![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Production |
The process by which resources are transformed into products or services that are used in other production processes or consumed. |
|
|
What are three important questions to ask for production? |
What to produce? (product-product tradeoffs) How much to produce? (input-product) How to produce? (input-input substitution) |
|
|
What are important decisions to make for production? |
Resources are scarce and frequently costly
Competition forces efficiency and good planning
Profit is necessary for firm survival |
|
|
What are the production-physical relationships? |
Input-input Product-product Input-product |
|
|
How are outputs and inputs measured in Production-physical relationships? |
pounds, tons, bushels, kg., and acres |
|
|
What are the production-input classes? |
Land Labor Management (Entrepreneurship) - Decision making Capital - every manufactured item that can be used in production |
|
|
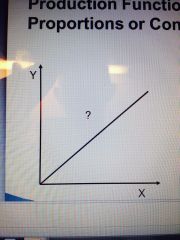
Fixed Proportions |
We increase all by the same percentage |
|
|
All ________ are increased in the same proportions. |
inputs |
|
|
Total Physical Product (TPP) |
|
|
Y = _______ = f (X1 l X2, X3...., Xn) |
TPP |
|
|
TPP or Y ___________ at a(n) ______________ rate, then ______________ at a ______________ rate before it reaches its peak/maximum. |
increases increasing increases decreasing |
|
|
Beyond the peak, TPP may begin to ________ even as X1 continues to _____________. |
decline increase |
|
|
Define Marginal Physical Product (MPP) |
The amount added to TPP when another unit of input is used; the slope of the TPP curve |
|
|
Define the Average Physical Product |
TPP divided by the quantity of input |
|
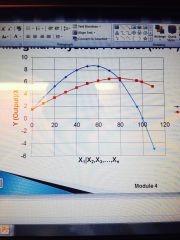
What is the blue line? What is the red line? |
Blue line = MPP
Red line = APP |
|
|
Where is stage 1 located on an MPP and APP graph? |
Before MPP and APP cross |
|
|
Where is stage 2 located on an MPP and APP graph? |
From when the line of MPP and APP cross until the line of MPP hits zero |
|
|
Where is stage 3 located on an MPP and APP graph? |
Starting when the line of MPP hits zero |
|
|
Define Stage 1 |
APP is increasing throughout, MPP is greater than APP, MPP increases then decreases; irrational
As long as the marginal contribution is greater than the average, add more input |
|
|
Define Stage 2 |
APP is decreasing throughout, MPP is less than APP, MPP goes to zero; rational |
|
|
Define Stage 3 |
MPP is negative; irrational |
|
|
When do you use more of the input? |
If the marginal benefit>marginal cost (in this case the input)
As you use more, the marginal benefit will decrease because MPP will decrease as you use more. |
|
|
When do you use less input? |
If the marginal benefit<marginal cost
As you use less, the marginal benefit will increase because MPP will increase as you use less.
Best decision: marginal benefit = marginal cost |
|
|
Define Total Value Product (TVP) |
TPP multiplied by the price of the product (output) |
|
|
Define Average Value Product (AVP) |
TVP divided by the number of units of the variable input |
|
|
Define Marginal Value Product (MVP) |
The change in TVP divided by the change in the variable input |
|
|
Define Total Factor Cost (TFC) |
the Variable Input multiplied by the price of the input (factor) |
|
|
Define Marginal Factor Cost (MFC) |
the change in TFC divided by change in the variable input |
|
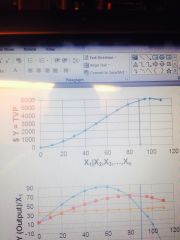
What does the blue line represent in the top graph? |
TVP |
|
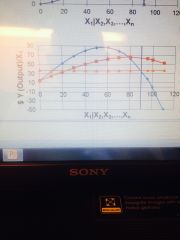
What does the blue line represent? Red line? Orange line? |
MVP AVP MFC |
|
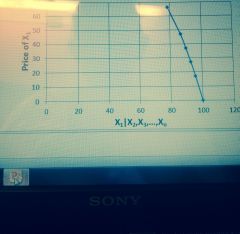
What does this line represent? |
Input demand |
|
|
If we have improved technology and doubled the output for every input level, what will happen to the lines in the graphs? |
Shift upward |
|
|
Use marginal unit of the input until the _____________________ is equal to the Marginal Factor Cost. |
Marginal Value Product
MVP = MFC |
|
|
Aggregate supply |
Profitability Number of firms Risk and government policies |
|
|
Opportunity costs are _________ costs.
Opportunity costs are true ___________________. |
Implicit
costs of production |
|
|
Define Opportunity Cost |
the value of output that could have been obtained from an alternative use |
|
|
Define implicit cost |
opportunity cost that does not involve a money payment or market transaction
Ex: owned land, tractor that is owned |
|
|
Define explicit cost |
cost that involves a money payment and usually a market transaction. Also called out-of-pocket or accounting cost. |
|
|
Define Bookkeeping profit (accounting profit) |
occurs when all operating costs and overhead costs are exceeded by revenues so that a net balance remains |
|
|
Define economic profit |
occurs when revenues exceed the total of all explicit as well as implicit costs. Considers alternative uses of the resources or opportunity costs |
|
|
Define fixed costs |
costs that do not change as the quantity of output changes |
|
|
Define variable costs |
costs that change as the quantity of output changes |
|
|
In the immediate short run, meaning now, all _____________ are fixed. |
resources |
|
|
_________________ is a short run concept. |
Diminishing returns |
|
|
Ultimate long run: all _____________ are variable. |
Resources |
|
|
What is the total revenue equation? |
Price of output * Price of the input |
|
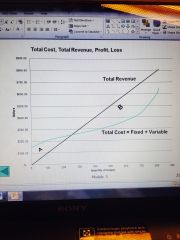
What is A? B? |
A = Profit
B = Loss |
|
|
Define marginal cost |
the change in total cost divided by the change in output; the price of the input divided by the MPP |
|

What does A represent? B? C? D? |
A = ATC B = AFC C = MC D = AVC |
|
|
Define marginal revenue |
the change in total revenue divided by the change in output |
|
|
What is the profit in the graph? (What area do you shade?) |
MC vertical to ATC then shade it all the way across |
|
|
What happens if price is below ATC? |
There is no economic profit. |
|
|
When will firms supply goods in the short run? |
If the price is greater than AVC.
The firm's short-run supply curve is Marginal Cost above Average Variable Cost |
|
|
Define Elasticity of supply |
Percentage change in quantity supplied divided by percentage change in price.
Generally positive
Supply can either be elastic (>1) or inelastic (<1) |
|
|
As length of run ___________, supply becomes more ________ because of the ability to change more of the resource base. |
increases elastic |
|
|
Supply shifters (longer run) |
Technology Price of the inputs Number of firms in the industry Change in the price of the output causes movement along the curve (does not shift the whole curve) |
|
|
Define surplus |
If the prices are above equilibrium, quantity supplied will be greater than quantity demanded |
|
|
Define shortage |
If the prices are below equilibrium, quantity demanded will be greater than quantity supplied |
|
|
Bumper crops do what? |
Shift supply to the right |
|
|
Crop failures do what? |
shift supply to the left |
|
|
What does factor-factor substitution look like? |
f (X1, X2 l X3, X4....., Xn) |
|
|
Isoproduct or Isoquant Curve |
Represent levels (amounts) of output, Yn. |
|
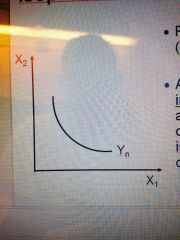
What curve is this? |
Isoproduct or Isoquant Curve |
|
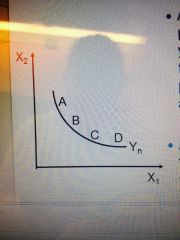
As you move from A to D, what happens? |
You substitute factor 1 for factor 2 while producing the same amount of output |
|
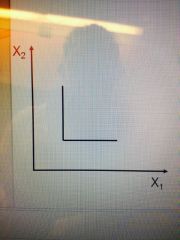
What does a right angle suggest? |
Isoquants at right angles suggest that fixed proportions or zero substitution of one input for the other
Factors 1 and 2 are one fixed combination of two inputs |
|
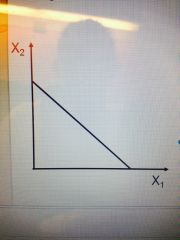
What does this straight line suggest? |
Isoquants in straight lines suggest perfect substitution of one factor for the other |
|
|
What is the negative of the slope of the isoquant called? |
Marginal rate of substitution (MRS) or the Marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS)
^positive since the slope is negative |
|
|
Isocost lines |
Show the cost of various input combinations
On each line, the total cost is constant
The slope of the line shows how the market values one input versus the other |
|
|
Define Marginal Rate of Product Substitution |
amount of one product given up to produce another product
calculated as the slope of the production possibilities curve |
|
|
Define expansion path |
shows how output will change as resources change |

