![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two parathyroid hormone drugs? |
Teriparatide (hPTH) (1-34) Full length hPTH (1-84) |
|
|
What are the two calcitonin drugs? |
Synthetic human cacitonin hCT Natural calcitonin from salmon |
|
|
What are the 9 vitamin D agents? |

|
|
|
What is the first generation bisphosphonate?
What are the three second generations?
What are the three third generations? |

|
|
|
What is the calcium sensing receptor mimetic? |
Cinacalcet |
|
|
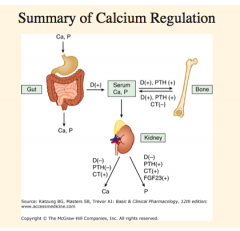
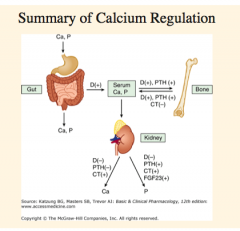
Calcium is controlled by that three calcitropic hormones? |

|
|
|
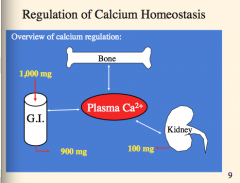
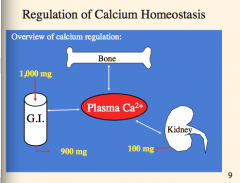
What are calcium and phosphate in the blood in equilibrium with?
What does this allow?
What is the total dietary intake and excretion of calcium?
What is excretion of calcium by the kidney (amount)? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
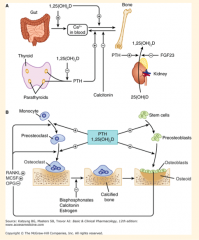
Draw this out. |
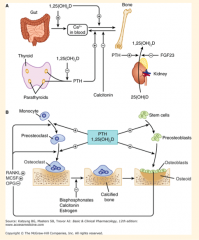
|
|
|
What is the function of parathyroid hormone?
What is it synthesized by?
What are the three major actions? |

|
|
|
Again, three effects of low concentration of calcium in blood? |
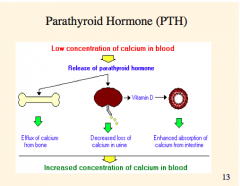
|
|
|
What are the two effects of activation of the calcium sensor? |
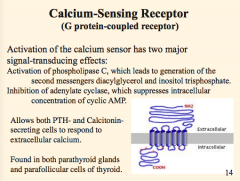
|
|
|
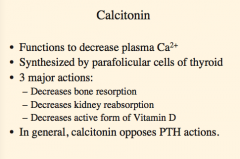
What is the function of calcitonin?
Where is it synthesized?
What are the three major actions? |
|
|
|
What is the function of calcitriol?
Where is it synthesized?
What is its most important physiological action?
Two additional pharmacological activities? |

|
|
|
What does loss of calcium homeostasis lead to? Six things |

|
|
|
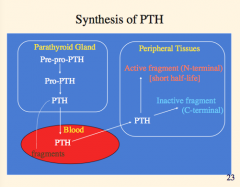
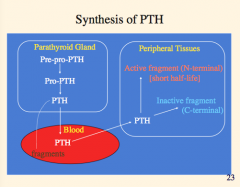
What detects low calcium? What does it cause increased synthesis of?
What does the increased PTH cause? |

|
|
|
What detects high calcium? What does this cause an increase of?
How does this affect PTH, resorption of bone, vitamin D, and PTH. |

|
|
Review |
Review |
|
|
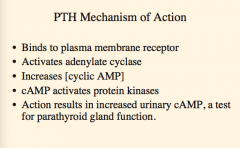
What is the PTH mechanism of action?
Where does it bind? What does it activate? What does it increase?
What activates protein kinases? What does this increase which is also a test for parathyroid gland function? |
|
|
|
What is hypoparathyroidis most common from?
What is the treatment? What is it more commonly treated with? |

|
|
|
What directly stimulates bone formation? (Drug name)
What causes bone resorption?
Exogenous PTH in low doses increases what without stimulation resorption?
What group of people may benefit from this? Any effect on IGF-1? |

|
|
|
What was the first SERM to be approved for osteoporosis? Does it stimulate breast cancer? |

|
|
|
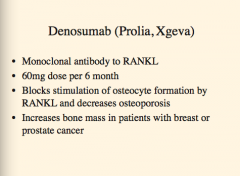
What type of drug is denosumab (mechanism)?
Does it increase or decrease bone mass in patients with breast or prostate cancer? |
|
|
|
What does FGF23 inhibit production of? What is the effect on PTH in kidney? What is it produced by? |

|
|
|
What is the pathway of calcium synthesis? What are the two cells that it acts on? |

|
|
|
What does calcitonin bind to? Does it increase or decrease the ruffled border surface area on osteoclasts?
Is it a global inhibitor of PTH? Does it have renal effects? |

|
|
|
What two drugs are very effective for short term hypercalcemia treatment? What develops with long term use?
Can a steroid be taken? How are the calcitonin drugs administered?
What is a bone remodeling disorder? |

|
|
|
What is another name for calcitriol?
What is it now recognized as? Where is it synthesized? Transported to? Binds to what?
It is the most important what? |

|
|
|
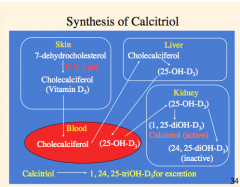
Outline the synthesis of calcitriol: |
|
|
|
What are the calcitriol mechanisms of action:
Intestine Calbindin Protein synthesis Ca2+ uptake |

|
|
|
What are the major uses of calcitriol? (think about diseases of low vitamin D) |

|
|
|
Where eis vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) found? What is the plant form?
|

|
|
|
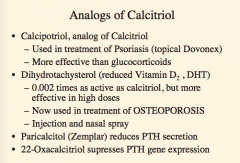
What is an analog of calcitriol used in the treamtne of psoriasis? What is it more effective than?
What is a reduced vitamin D now used in the treatment of osteoporosis?
What reduces PTH secretion?
What suppresses PTH gene expression?
|
|
|
|
What are nonhydrolyzable analogs of inorganic pyrophosphate?
What do they inhibit?
What were they first used in?
Effective in treatment of what?
The drugs etidronate and pamidronate are not effective in management of hypercalcemia but a 4 to 24 hours infusion is effective in ________ for several weeks. |

|
|
|
What three bisphosphonates are used in Paget's disease?
Which one is used for osteoporosis?
Are they all absorbed well in the intestine?
How must they be taken? How often? |

|
|
|
Recognize the potency of the first, 2nd, third generation bisphosphonates. |

|
|
|
What is s serious complication of bisphosphonates? Which generation in particular?
Effects on teeth? |

|
|
|

|
|
|
Which drugs are a common cause of osteoporosis in adults?
What do they antagonize?
What are they useful in reversing? |

|
|
|
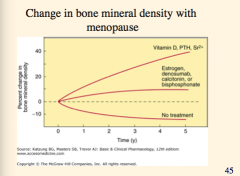
Which drugs are effective in preventing osteoporosis?
Replacement risks have shown an increase of what? |

|
|
|
What is the positive effect on bisphosphonates in cancer therapy?
Which cancer patients should get bisphosphonates?
90% of patients in US are on _____ or _____.
The use of bisphosphonates shows a decrease in _________ complications by up to one third. |

|
|
|
Calcium sensor receptor mimetics bind to what?
Which drugs is approved for hyperaparthyroidism in patients with parathyroid carcinoma?
What is the mechanism? Effectively lowers what? |
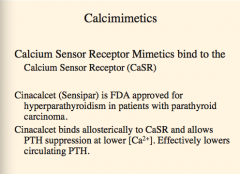
|
|
|
What is the antibiotic used for Paget's disease and hypercalcemia for many years, now seldom used? |
Plicamycin |
|
|
What drug is used in Europe for osteoporosis?
What does it block and two things it promotes?
What does it increase and decrease (think bone effects)?
Side effects?
|

Venous embolism, PE, and serious CV effects (heart attacks!) |
|
|
What is fluoride used for?
What does F- bind? Can be used to prevent what? Potential agent in preventing _____________.
What are two toxicities?
Is there a cancer risk? |

|

