![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
239 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the 3 muscles of the hamstrings.
|
1. Semitendinosus
2. Semimembranosus 3. Biceps femoris |
|
|
Name the 3 joint actions of the pelvic girdle.
|
1. anterior pelvic tilt
2. posterior pelvic tilt 3. lateral pelvic tilt |
|
|
Name the 4 primary joint actions of the spine.
|
1. flexion
2. extension 3. rotation 4. lateral flexion |
|
|
Name the 4 primary joint actions of the trapezius.
|
1. Upper trap: scapular elevation
2. Mid trap: scapular retraction 3. Lower trap: scapular depression 4. Lower trap: upward rotation |
|
|
What is the shoulder girdle?
|
The clavicles and scapulae.
|
|
|
Name the 8 primary joint actions of the shoulder girdle.
|
1. scapular elevation
2. scapular depression 3. scapular retraction (adduction) 4. scapular protraction (abduction) 5. scapular upward rotation 6. scapular downward rotation 7. scapular upward tilt 8. scapular reduction of upward tilt |
|
|
Name the 4 muscles of the quadriceps.
|
1. Biceps femoris
2. Vastus lateralis 3. Vastus medialis 4. Vastus intermedialis |
|
|
Where is the talocrural joint?
|
The ankle. It joins the tibia and fibula to the talus.
|
|
|
Where is the calcaneus bone?
|
The heel.
|
|
|
Where is the subtalar joint?
|
The ankle. It joins the talus to the calcaneus.
|
|
|
List the 2 joint actions of the talocrural joint.
|
1. Dorsiflexion
2. Plantar flexion through axis in the talus |
|
|
List the 2 joint actions of the subtalar joint.
|
1. Inversion (supination)
2. Eversion (pronation) |
|
|
Define agonist and antagonist.
|
1. Agonist: prime mover
2. Antagonist: opposition to the prime mover |
|
|
What is a stabilizer?
|
Maintains isometric contraction to anchor primary movers.
|
|
|
What is an isometric contraction?
|
A static contraction.
|
|
|
Define concentric and eccentric.
|
1. Concentric: muscle shortens (contracts)
2. Eccentric: muscle lengthens (negative contraction) |
|
|
Hypertension BP Levels
|
140-159/90-99 mmHg
|
|
|
Pre-Hypertension BP Levels
|
120-139/80-89 mmHg
|
|
|
Optimal BP Levels
|
120/80 mmHg
|
|
|
Average BF% for men and women:
|
1. Men: 15%
2. Women: 25% |
|
|
List the protocols for skinfold testing.
|
1. Measure on the right side, standing.
2. Caliper on skin, 1cm away from fingers. 3. Pinch 1-2 seconds while reading. 4. Measure twice. |
|
|
Myocardial infarction
|
heart attack
|
|
|
Ischemia
|
Restriction of blood supply to tissues
|
|
|
Stroke volume
|
Volume of blood pumped from one ventricle with each beat
|
|
|
Systole
|
heart beat
|
|
|
Cardiac output (Q)
|
Volume of blood pumped by a ventricle in 1 minute. Q= stroke volume (SV) x heart rate (HR)
|
|
|
Venous return
|
Flow of blood back to the heart. Limits Q.
|
|
|
Minute ventilation
|
Volume of gas inhaled or exhaled per minute
|
|
|
Residual lung volume
|
Amount of air in lungs after exhale
|
|
|
Forced vital capacity
|
Max air expelled after max inhalation
|
|
|
Total lung capacity
|
Volume of air (residual volume + forced vital capacity)
|
|
|
Describe the blood flow patterns of the Circulatory System.
|
Blood enters the L&R superior atria. It flows to the interior ventricles through the AV valves. From there, it travels to the lungs (R vent > semilunar valves) or the body (L vent > aorta). From the aorta, blood flows to the arteries, arterioles, capillaries, then back to the heart through the veins.
|
|
|
List the 3 metabolic pathways.
|
1. Aerobic (oxidative)
2. Anaerobic (lactic acid) 3. Phosphagen (ATP-PC) |
|
|
Which energy system uses glucose, fat, and protein for fuel?
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
Which energy system has a limiting factor of a small supply of stored CP?
|
Phosphagen
|
|
|
What activities use the aerobic system?
|
sleeping, jogging, zumba (cardio/endurance)
|
|
|
What activities use the anaerobic glycolic system?
|
hurling, football, basketball (1-3 minutes)
|
|
|
What activities use the phosphagen system?
|
sprinting, jumping, lifting (up to 10 seconds)
|
|
|
Describe glycolysis.
|
An anaerobic process which changes glucose into pyruvic acid then lactic acid to create ATP.
|
|
|
Describe beta oxidation.
|
Free fatty acid is broken down into either acetyl-CoA (Krebs) or NADH/FADH2 (electron transport chain).
|
|
|
Describe the Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle.
|
Aerobic process which takes carbs, fats, and proteins and converts it to CO2.
|
|
|
Electron Transport Chain
|
The cellular respiration site of aerobic (oxidative) phosphorilation. It takes NADH from Krebs and turns it into ATP.
|
|
|
Anaerobic threshold
|
The shift from aerobic to anaerobic when exercise increases intensity and lactic acid begins to accumulate.
|
|
|
Maximal oxygen uptake VO2max
|
Max rate of O2 consumed during exericse to exhaustion. vol O2/minutes
|
|
|
EPOC
|
Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption Increased oxygen intake after strenuous activity. Restores body to resting state and gets rid of lactic acid.
|
|
|
Describe the structures of the Pulmonary System.
|
Air enters the mouth/nostrils > nasal cavity > pharynx (throat) > larynx (voice box) > epiglottis > trachea > 2 main bronchi > R&L lungs > bronchioles > alviolar ducts > alviolar sacs > millions of alvioli > oxygen to capillaries
|
|
|
What is ATP?
|
Adenosine Triphosphate. Coenzyme used for energy transfer of cells. Changed into ADP, it's a form of stored energy that can be directly used by cells. adenosine + ribose 9sugar) + 3 phosphates
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of muscle tissue.
|
1. Skeletal
2. Smooth 3. Cardiac |
|
|
Name the 2 types of muscle fibers.
|
1. Fast twitch
2. Slow twitch |
|
|
Describe slow twitch fibers.
|
Aerobic. Slower speed of contraction. Fatigue resistant.
|
|
|
Describe fast twitch fibers.
|
Glycolic system. Myosin can split ATP quickly. Short bursts of energy.
|
|
|
What is a motor unit?
|
Coordinates the contractions of a single muscle. nerve cell + muscle fibers
|
|
|
Describe actin.
|
Protein microfilaments which hydrolize ATP. (holds onto the golf club of the myosin fiber)
|
|
|
Describe myosin.
|
Motorprotein that binds with actin for muscle contraction. Golf club shape made up of a head, neck, and tail.
|
|
|
Define sarcomere.
|
Myofibrils inside the muscle fibers which hold actin. Takes in calcium to break the actin/myosin connection.
|
|
|
Describe the function of a muscle spindle.
|
Detects length changes inside the muscle. Tells brain so it knows where the body is. Also resists stretching too far. Fast twitch has more than slow twitch.
|
|
|
What fuels the phosphagen system?
|
creatine phosphate (CP)
|
|
|
What fuels the anaerobic glycolytic system?
|
glucose
|
|
|
What fuels the aerobic system?
|
glucose, fat, and protein
|
|
|
Describe the function of a Golgi tendon organ.
|
Senses changes in muscle tension. Located at muscle origins and insertion into tendons. Stretch receptor. Inhibits contraction.
|
|
|
Describe synovial (diathroidal) joints.
|
Most common. Small space. Cartilage capped.
|
|
|
Describe the synovial membrane.
|
Secretes synovial fluid to lubricate and cushion joints.
|
|
|
Describe Fascia.
|
Fibrous connective tissue that sheaths individual muscles.
|
|
|
SITS
|
The four muscles of the rotator cuff:
1. Supraspinatus 2. Infraspinatus 3. Teres minor 4. Subcapularis |
|
|
List the 9 primary joint actions of the shoulder joint.
|
1. Shoulder flexion
2. Shoulder extension 3. Shoulder abduction 4. Shoulder adduction 5. Shoulder horizontal adduction (flexion) 6. Shoulder horizontal abduction (extension) 7. Shoulder internal rotation (medial) 8. Shoulder external rotation (lateral) 9. Shoulder circumduction |
|
|
Scapular adduction is commonly referred as:
|
scapular retraction
|
|
|
Name the 4 primary joint actions of the spine.
|
1. Spinal flexion
2. Spinal extension 3. Spinal rotation 4. Spinal lateral flexion |
|
|
List the 6 steps used to evaluate the Medical History Form.
|
1. Determine client's age (men >45; women >55)
2. Analyze coronary heart disease risk factors 3. Ask if there are signs suggestive of disease 4. Decide if client is low, medium, or high risk 5. Determine whether you need dr clearance 6. Ascertain if your client is pregnant |
|
|
List 8 positive ASCM atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors.
|
1. Family history (male <55; female <65)
2. Smoking (current up to 6 months) 3. Hypertension (140/90 measured twice) 4. Dyslipidemia (LDL >130 or HDL <40) 5. Impaired fasting glucose (>100 twice) 6. Obesity (BMI >30) 7. Sedentary lifestyle8.) |
|
|
List 5 symptoms of cardiovascular disease.
|
1. Chest pain
2. Shortness of breath 3. Dizziness 4. Ankle swelling 5. Palpitations or irregular heartbeat |
|
|
List 3 situations when you might recommend a physician's clearance for exercise.
|
1. 2+ risk factors for CHD
2. Symptoms or known CHD 3. Age (male >45, female >55) |
|
|
What is a PAR-Q?
|
Physical Activity Readiness Questionaire
|
|
|
List 6 components of a fitness assessment session.
|
1. Assess resting HR & BP
2. Assess body comp 3. Assess cardio fitness (Rockport or 3 min step) 4. Assess muscular strength/endurance 5. Assess flexibility & posture 6. Optimal fitness assessment components |
|
|
Purpose of max testing:
|
Measures cardio fitness.
|
|
|
Purpose of submax testing:
|
Measures aerobic fitness and improvement over time.
|
|
|
Describe the protocols for the 3 Minute YMCA Step Test.
|
1. Informed consent.
2. Set metronome @96bpm 3. client steps on 12" step for 3 minutes 4. Find HR and count for 1 minute 5. Math it |
|
|
Describe the protocols for a 1RM test.
|
1. Warm up/stretch
2. Start at 50% perceived weight 3. 1 rep @ each weight until fail 4. 1 RM weight / client's weight = % ranking |
|
|
Define kyphosis.
|
Hunchback. Sometimes paired with chin jut. Assess by having client stand against a wall. If there is more than a palm-width of space between the back and the wall, then yes.
|
|
|
Define Lordosis.
|
Swayback. Often caused by weak abs or obesity. Assess by having the client march in place. Stop and have them stand normally, observing from the side. If slouch, then yes.
|
|
|
Define scoliosis.
|
Bent spine. Assess by measuring shoulder height. If more than .25 inches, then maybe.
|
|
|
How often should one reassess fitness?
|
Every 3-4 weeks or at the end of each goal period.
|
|
|
Define specificity in training.
|
You get good at what you practice.
|
|
|
Define mets.
|
Metabolic equivalents. Resting oxygen uptake = 1 met
|
|
|
VO2max
|
Max rate of oxygen consumed during incremental exercise.
|
|
|
What is THRR?
|
Training Heart Rate Range
|
|
|
Define the Karvonen formula.
|
A mathmatical formula that helps you determine your target heart rate training zone (THRR). The formula uses maximum and resting heart rate with the desired training intensity to get a target heart rate.
|
|
|
What is the equation for the Karvonen formula?
|
[(max HR - resting HR) x %intensity] + resting HR =target heart rate
|
|
|
How does one estimate max HR?
|
220 - age = estimated max HR
|
|
|
Opposes the triceps.
|
biceps
|
|
|
Opposes the posterior deltoid.
|
pectoralis major
|
|
|
Opposes erector spinae.
|
abdominals
|
|
|
Opposes hamstrings.
|
quadriceps
|
|
|
Opposes hip adductors.
|
hip abductors
|
|
|
Volume lifted =
|
reps x weight
|
|
|
Define Progressive Resistance Exercise.
|
(PRE) resistance is gradually increased
|
|
|
Define periodization.
|
changing up the routine
|
|
|
Opposes biceps.
|
triceps
|
|
|
Opposes deltoid and trapezius.
|
latissimus dorsi
|
|
|
Opposes pectoralis major.
|
posterior deltoid
|
|
|
Opposes abdominals.
|
erector spinae
|
|
|
Opposes quadriceps.
|
hamstrings
|
|
|
Opposes hip abductors.
|
hip adductors
|
|
|
Pre-exhaustion
|
use large muscle groups before small to stave off exhaustion
|
|
|
Spilt routine
|
leg day/chest and back day
|
|
|
super circuit
|
cardio mixed with resistanceq1-3:1min
|
|
|
Eccentric training
|
negs (eccentric phase) workout. often causes DOMS
|
|
|
List 5 common training errors.
|
1. improper warm up
2. safety devices not used 3. breath holding 4. range of motion problems result in poor alignment 5. too quick |
|
|
DOMS
|
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
|
|
|
List several genetic factors that may influence the ability to lift heavier weights.
|
limb length muscle fiber composition testosterone tendon insertion muscle belly length
|
|
|
Give an example of an alignment cue.
|
align joints like this (knee over toe)
|
|
|
Give an example of a visual cue.
|
Do what I do.
|
|
|
Give an example of an informational cue.
|
This works your glutes.
|
|
|
Give an example of a breathing cue.
|
Inhale.
|
|
|
Give an example of a motivational cue.
|
You can do it!
|
|
|
Give an example of a wrong/right cue.
|
feel proper vs. improper form
|
|
|
Define flexibility.
|
the range of motion possible around a joint or series of joints. it is joint and joint-action specific (flexible in one joint but not another)
|
|
|
List the muscles that are commonly tight.
|
upper trapserector spinaehamstringspectoralis maj & anterior deltsiliopsoas (hip flexors)gastrocnemius & soleus
|
|
|
proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation
|
stretch until range, relax and stretch more
|
|
|
List several factors that determine and influence flexibility.
|
genetic tissue structure
tight or loose ligaments stress and muscle tension injury, pregnancy, and age core temp |
|
|
What is an intrinsic risk factor for injury?
|
previous injury; obesity; joint laxity; inflexibility
|
|
|
What is an extrinsic risk factor for injury?
|
No warm-up; fatigue; poor technique; improper form
|
|
|
Define subluxation.
|
partial dislocation
|
|
|
Tendinitis
|
inflamed tendons. leads to scarring or calcium deposits
|
|
|
Define synovitis.
|
inflammation of synovial joints
|
|
|
Define bursitis.
|
inflammation of bursae (pads@ shoulder and knee)
|
|
|
Define contusion.
|
bruise from a direct blow
|
|
|
Define adhesions.
|
fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs. internal scar tissue decreases elasticity
|
|
|
Define contractures.
|
permanent shortening of muscles, tendons, or ligaments
|
|
|
List the muscles that generally need to be stretched.
|
pectoralis major anterior
delts upper traps levator scapulae internal rotators of the shoulder erector spinae hip flexors hamstrings calves |
|
|
List the muscles that generally need to be strengthened.
|
mid traps rhomboids posterior delts lower traps pectoralis minor external rotator cuff muscles abs vastus medialis
|
|
|
Name 4 shoulder joint injuries.
|
1. rotator cuff tendinitis
2. impingement syndrome 3. biceps tendinitis 4. shoulder dislocation/subluxation |
|
|
List two injuries that cause pain at the elbow.
|
tennis elbow (wrist extensor) golf elbow (wrist & finger flexor)
|
|
|
What are the 4 curves of neutral spinal alignment?
|
1. lordotic cervical
2. kyphotic thoracic 3. lordotic lumbar 4. kyphotic sacral |
|
|
Define IT band syndrome.
|
tight IT band aggrivated by rotating femur & tibia. hurts above knee. RICE and stretch.
|
|
|
Piriformis Syndrome
|
tendinitis of hip external rotators. Causes sciatic-like pain. Massage and stretch.
|
|
|
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
|
Chronic anterior knee pain. Caused by muscle imbalances. Ice, brace, orthotics.
|
|
|
Plantellar tendinitis
|
Inflammation of distal patellar tendon. Hurts on or below patella. Caused by jumping. Ice, quad exercises.
|
|
|
Ligament injuries of the knee
|
70% caused by anterior cruciate ligament; pops; RICE, massage, patella straps.
|
|
|
Define open kinetic chain.
|
End joint is free. (knee extension)
|
|
|
Define closed kinetic chain.
|
End joint is fixed. (squats)
|
|
|
What three things need to be avoided for proper knee mechanics?
|
1. Hyperflexion (below parallel) while weight bearing
2. knee torque 3. knee hyperextension |
|
|
Define anterior compartment syndrome.
|
Pain on lateral side of tibia which swells because of injury. Causes numbness, pain, and paralysis.
|
|
|
Metatarsalgia
|
Pain in metatarsals caused by jumping. Wear good shoes.
|
|
|
Define sarcopenia.
|
Loss of muscle strength due to declining muscle mass and inactivity.
|
|
|
Osteoarthritis
|
Wears away articular cartilage leading to bone on bone abrasion
|
|
|
Rheumatiod arthritis
|
Similar to osteoarthritis, but inflammatory, not degenerative; autoimmune
|
|
|
Define osteopenia.
|
Premature bone thinning.
|
|
|
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
|
loss of blood flow to the brain via blood clot; third leading cause of death.
|
|
|
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
|
atherosclerosis in extremities, especially calves; causes lesions, burning, and cramping.
|
|
|
Claudication
|
cramping, burning pain during exercise with PVD
|
|
|
COPD
|
airway resistance is increased making it difficult to breathe; #1 cause is smoking; coupled with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma
|
|
|
Dyspnea
|
shortness of breath
|
|
|
Multiple sclerosis
|
gradual damage to myelin sheath of motor neurons
|
|
|
Parkinson's disease
|
basal ganglia disorder; loss of dopamine makes motor function difficult
|
|
|
Name some lifestyle factors that can influence blood pressure.
|
1. high sodium
2. high fat 3. cigarettes 4. alcohol 5. obesity 6. high stress 7. inactivity |
|
|
What are the signs of hypoglycemia?
|
1. Excessive fatigue
2. nausea 3. lightheadedness 4. dizziness 5. profuse sweating 6. seeing spots 7. confusion 8. shakiness |
|
|
Name 4 preventative steps a personal trainer can take to help persons with diabetes avoid a hypoglycemic reaction.
|
1. Work with client's doctor
2. Avoid working injected muscles 1 hr post injection 3. Have client eat carbs before & during; have sugar and water ready 4. monitor blood glucose frequently |
|
|
What are 5 major diseases/conditions affected by nutrition/body composition?
|
1. coronary heart disease
2. cancer 3. diabetes 4. metabolic syndrome 5. osteoporosis |
|
|
What is the current recommendation for carbs per day?
|
45-65%
|
|
|
What is the current recommendation for fiber per day?
|
20-30g/day or 14g/1000 calories
|
|
|
What is the current recommendation for protein per day?
|
.8g/each kg (2.2lbs) of body weight+30 if pregnant+20 if EBF
|
|
|
What is the current recommendation for fat per day?
|
20-35% of total calories/day trans fats as low as possible
|
|
|
What is the current recommendation for cholesterol per day?
|
no more than 300mg/day
|
|
|
What is the ACSM position on exercise and fluid replacement?
|
1. Drink 17oz 2 hrs before exercise
2. Drink during exercise = to sweat lost 3. 59-72F and flavored 4. Drink sports drinks w/carbs and electrolytes for events > 1hr |
|
|
Define glycemic index.
|
Carb ranking list showing insulin surge foods.
|
|
|
Define the female athlete triad.
|
1. eating disorders
2. amenorrhea (period stops) 3. osteoporosis |
|
|
The ADA recommends _______ calories for men and ______ calories for women.
|
Men = 1400 Women = 1200
|
|
|
What are the three components of energy expenditure?
|
1. Resting metabolic rate
2. Energy expended with exertion 3. The thermic effect of food [10% of calories are used to digest food] |
|
|
How many calories are in 1g of carbs?
|
4
|
|
|
How many calories are in 1g of fat?
|
9
|
|
|
How many calories are in 1g of protein?
|
4
|
|
|
How would one calculate the % of total carbs in one serving?
|
(carbs in serving x 4 cal/g) = total carb calories total carb cals / total calories = % carbs
|
|
|
How would one calculate the % of total fat in one serving?
|
(fat in serving x 9 cal/g) = total fat calories total fat cals / total calories = % fat
|
|
|
How would one calculate the % of protein in one serving?
|
(protein in serving x 4 cal/g) = total protein cals total protein cals / total cals = % protein
|
|
|
List the 5 stages of change.
|
1. Precontemplation
2. Contemplation 3. Preparation 4. Action 5. Maintenance |
|
|
SMART
|
Specific
Measurable Action-oriented Realistic Timed |
|
|
Definition of wellness |
Multi-dimensional concept incorporating the physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects of a human being. |
|
|
Prevention |
The practice of behaviors that minimize the risk of lifestyle-related diseases and disabilities |
|
|
Holism |
The integration of the mind, body, and spirit for optimal functioning |
|
|
Five dimensions of the total person |
emotional, social, intellectual, spiritual, and physical |
|
|
Cardiac output |
amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute Heart rate x stroke volume |
|
|
Systole |
Ventricular contraction |
|
|
diastole |
relaxation phase |
|
|
Stroke volume |
Amount of blood pumped in each beat or systole |
|
|
Heart rate |
number of times the heart beats each minute |
|
|
Septum |
Wall dividing right and left sides of the heart |
|
|
Myocardial infarction (MI) |
Lack of blood flow (Ischemia) through the coronary arteries to the heart muscle |
|
|
Pericardium |
Loose protective sac that contains the heart
|
|
|
3 layers of hear tissue |
1. epicadium (thin outter layer) 2. myocardium (thickest and strongest layer) 3. endocardium (smooth membrane) |
|
|
Cardiac Cycle |
Contraction/relaxation pattern produced by the heart |
|
|
Conduction system |
Conduction in the heart begins with an electrical impulse of the sinoatrial (SA) node within the right atrium |
|
|
Circulatory system |
Blood-carrying vessels: the arteries, the capillaries, and the veins |
|
|
Describe the circulatory system |
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the vena cava and then flows into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood exchanged for oxygen. The newly oxygenated blood leaves the lungs and returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins, entering the left atrium. From the left atrium, the blood flows into the left ventricle, and with a powerful contraction, it is forced into the aorta. From the aorta, the blood enters a network of arteries, arterioles, capillaries and returns through the veins. |
|
|
Venous return |
Blood returns back to the heart through the veins |
|
|
Respiratory System |
Responsible for providing air distribution and gas exchange |
|
|
Describe the respiratory system |
Air enters the body through the mouth or nostrils and passes into the nasal cavity where it is warmed and humidified. The oral and nasal passafes lead to the throat, or pharynx. After passing through the pharynx, the inspired air enter the larynx. The larynx is composed of pieces of voice box, produces sound as air passes the vocal cords, located inside the larynx itself. Another cartilaginous structure found in the larynx is the epiglottis, which partially covers the opening in the larynx and closes during swallowing to prevent food from passing in the trachea. Air flows from the larynx into the trachea, which connects the larynx to the lungs. The trachea branches into two main bronchi, the right and left bronchus, which travel into the respective lung. |
|
|
Valsava maneuver |
Occurs when a person holds his or her breath during strenuous activity. The glottis is closed against pressure, which causes an increased thoracic pressure leading to an interruption of the venous return to the heart, reducing blood flow to the coronary arteries, and decreasing oxygen supply to the brain. |
|
|
Minute ventilation |
Amount of air breathed per minute |
|
|
Residual lung volume |
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a complete and total forced exhale |
|
|
Forced vital capacity |
Value measured during some fitness assessments; amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a maximal inhale |
|
|
Total lung capacity |
sum of the residual volume and the forced vital capacity |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine triphosphate - form of stored energy that can be directly utilized by the cells of the body - molecule found in every cell that is composed of adenosine, ribose and three phosphate groups |
|
|
3 metabolic pathways |
1. Phophagen (ATP-PC) 2. Anaerobic glycolitic (lactic acid) 3. Aerobic (oxidative) |
|
|
Mole |
unite of measurement used for counting extremely large numbers of atoms |
|
|
Pulmonary system |
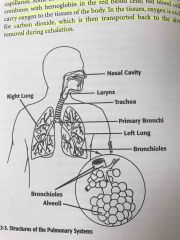
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Concept of wellness |
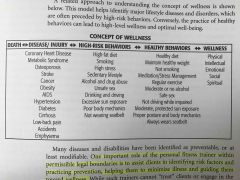
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Plan for prevention |
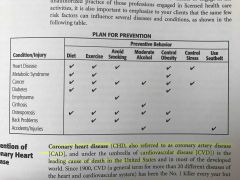
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Blood flow pattern |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anatomy of femur |
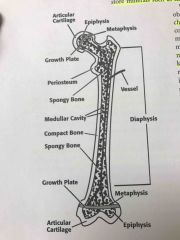
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Skeleton anterior view |
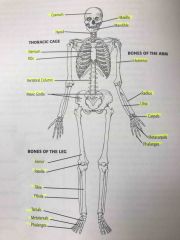
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Skeleton posterior view |
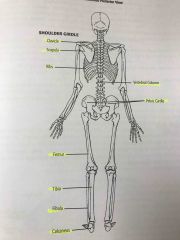
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Shoulder joint posterior view |
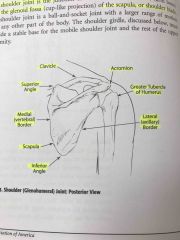
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anterior muscles of shoulder joint |
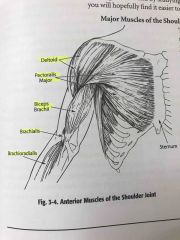
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Posterior muscles of the shoulder joint |
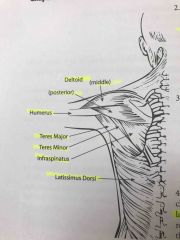
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Shoulder girdle |
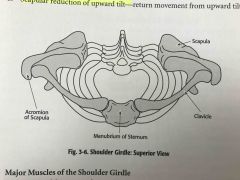
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Posterior muscles of the shoulder girdle |
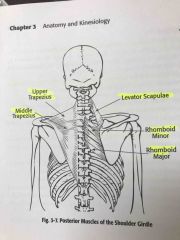
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anterior muscles of the shoulder girdle |
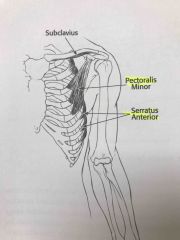
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Radioulnar joint |
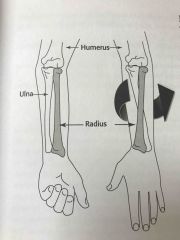
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anterior muscles of the elbow |
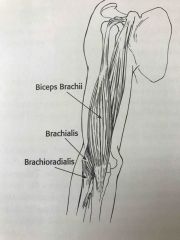
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Posterior muscles of the elbow |
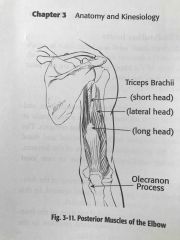
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Spine |
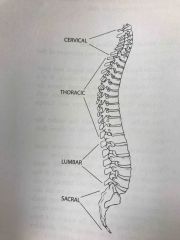
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anterior muscles of the torso |
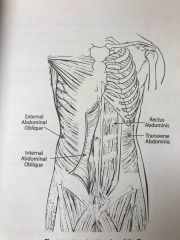
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Erector spinae Posterior muscles of the torso |
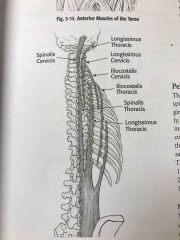
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pelvic girdle and hip joint |
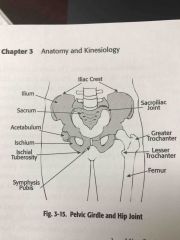
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Major muscles of the anterior leg and hip |
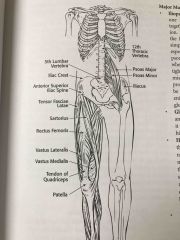
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Major muscles of the posterior leg and hip |
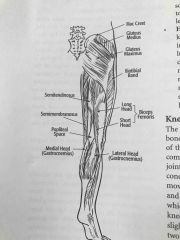
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Knee joint |
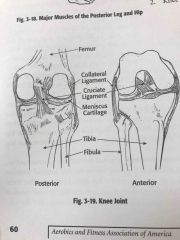
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Ankle joint |
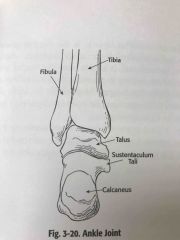
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Posterior leg muscles |
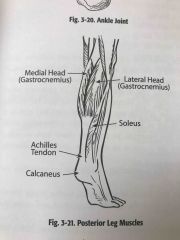
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anterior leg muscles |
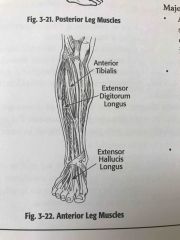
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Lateral leg muscles |
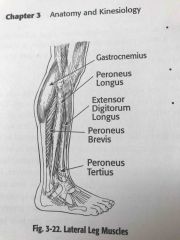
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Opposing muscles groups |
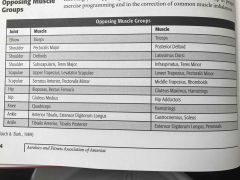
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Shoulder joint muscles and their actions |
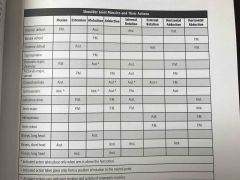
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Shoulder girdle muscles and their actions |
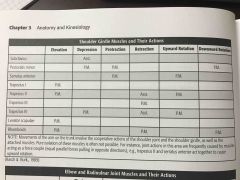
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Elbow and radioulnar joint muscles and their actions |
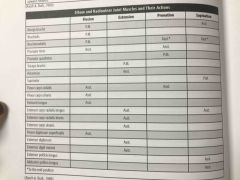
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Spinal muscles and their actions |
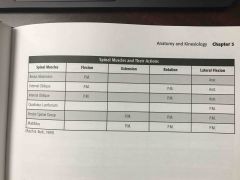
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Hip joint muscles and their actions |
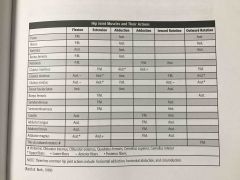
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Knee joint muscles and their actions |
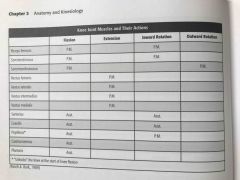
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Ankle joint muscles and their actions |
Back (Definition) |

