanent (12 million acres) and rotational (6 million acres) |
|
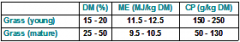
How much dry matter is there in young and mature grass?
|
15-20% young
25-50% mature |
|
|
How much metabolisable energy is there in young and mature grass?
|
11.5-12.5
9.5-10.5 MJ/kg |
|
|
How much crude protein is there in young and mature grass?
|
150-250 young
50-130 mature g/kg |
|
|
What type of plant species would be found in rough grazing?
|
Heathers, low-quality grasses, rushes, mosses
|
|
|
How is permanent pasture (cultivated) maintained?
|
Without reseeding
|
|
|
What types of grasses are found in permanent pasture?
|
Ryegrasses, meadowgrass, timothy, fescues, cocksfoot
|
|
|
Is permanent or rotational pasture > or < 5 years old?
|
Permanent > 5 years old
Rotational < 5 years old |
|
|
What are common herbage species in rotational pasture?
|
Ryegrass
Ryegrass and legume mixes |
|
|
Is permanent or rotational pasture used for conservation/grazing?
|
Permanent - grazing
Rotational - grazing/conservation or both |
|
|
Give 2 examples of legumes
|
Clover - white/red
Higher CP and minerals than grasses Lucerne Higher CP than grasses |
|
|
What are some associated problems with grazing legumes?
|
Bloat
Phytoestrogens (red clover) |
|
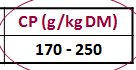
Which legume has this amount of CP?
|
Clover
|
|
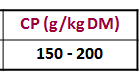
Which legume has this amount of CP?
|
Lucerne
|
|
|
What factors affect grass growth?
|

those
|
|
|
Below which temperature does growth of grass not occur?
|
<5 degrees C
|
|
|
Which principle nutrients are required in fertiliser?
|
Nitrogen
Phosphorus Potash NPK K = potassium |
|
|
What is the pH of mineral soils compared to peaty soils?
|
Mineral soils - 6-6.5
Peaty - 5.6 |
|
|
What are lime and sulphur used for?
|
Lime increases soil pH
Sulphur decreases soil pH |
|
|
When does soil testing take place?
|
Late winter, pH and NPK requirement
|
|
|
What is harrowing and when does it take place?
|

Spring
|
|
|
What is rolling and when does it take place?
|

Spring
|
|
|
When does topping take place?
|
Ongoing
|
|
|
What are 4 types of grazing?
|
Continuous
Rotational/strip - paddocks or electric fence Mixed/alternate - sheep and cattle Zero - grass cut and fed |
|

Nutrition of grass bla
|
blka
|
|
|
Which factors affect the nutritive value of grass?
|
Stage of growth
Species Soil type Environmental conditions |
|
|
How is conservation of forage achieved?
|
Reduce the moisture content - chemical breakdown and microbial degradation
Acidification - prevents spoilage organisms, plant enzyme activity |
|
|
What is hay made from, at what stage and how is it conserved?
|
Grass
Mature stage Field/barn dried Dry matter = 85% |
|
|
What do cutting/drying changes in hay occur due to?
|
Oxidation
Leaching Microbial and plant enzymes Mechanical damage |
|
|
How does the speed of drying affect nutrient loss in hay?
|
Rapid drying = less nutrient loss
|
|
|
How can an animal owner reduce dust content in hay?
|
Soak for 30 minutes
|
|
|
What type of forage is conserved by artificial dehydration?
|
Younger, higher digestibility forage
|
|
|
How is forage artificially dried?
|
800 degrees c for 0.5 mins
|
|
|
Compare how changes in storage affect nutritive value of forage in hay drying and artificial drying?
|
Minimal problems with storage with artificial drying
|
|
|
How is forage conserved?
|
Anaerobic fermentation
|
|
|
What is ensiling?
|
Anaerobic fermentation of plant WS to lactic acid by epiphytic lactic acid bacteria
|
|
|
From which crops can silage be made?
|
Grass
Legumes Cereal grains Crop by-products |
|
|
Why are legumes usually wilted prior to ensilage and treated with an additive?
|
They have low DM, WSC, LAB and a high buffering capacity
|
|
|
What are the two types of fermentation?
|
Primary - desirable lactic acid fermentation
Secondary - undesired clostridial (butyric) fermentation |
|
|
What characteristics does well-preserved silage have?
|
Low pH
Low levels of butyric acid Low concentration of ammonia-N Higher conc of lactic acid |
|
|
What can silage with higher DM have?
|
Higher pH
Low lactate (more mature silage or wilted) Low butyric acid Small amount of ammonia-N |
|
|
What kind of crops is badly preserved silage made from?
|
High moisture content
Low LAB Low levels of WSC = high levels of clostridia or enterobacteria |
|
|
What is the main component of DM of cereal grains?
|
Starch
|
|
|
What is the protein quality and Ca:P ratio like in cereal grains?
|
Low protein quality - low essential acids
Poor Ca:P ratio - low Ca |
|
|
What is the percentage of starch in oats, barley and maize?
|
Oats - 40%
Barley - 55% Maize - 70% |
|
|
What is the purpose of cereal processing?
|
Increases digestibility
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of processing?
|
Mechanical - rolling, grinding
More sophisticated - micronisation, extrusion |
|
|
Give 2 examples of root crops
|
Turnip, suede
|
|
|
Describe the composition of root crops
|
High sugar content
High digestibility Low CP |
|
|
Describe the composition of sugar beet pulp
|
Low P, high Ca
Moderate protein High fibre content |
|
|
Describe the composition of tuber crops
|
High starch
Low fibre Low minerals |
|
|
Name 3 types of protein concentrate
|
Oilseed cake/meal - rapeseed, sunflower seed, soyabean, linseed
Leguminous seeds - peas, beans Animal protein concentrates - meat and bone meal, fish meal, blood meal |
|
|
What is digestibility?
|

Proportion of food not excreted in faeces (apparent or true)
|
|
|
What are types of digestibility?
|
Dy matter digestibility
Organic matter digestibility Digestibile organic matter digestibility |
|
|
What are the limitations of in vivo measurement of digestibility?
|
Can't determine site of digestion/absorption
Expensive Time-consuming (in situ - fistulated - welfare) |
|
|
Which factors affect digestibility?
|
Food composition
Food processing Feeding level Ration composition Animals |
|
|
Which factors affect the metabolisable energy of a feed?
|
Faecal losses
Excess N Nature of digestion |
|
|
What is net energy?
|
ME - heat losses
|
|
|
Why is ME less variable than NE?
|
NE uses two values - energy used for maintenance and one for production (stored and used)
|
|
|
pigs and horses
|
digestible energy
|
|
|
In ruminants what are essential and non-essential amino acids?
|
E - supplied in diet
Non-E - supplied by microbes in rumen |
|
|
What is the metabolisable protein system?
|
The total digestible true protein available for the animal for metabolism after digestion and absorption
|
|
|
What are the 2 components to the metabolisable protein system?
|
Digestible microbial true protein (DMTP) - supplied by ruminal microbes
Digestible undegraded dietary protein (DUP) - absorbed in abomasum and SI |
|
|
What are the 2 components of feed crude protein?
|
Rumen degradable protein
Undegradable dietary protein |
|
|
What is the effective rumen degradable protein?
|
The total N captured from rumen degradable protein (RDP) and used for microbial growth
|
|
|
What are the 2 fractions of ERDP?
|
Quickly degradable protein QDP
Slowly degradable protein SDP 80% 100% utilised |
|
|
What is digestible microbial crude protein?
|
Total protein and non-protein N produced by microbes
|
|
|
What is microbial true protein?
|
Protein synthesised by microbes
|
|
|
What are the 4 steps of ration formulation?
|
1 - determine weight/condition of animal
2 - establish use of animal 3 - calculate nutrient requirements 4 - formulate diet |
|
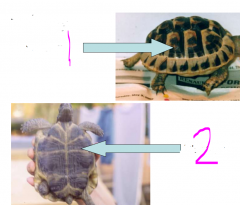
Name
|
1 - carapace
2 - plastron |
|
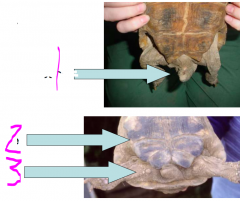
name
|
1 - cloaca
2 - plastron hinge 3 - spurs |
|
|
Describe the spur-thighed tortoise
|
Spurs on back legs
Flexible plastron hinge No tubercle on end of tail |
|
|
Describe Hermann's tortoise
|
Black and yellow shell
Tubercle, no spurs Dark skinned |
|
|
Describe Horsfield's tortoise
|
Yellow shell
Pale skinned Tubercle and spurs |
|
|
Most tortoise species hibernate
|
Likely pale skinned ones won't
|
|
|
What are CITES appendix I species?
|
Require an article 10 certificate for trade
Hermann's, spur thighed, Marginated |
|

Identify the species
|
African spurred tortoise - do not hibernate, require more fibrous food and hotter temperatures
|
|

Identify the species
|
Leopard tortoise
|
|

Identify the species
|
Red footed tortoise
|
|
|
How should the diet of rainforest floor tortoises be changed?
|
Fruit, mushrooms should be 10% of diet
Do not hibernate Humidity should be increased |
|
|
Sex a tortoise
|
Females - flatter plastron, shorter tail, more proximal cloaca, flare of carapace
|
|
|
How does the diet of bearded dragons change as they grow?
|
Juveniles - insectivorous
Adults - herbivorous |
|
|
What do Asian water dragons require?
|
Insectivores/carnivores
|
|
|
What is the diet of veiled chameleons?
|
Omnivorous
|
|
|
What is the diet of green iguanas?
|
Herbivorous but aggressive
|
|
|
What is the diet of leopard geckos?
|
Insectivorous - deserts/nocturnal
|
|
|
How do you sex lizards?
|
Males are more coloured, with more adornments
Hemipenes Males have more prominent preanal or femoral pores |
|
|
Corn and rat snake
Python |
South American colubrid python
Royal python (S. African) |
|
|
How do you sex a snake?
|
Males have longer, wider tails
Larger number of subcaudal scales Males probe will pass 6-12 scales, females 4-6 |
|
|
What is the range called in which reptiles can thermoregulate?
|
Activity temperature range
|
|
|
What is Ts?
What is To |
Selected body temperature - temperature at which body temperature can be varied
Optimal body temperature |
|
|
What is heliothermic and thigmothermic?
|
Helio - heat gained from radiation from the Sun
Thigmo - heat gained from conduction from surrounding objects |
|
|
What is the common bottom end limit of the ATR?
|
24 degrees C
|
|
|
What does a lack of UV-b light (along with low temperatures and a calcium deficiency) lead to?
|
Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
Do basking reptiles require UV-b light?
|
nope
|
|
|
What are properties of UV-b light?
|
Has to be replaced every 6 months as it diminishes over time
Has to be close to reptile as it diminishes over distance |
|
|
How must water be presented to chameleons?
|
Dripping from foliage
|
|
|
How much energy does a reptile use compared to a mammal of the same size?
|
2-5%
|
|
|
What is gut loading?
|
Feeding crickets and **** to murder them for snakes and ****
|
|
|
What is the minimum Ca:P ratio needed by reptiles?
|
2:1
Ca 2% dry matter |
|
|
How often do small snakes and large snakes feed?
|
Small - every 1 to 2 weeks
Large - monthly |
|
|
How should a snake be fed?
|
Prey at 39 degrees C, handled with tongs
|
|
|
What is the dental formula for myomorphs and hystricomorphs?
|
1/1 0/0 0/0 3/3
1/1 0/0 1/1 3/3 Molars continuously grow in hystricomorphs |
|
|
What do male hamsters have?
|
Flank sebaceous glands
|
|
|
Which rodent should you not grab by the base of tail and which should you not grab by the scruff of the neck?
|
Gerbil
Rat |
|
|
How do you sex myomorphs?
|
Males have greater anogenital distance
|
|
|
How do you sex guinea pigs?
|
Males round, females, y-shaped
|
|
|
How do you sex chinchillas?
|
Males - greater anogenital distance, no scrotum
|
|
|
What is the oestrus period and young of mice/rats/hamsters/gerbils like?
|
Polyoestrus - every 4/5 days
Altricial young |
|
|
Breeds of guinea pig?
|
Abyssinian, peruvian
|
|
|
What are the young of guinea pigs like?
|
Precocial
Guinea pigs polyoestrus (every 15-17 days) breed at 12 weeks |
|
|
What is the oestrus period of a chinchilla and their young?
|
Polyoestrus - every 30-50 days
Precocial young |
|
|
Degus - females communally raise young
|
no regular oestrus cycle - requires male
gestation 90 days |
|
|
What are the young of rabbits like?
|
Altricial
|
|
|
Do ferrets have os penis?
|
AYE
|
|
|
Describe oestrus of ferrets
|
Seasonally monooestrus
Induced |
|
|
What is hyperoestrogenism?
|
If unmated, high oestrogen can lead to bone marrow suppression - anaemia
|
|
|
Describe the young of ferrets
|
Altricial
|
|
|
What is nidicolous young?
|
Ones that stay by the nest
|
|
|
Where is the microchip placed in psittacines?
|
L pectoral muscle
|
|
|
What is iron storage disease?
|
Haemosiderosis or haemochromatosis
|
|
|
What leads to angel wing?
|
Too much protein in young's diet
|
|
|
4 steps to training raptor?
|
Manning
Early training Fitness Hunting |
|
|
jesse
|
swivel and leash
|
|
|
block perches
bow perches |
falcons
other species e.g. hawks, eagles |
|
|
When do you adjust horses' ration formulation during gestation?
|
First 4 months - maintenance
Last 7 - adjust ration |
|
|
horse lac
|
Early lactation = 2 x maintenance
Late lactation = 1.75 x maintenance |
|
|
horse breeding stallion
|
Breeding season = 1.2 x maintenance energy and protein
|
|
|
newborn and 1 year old weights
|
Newborn = 10 % of adult weight
One year old = 60 to 70 % of adult weight (80 to 90 % of adult height) |
|
|
foals come off milk
|
after 3 months
weaned 4-6 months |
|
|
what energy unit does horse nutrition use?
|
Horse diets use megajoules (1 MJ = 239 calories)
|
|
|
two systems of deer farming
|
Lowland farms: Breeding and finishing
Upland farms : Sell weaned animals in autumn to lowland farms for finishing |
|
|
when are boarlets weaned?
|
• Boarlets are weaned at 8-14 weeks
|
|
|
when do boars reach slaughter weight?
|
75-85 kg by 9-12 months
|
|
|
when are ostriches killed?
|
♂ killed @ 14 months (120 kg)
|
|
|
camelids weaning ages
|
• Weaned 4-6 months
|
|
|
live weight to dead weight
|
To convert Liveweight into Deadweight Divide by 1.36
|
|
|
when can boars be used for service?
|
7-8 months old
|
|
|
what weight do you buy weaners in?
|
Buy in weaners at 8kg –
30kg – Ready for slaughter around 5-6 months later |
|
|
quarantine in pigs
|
•
Ideally 2 - 3km from main herd • At least 100m from main herd 4 weeks minimum on commercial farms |

