![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The normal path of impulse transmission throughout the heart
|
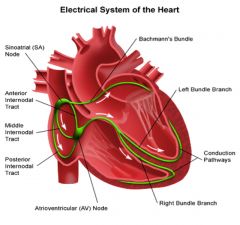
Sinoatrial Node
Atrioventricular Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches (L & R) Purkinje Fibres |
|
|
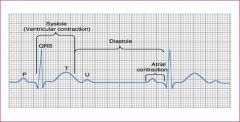
Identify each component of the ECG
|
P Wave
P-R interval QRS Complex T Wave Q-T interval Sometimes a U wave |
|
|
|
The 5-Step Method of ECG Analysis
|
1. Calculate the Heart Rate
2. Determine if the Ventricular Rhythm is regular or Irregular. 3. Measure the Width of the QRS Complex. < 0.12 sec - (normal supraventricular origin) 4. Analyse the P Wave (positive deflection, rounded shape, present befor QRS) 5. Measure the P-R Interval 0.12 - 0.20 sec |
|
|
|
Correct Lead Configuration
for Cardiac Monitoring Einthoven's Triangle |
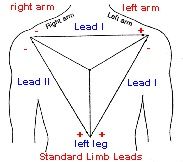
Bipolar Limb Leads I,II,III
Identify negative and positive electrodes |
|
|
|
Definition of 'Lead and 'electrode
|
A lead is an electrical system used to record electrical activity. A lead is composed of a negative and a positive electrode (Bipolar), which sense the magnitude and direction of electrical impulses between the two electrodes.
|
As an impulse travels towards the positive electrode, a positive deflection (vector) is seen on the ECG while an impulse that travels away from the positive electrode is seen as a negative deflection on the ECG. (below the isolectric line)
|
|
|
The normal speed of the ECG paper
|
25 mm per second
|
|
|
|
What both horizontal and vertical axes of the ECG represents
|
Horizontal plane = Time
Vertical plane = Amplitude (voltage) |
|
|
|
The time representation of a
1mm box on the ECG paper |
0.04 sec
|
|
|
|
The time representation of a
5mm box on the ECG paper |
0.20 sec
|
|
|
|
The time representation of a
25mm box on the ECG paper |
1 sec
|
|
|
|
Three methods of calculating heart rate on the ECG
|
1. Count back method
1 sq = 300bpm 2 sq = 150bpm 3 sq = 100bpm 4 sq = 75bpm 5 sq = 60bpm 6 sq = 50bpm 2. HR calculator/Ruler 3. 6 sec strip Count R waves x 10 = 60sec starting on line. |
|
|
|
Define ectopic complexes?
|
Ectopic
Premature Contraction Extrasystole Anypart of the heart is able to depolarise earlier than it should, they can arise in the atria, A-V node or the ventricles. |
|
|
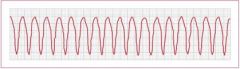
Identify this rhythm?
|
Ventricular Tachycardia
VT Defined by three of more consecutive PVC's occuring at a greater rate than 100 complexes per minute |
|
|
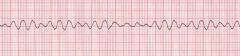
Identify this rhythm?
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
VF is a death producing dysrhythmia in which electrical activity in the heart is chaotic due to multiple ectopic ventricular sites. Its a quivering of the heart not allowing cardiac cells to depolarise and repolarise. It does not pump blood , therfore circulation stops. |
|
|
|
The 5 Steps of ECG rhythm recognition
|
1. Rate (60-100bpm)
2. Rhythm regularity P-P interval & R-R interval 3. P wave positive (upright) in lead ii and precedes each QRS complex, P waves should look alike 4. PR interval 0.12-0.20 sec and constant from beat to beat 5. QRS 0.04-0.12 sec |
|
|
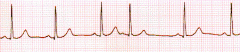
Identify this rhythm
|
A premature atrial complex
is an extra P-QRS-T complex consisting of an abnormal (sometimes normal) P wave followed by a normal or abnormal QRS complex, occurring earlier than the next expected beat of the underlying rhythm, usually a sinus rhythm. A PAC is generally followed by a non-compensatory period. |
Types of PAC's
Infrequent PAC's (<5/min) Frequent PAC's (>5/min) Isolated PAC's (Single) Atrial Tachycardia (>3 in a row) Atrial Bigemity PAC's alternating with QRS of the underlying rhythm. Atrial Trigemity/Quadrigemity PAC's following every two or three QRS complexes of the underlying rhythm, respectively. |
|
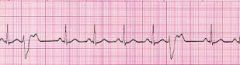
Identify this rhythm
|
Rate: Underlying rhythm
regularity: Irregular when PVC occurs P Waves: of underlying rhythm PR intervals: of underlying rhythm QRS complexes: Wide >0.12 sec |
A premature ventricular complex (PVC)
is an extra ventricular complex consisting of an abnormally wide and bizzare QRS complex that originates in an ectopic site in the ventricles, in the bundle branches, purkinji network, or ventricular myocardium. It occurs earlier than the next expected beat of the underlying rhythm and is usually followed by a compensatory pause. |
|
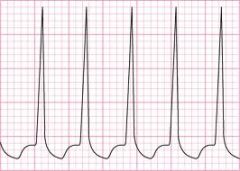
Identify this rhythm with the 5 steps of ECG rhythm recognition
|
Rate: 150-250
Regularity: Regular P Wave: Usually absent PR interval: P'R interval equal <0.12 sec QRS Complex: Normal, wide if conduction delay exists |
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
is a dysrhythmia originating abruptly at the site of a rapid reentry circuit in the AV junction with a rate between 150-250 bpm. The PSVT may present as an AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) or an AV reentry tachycardia (AVRT) |
|
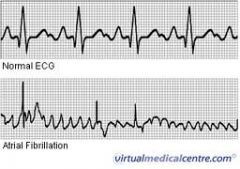
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: Atrial rate 350-600, ventricular rate 160-180 if AF uncontrolled; 60-70 if AF controlled or AV block is present
Rhythm: irregularly irregular P Wave: No identifiable P waves, fibrillatory waves present; erratic, wavy baseline PR interval: not measurable QRS: normal (0.12 or <) but may be wide if an intraventricular conduction delay exists. |
Atrial fibrillation
is a dysrhythmia arising in multiple ectopic atrial sites or sites of rapid reentry circuits in the aria, characterised by very rapid atrial fibrillation (f) waves and an irregular, often rapid ventricular response. |
|
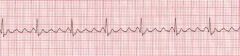
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: Atria 240-260, Ventricular 1/2 atrial rate or less
Regularity: Regular P Waves: Normal P waves absent, F waves (sawtooth) PR intervals: difficult to measure QRS: Normal <0.12 sec, wide if conduction delay exists |
Atrial Flutter
is a dysrhythmia arising in an ectopic pacemaker or the site of rapid reentry circuit in the atria, characterised by rapid atrial flutter (f) waves with a sawtooth appearance and, usually a slower, regular ventricular response. |
|
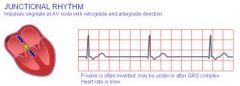
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: 40-60
60-100= accelerated junctional rhythm, >100= junctional tachycardia Regularity: regular P Waves: absent or inverted PR interval: If present <0.12 sec QRS: Normal, wide if conduction delay exists |
Junctional Rhythm
ia s dysrhythmia originating in an escape pacemaker in the AV junction with a rate of 40-60 bpm. When less than three consecutive QRS complexes arising from the escape are present, they are called junctional escape beats or complexes. |
|
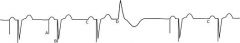
Identify this rhythm
|
Paced Rhythm
2 Types= Fixed Rate & Demand Fixed Rate, are designed to fire constantly at a preset rate without regard of the hearts own electrical activity. Demand PM, have a sensing device that senses the hearts electrical activity and fires at a preset rate only when the hearts electrical activity drops below a predetermined rate. |
Single Chamber Pacemakers:
Atrial Demand and Ventricular Demand Dual Chamber Pacemakers: |
|
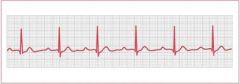
Identify this rhythm using the five step method
|
Rate: normal
Rhythm: regular P Waves: Normal in size and shape, one positive P wave befor each QRS PR interval: Prolonged (>0.20) but constant QRS Duration: Normal < 0.12 sec unless a conduction delay exists |
First Degree AV Block
is a dysrhythmia in which there is a constant delay in the conduction of electrical impulses, usually through the AV node. It is characterised by abnormally long PR intervals that are greater than 0.20 sec and constant in duration. |
|
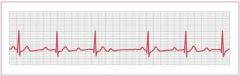
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: Atrial rate is greater than the ventricular rate
Rhythm: Atrial regular (P's plot through on time); ventricular irregular P Wave: Normal in size and shape; some P waves are not followed by a QRS complex PR interval: Lengthens with each cycle, until a P wave appears without a QRS complex QRS Duration: Normal <0.12 sec but is periodically dropped |
Second Degree AV Block type i - Wencheback
Is a dysrhythmia in which there is a progressive delay following each P Wave until conduction is completely blocked. The sequence of increasing PR intervals and an absent QRS complex is repetitive. |
|
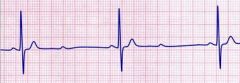
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: Atrial rate is greater than the ventricular rate; ventricular rate is often slow
Rhythm: Atrial regular (P's plot through on time), ventricular irregular P Wave: Normal in size and shape; some P waves are not followed by a QRS complex PR interval: within normal limits or slightly prolonged but constant for the conducted beats; there may be shortening or the PR interval that follows a nonconducted P wave QRS Duration: Normal <0.12 sec but periodically absent after P Wave |
Second Degree AV Block type ii - Mobitz type ii
The conduction delay in this block occurs below the AV node, either at the bundle of His or the bundle branches. It is characterised by a constant PR interval befor conducted beats, with some beats not conducted at all. (more serious than type i) |
|
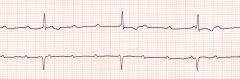
Identify this rhythm using the 5 step method
|
Rate: Atria rate is greater than Ventricular rate, independent escape rhythm
Rhythm: Atria regular; ventricular rate regular, there is no relationship between the atrial and ventricular rhythms P Wave: Normal in size and shape PR interval: none - the atria and ventricles beat independently of each other. QRS duration: Narrow or wide depending on the location of the escape rhythm Narrow= junctional pacemaker Wide = Ventricular pacemaker |
Third Degree AV Block
Is the complete absence of conduction of the electrical impulses through the AV node, bundle of His or bundle branches, characterised by independent beating of the atria and ventricles. |

