![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Conceptual framework
|
Existing and potential investors, lenders and other creditors need information to help them assess the prospects for future net cash inflows to an entity
|
|
|
Requirements for assessment
|
The users need information about the resources of an entity, claims against the entity and how efficiently and effectively the entity's management and governing body have discharged their responcibilities to use the entity's resources
|
|
|
Different users across the world
|
US and UK companies funded mainly by equity Many european companies funded by debt |
|
|
Important capital providers across the EU
|
1) Pension funds 2) Insurance companies 3) Investment/mutual funds |
|
|
Equity providers main decisions
|
Financial/investment decisions: buy/hold/sell shares based on forward looking information Stewardship/accountability/control decisions: assessing how well management are doing based on backward looking and present information |
|
|
Equity providers investment decisions Valuation models |
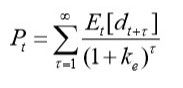
Dividend discount model: -Dividends don't capture operations -Non-dividend paying firms? |
|
|
Equity providers investment decisions Accounting valuation models |
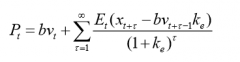
Residual income valuation model: -Gives a central role for financial statement data -Model often outperforms DDM and DCF |
|
|
Equity providers stewardship decisions
|
-Financial reporting is useful with comparable and consistent information -Used alongside other information -Use financial information to assess stewardship however part of this is out of their control -Valuation does not encompass stewardship |
|
|
Private debt market decisions
|
-To provide debt or not -Covenants -Set interest rates, maturity and collateral |
|
|
Private debt providers information requirements
|
Probability that the firm won't be able to repay its financial obligations
|
|
|
Accounting data for debt markets
|
Accounting data works well for predicting default Ratios: -Cash flow -Income -Debt to assets -Liquidity |
|
|
Public debt holder decisions
|
Based on bond ratings decided using accounting and non-accounting data
|
|
|
Conclusions
|
-How users use financial reports depends on the type of user -The importance of different capital providers across the world -Financial reports cannot meet the needs of all users at the same time -Financial reports are used alongside other information |
|
|
Merlin Conclusions
|
-Shareholders of a public company have a much more limited access to information-Shares are publically traded so their price is very sensitive to information-Need additional information eg. talking to management and understanding prospects and the industry
|

