![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the general formula for a carbohydrate?
|
(C * H2O)n
n must be greater than or equal to 3. |
|
|
where does the word carbohydrate come from
|
from the french, hydrate de carbone
|
|
|
equation for photosynthesis
|

|
|
|
most carbohydrate are found naturally in _____ rather than as simple sugars.
|
bound form
Polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, gums) b) Glycoproteins and proteoglycans (hormones, blood group substances, antibodies) c) Glycolipids (cerebrosides, gangliosides) d) Glycosides e) Mucopolysaccharides (hyaluronic acid) f) Nucleic acids |
|
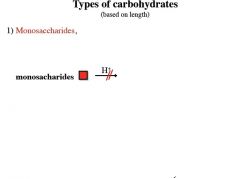
|
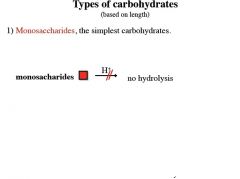
|
|
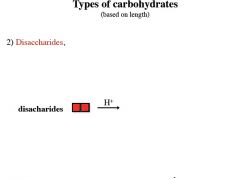
|
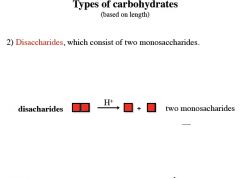
|
|
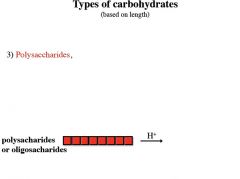
|
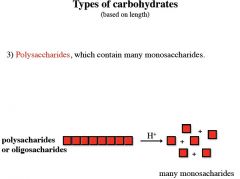
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
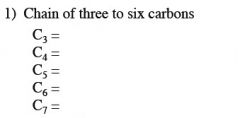
|
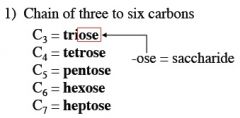
|
|

|

|
|
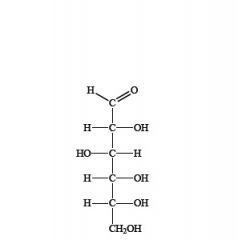
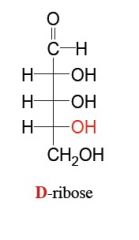
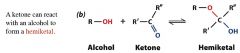
what is this?
is it an aldehyde or ketone? |
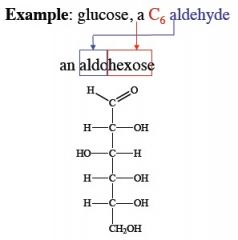
|
|

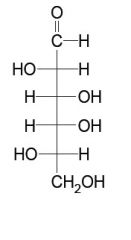
be able to draw these aldoses and name them (general form)
|
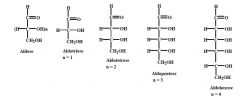
|
|
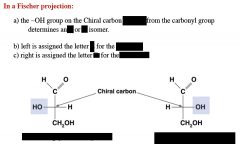
|
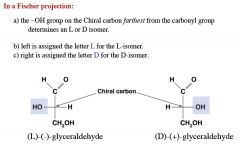
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
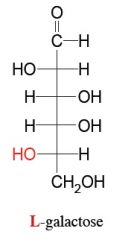
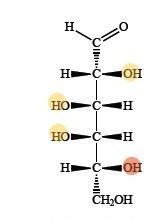
Epimers
|
Differ only by the configuration around 1 carbon atom
|
|
|
|
|
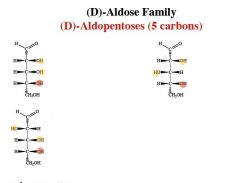
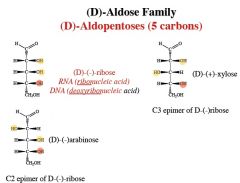
name, number of chiral centers.
which is most abundant in nature? |
|
|
|
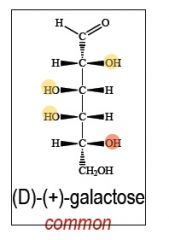
|
|

|

|
|
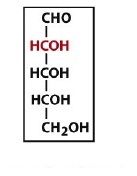
|
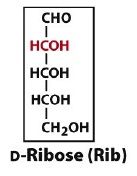
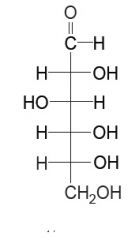
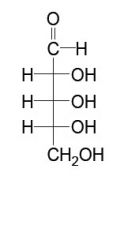
an aldopentose
|
|
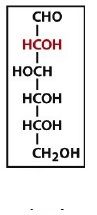
|
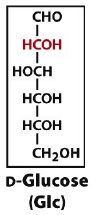
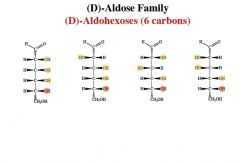
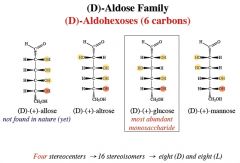
an aldohexose
|
|
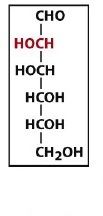
|
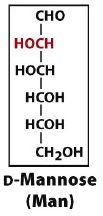
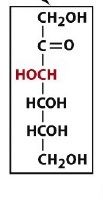
an aldohexose
|
|
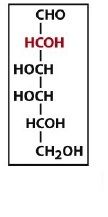
|
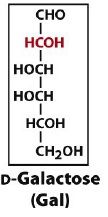
an aldohexose
|
|
|
|
|
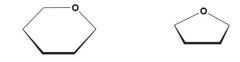
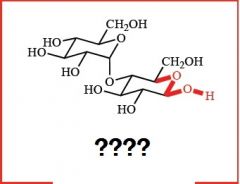
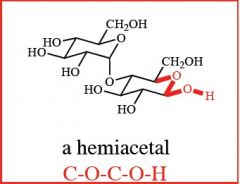
what are these, and how are they formed?
|
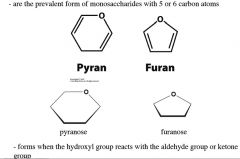
|
|
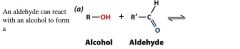
|
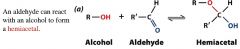
|
|
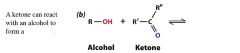
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
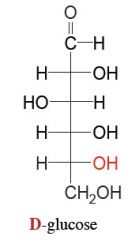
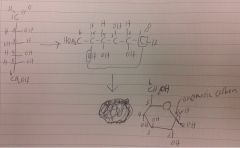
draw d glucose and then make it cyclic
|
|
|
|
explain the two anomers of cyclic glucose
|
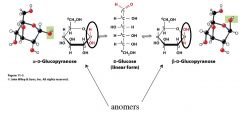
|
|
|
draw the furanose form of D-arabinose. Hemiketal, or hemiacetal?
|
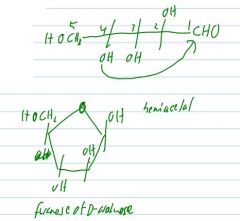
|
|
|
Draw the furanose form of beta-L-arabinose
|

|
|
|
Draw the furanose form of beta-D-fructose.
hemiketal or hemiacetal? |
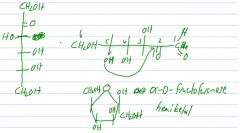
|
|
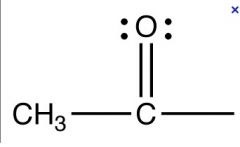
what group is this
|
acetyl group
|
|
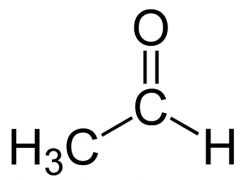
what is this
|
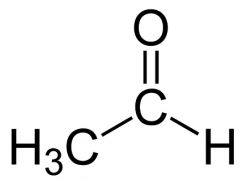
acetaldehyde
|
|
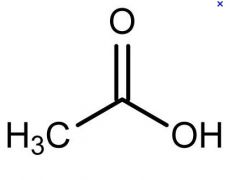
what is this
|
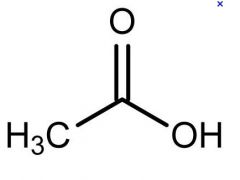
acetic acid
|
|
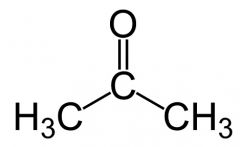
what is this
|
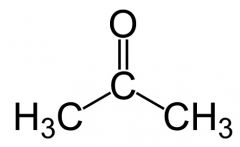
acetone
|
|
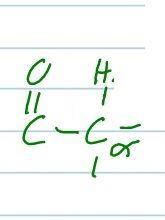
produce an enolate ion from this, using only a base.
draw both resonance structures of the enolate ion. |
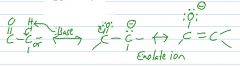
|
|

Identify this molecule, epimerize it, then identify the product.
|
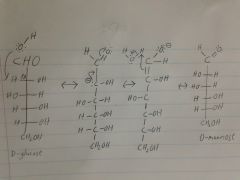
|
|

identify the molecule, put it through an endiol rearrangment, and then name the product
|
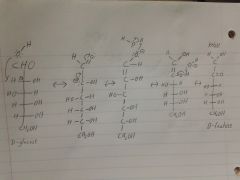
|
|

reduce and oxidize this sugar group.
which direction has the higher oxidation state? |

|
|
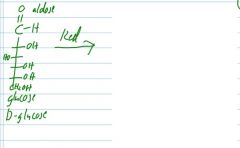
reduce and name its product
|
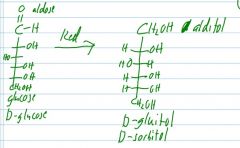
|
|
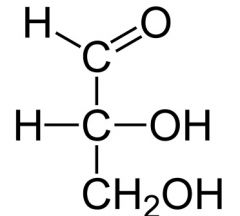
name, reduce, and name product
|
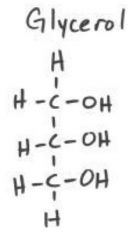
D-glyceraldehyde
glycerol |
|
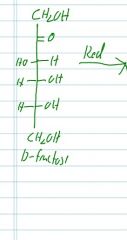
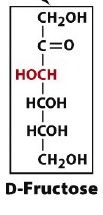
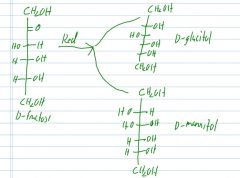
If D-fructose is reduced, what are the two possible products?
|
|
|
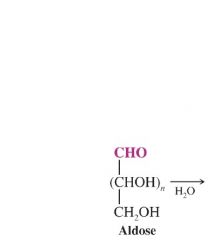
explain The Synthesis of Aldonic Acids
|

|
|
|
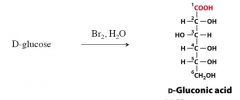
this is an oxidation rxn
|
|
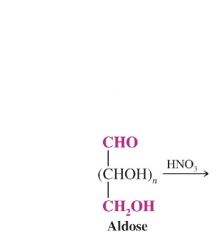
|
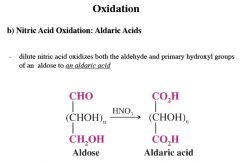
|
|
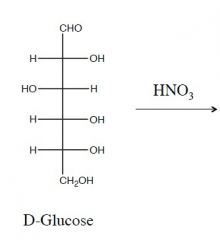
|
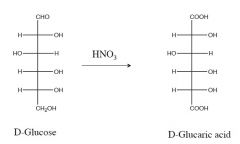
|
|
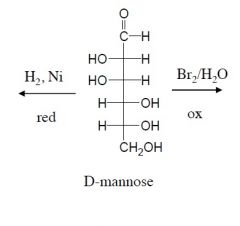
|
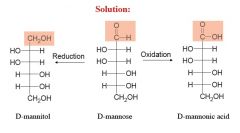
|
|
|
chemical in Tollen’s reagent:
|
Ag(NH3)2OH
silver diamine hydroxide solution |
|
|
chemicals in fehling's solution:
|
KOH or NaOH and CuSO4
|
|
|
chemicals in Benidict's solution
|
Na2CO3 and CuSO4
|
|
|
can Tollen's reagent distinguish between aldoses and ketoses?
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
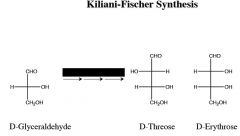
|
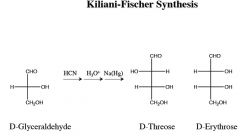
|
|
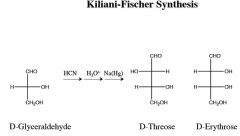
where does the carbon get added, and where does it come from in this rxn
|
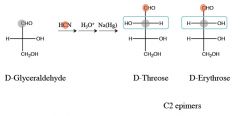
|
|

|
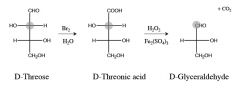
|
|
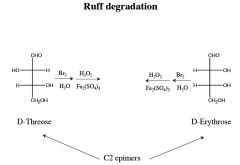
|
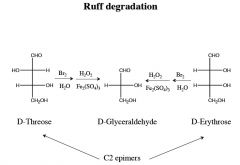
|
|
|
polysaccharides are also known as
|
glycans
|
|
|
polymers of glucose
|
glucans
|
|
|
polymers of galactose
|
galactans
|
|

|
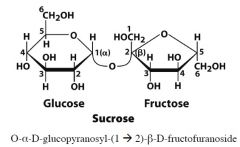
|
|

|
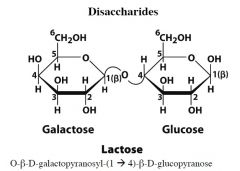
|
|

|
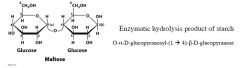
|
|

|

|
|

|
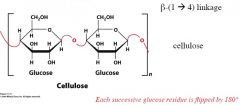
|
|

|
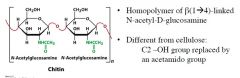
|
|
|
amylopectin structure
|
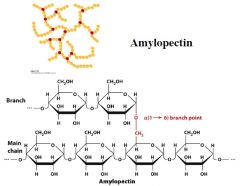
|

