![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Some practitioners prefer which blade for double lumen tube insertion?
A. MAC B. Miller |
A. MAC because it offers greater clearance for the tube and may decrease the chance of balloon rupture from the teeth.
|
|
|
For laryngoscopy the double lumen tube is lubricated and advanced with the distal curve ____________ anteriorly until the vocal cords are passed.
A. Convex B. Concave |
B. Concave, after the cords are cleared the stylet is removed as in standard intubation.
|
|
|
During DLT insertion, the cords are cleared and the tube is rotated _____degrees toward the bronchus to be intubated and andvaced to around ______cm in females or _______cm in males.
|
During DLT insertion, the cords are cleared and the tube is rotated _90____degrees toward the bronchus to be intubated and andvaced to around __27____cm in females or ____29___cm in males
|
|
|
The tracheal cuff of a DLT requires _______ml of air and the bronchial cuff requires ______ml of air.
|
Tracheal=5-10
Bronchial =1-2 |
|
|
Overinflation of the bronchial cuff of a DLT can cause which of the following:(choose all that apply)
a. narrowing of the lumen b. occulsion of the lumen c. increased risk of tearing the bronchus. d. I dont know and I hope I no one pimps me on this question. |
All are technically true :)
|
|
|
The bronchial cuff is a:
a. low volume low pressure cuff b. low volume high pressure cuff c. high volume low pressure cuff d. high volume high pressure cuff. |
B. Low volume high pressure
-The cuff should therefore be deflated during the prcedure once OLV is no longer needed. |
|
|
True or False: Ausculatation of breath sounds is a simple and highly reliable method of assessing the position of a DLT.
|
False: Simple NOT highly reliable
|
|
|
What is the gold standard of verification of DLT placement?
a. vaginal hysteroscopy b. laryngoscopy c. laprsocopy d. fiberoptic bronchoscopy |
D. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
|
|
|
Which of the following are advantages of fiberoptic inspection of the DLT over auscultation (choose all that apply)
a. guidance during initial placement b. ability to visualize correct depth of bronchial cuff c. visualization of proper positioning of the right upper lobe if present d. removal of aspirated corn from the lung. |
A, B, C, D
|
|
|
You have verified DLT placement in the supine position and need to turn your patient to the lateral position. Do you need to revisualize placement?
|
Yes, because in turning to the lateral position the DLT will commonly wihtdraw from the bronchus by 1 cm.
|
|
|
A fiberoptic bronchoscope of 4.9 mm external diameter can be lubricated and passed through an endobronchial tube of size ______french or larger.
a.20 b.25 c.30 d.35 e.37 |
37
|
|
|
A fiberoptic bronchoscope of 3.6mm can pass through a _____french tube.
a. 25 b.35 c.45 d.55 |
B. 35
|
|
|
When the bronchoscope is placed down the right lumen to determine precise left sided double lumen tube position, the endoscopist should see a clear straight ahead view of the tracheal carina, the left lumen going off into the left mainstem bronchus, and most important the upper surface of the left endobronchial cuff just below the carina.
|
.
|
|
|
Box 28-4
Auscultation of breath sounds after placement of a DLT 1. Inflate the tracheal cuff 2. Verify bilateral equal breath sounds. If breath sounds are present on one side , both lumens are in the same bronchus. Deflate the cuff and withdraw the tube 1 to 2 cm at a time until breath sounds are equal bilaterally. 3 . inflate the endobronchial cuff 4. Clamp the endobronchial lumen and open its lumen cap proximal to the clamp 5. verify breath sounds in teh correct lung and the absence of breath sounds in the opposite lung. 6. Verify that breath sounds are equal at the apex of the lung and at the lateral lung. If the apex is diminished withdraw the tube until upper lung sounds return. 7. Verify the absence of air leakage through the opposite lumen cap. 8. Unclamp the endobronchial lumen and verify bilateral breath sounds. 9. Clamp the tracheal lumen and open its cap. 10. Verify breath sounds opposite the lung with the endobronchial lumen and the absence of breath sounds on the other. 11. when absolute lung separation is needed, as in bronchopulmonary lavage, connecting a clamped lumen to an underwater drainage system will show air bubbles if a leak is present. |
I will definitley not remember all of this.
|
|
|
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy to verify placment of a DLT box 28-5
1. insert the scope through the tracheal lumen. Visualize the carina distally. 2. Visualize the endobronchial (BLUE) cuff 1-2mm beyond the carina. Ensure that the cuff is not too proximal or overinflated such as to herniate across the carina and obstruct the contralateral bronchus. 3. Insert the scope through the bronchial lumen. Visualize that the tip of the bronchial lumen is unobstructed. For left side tubes, visualize the LUL bronchus distal to the tube tip. For right sided tubes with a RUL ventilation port, visualize that the RUL bronchus is aligned with the ventilation port. |
.
|
|
|
True or False: Placement of DLT's carry a higher risk compared to laryngoscopy and intubation with endotracheal tubes.
|
False: The risk is the same.
|
|
|
Ideal placement of a right sided DLT will reveal the fenestrated bronchial cuff situated adjacent to the RUL takeoff.
|
True. If insertion is too shallow the bronchial cuff may herniate over the carina or frankly obstruct tracheal flow . This would allow ventilation through the brochial lumen only and depending on how shallow the tube is, would ventilate one or both lungs. (figure 28-13 B pg 640)
|
|
|
True or False: The threat of obstructing the LUL bronchus with a DLT is great.
|
False: the risk is slight because of the longer distance to the LUL bronchus.
|
|
|
T/F: When 80% of the lung is hypoxic (ie. during OLV), HPV will increase PVR and thus increase workload for the right heart.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
All of the following decrease HPV except which one:
a. acidosis b. alkalosis c. hypocapnia d. hypoxia e. high card output f. hypervolemia |
D. hypoxia increases hpv
|
|
|
What purpose does HPV serve?
a. decreases shunt flow b. increases shunt flow c. decreases dead space d. reduces pulm vascular resistance |
A. Reduces blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli thus reducing the shunt
|
|
|
Which of the following drugs does not effect HPV?
a. propofol b. fentanyl c. NTG d. cardene |
A & B do not effect HPV.
note: dopamine, neo, epi preferentially constrict the good areas of the lung over the poorly ventilated (areas of HPV) so the shunt is re-established (pg 642) |
|
|
T/F: inhalation agents should not be used during one lung vent (OLV) b/c they inhibit hypoxic pulm vasoconstriction (HPV).
|
False: They do not affect HPV at less than 1.5MAC. They are preferred b/c they allow the use of high FiO2, provide bronchodilation, decrease airway irritability during manipulation, and are cleared quickly allowing for extubation.
|
|
|
T/F: N2O is the preferred agent for OLV.
|
False: it is avoided b/c it can cause increased PVR and prohibits the use of 100% O2.
|
|
|
T/F: N2O is a good choice of anesthetic for a pt with Cor Pulmonale.
|
False. N2O increases PVR and thus increases Right heart workload
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a goal of OLV management:
a. TV 10-15ml/kg b. TV 6ml/kg c. modest peep d. plateau pressures <25cmH2O |
A is not
|
|
|
During OLV your pt becomes hypoxemic. After ruling out physiologic causes, what is one intervention that is almost 100% effective in increasing PaO2?
a. CPAP to the nonventilated lung b. increase RR of ventilated lung c. increase TV of ventilated lung d. manually bag the pt |
A (pg 643, NAG). This is b/c shunt flow thru the non-ventilated lung is usually the cause of hypoxia
|
|
|
During OLV, if PEEP and CPAP aren't maintaining an approp PaO2, what can the surgeon do to improve oxygenation if doing a pneumonectomy?
a. early ligation of the pulm artery b. work faster c. allow reverse t-burg positioning d. nothing |
A. ligating the PA will resolve the shunt
|
|
|
Pleural pressure increases how much for each cm farther down the lung you go?
|
.25 cm for every 1 cm down the lung
|
|
|
The increase in pleural pressure as you go down the lung does what to the volume?
|
decreases fourfold
|
|
|
Which lung gets more of the TV int eh lateral position: dependent of nondependant?
|
dependent
|
|
|
Where is perfusion the greatest in the lateral position: dependent lung or nondependent lung?
|
dependent
|
|
|
anesthesia induction has what effect on FRC?
|
decreases almost immediately
|
|
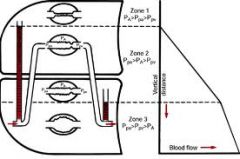
|
effects of gravity on distribution of pulmonary ventilation and blood flow
|
|
|
How does anesthesia affect the dependent lung in the lateral position?
|
it loses a greater amount of FRC than the nondependent lung
|
|
|
Why is there a VQ mismatch in the lateral position?
|
relative FRC in nondependent lung increases in contrast to dependent lung, which decreases compliance in the dependent lung. Ventilation is preferentially distributed to nondependent lung, but blood goes ( gravity) to dependent lung-making a VQ mismatch
|
|
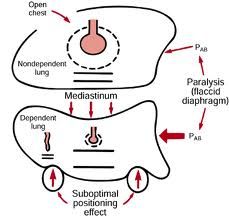
|
VQ relationship in anesthetized, open chest pt
|
|
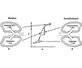
|
ventilation in awake vs. anesthetized closed chest pt.
|
|
|
Once a pt is induced and mechanically ventilated, what happen to FRC? What can be done about it?
|
Further declines. Can add PEEP to restore FRC
|
|
|
An open chest, mechanically ventilated lung has
(increased or decreased) compliance? |
increased
|
|
|
Aggressive treatment of acute or reversible components of respiratory disease greatly decreases the risk of postop complications for Thoracic surgery.
What are some treatable preoperative conditions? |
-Infection
-excess bronchial secretions -bronchospasm -dehydration -electrolyte imbalance -cigarette smoking -alcohol abuse -malnutrition |
|
|
Transient increases in mucus production may increase complications in pt's who have surgery within ________ months of stopping smoking.
a. 1 month b. 1/2 month c. 2 months d. 3 months |
2 months
|
|
|
All pt's require contiuous monitoring of the ECG during Thoracic surgery. Which leads will help detect more than 85% of ischemia
|
leads II and V5
|
|
|
Where are arterial cannula's generally placed for thoracotomies?
|
In dependent arm, where it is more easily stabilized.
|
|
|
For mediatinoscopy, the arterial line is typically placed in the right arm for which reason?
|
detects compression of the innominate artery and helps prevent a decrease in cerebral blood flow.
|
|
|
What is another monitoring technique that can be used to detect compression of the innominate artery (other than A-line)
|
pulse oximeter probe placed on right hand.
|
|
|
This type of monitoring is not required for thoracic surgery but may be useful if the pt's volume status is unclear or if large fluid shifts are anticipated
|
CVC
|
|
|
What type of CVP line is more easily kinked in the lateral position
|
external jugular line
|
|
|
This type of monitoring may be indicated in the presence of a history of severe C.V. disease, valvular heart disease, or significant PHTN
|
Pulm Artery Cath
|
|
|
Type of monitoring intended to provide estimation of left ventricular pressures and facilitate the improvement of cardiac perform. with fluids and cardiovascular drugs
|
Pulmonary artery pressure
|
|
|
What 2 things may alter the resistance in pulmonary vessels and reduce the correlation between pulmonary artery occlusion pressure and left ventricular pressure
|
-Lung pathology
-hypoxic pulm. vasoconstriction |
|
|
More than ____% of pulmonary artery catheters float into the right lung
|
90%
|
|
|
If the Pulm Catheter floats into the right lung during a right thoracotomy, then, the catheter will likely be in the nondependent, collapsed lung. What would this cause?
|
it would give a false low reading for cardiac output
|
|
|
What is the most frequent position chosen for surgical exposure during thoracotomy
|
lateral decubitus
|
|
|
Why is an axilla roll used for the lateral decubitus position?
|
to prevent compression of the neurovascular bundle and forward rotation of the humeral head
|
|
|
Hyperabduction of the arms in the lateral decubitus position is prevented to keep what from happening?
|
keeps the brachial plexus from stretching against the humeral head
|
|
|
Lateral flexion of the neck can cause what?
|
compression of the jugular veins or vertebral arteries, compromising cerebral circulation
|
|
|
What are two pressure points of concern in the lateral position
|
-peroneal nerve:
* in area of the fibular head of dependent leg * and the femoral head of the nondependent leg if a stabilizing strap is placed over the patient |
|
|
In the spontaneously breathing, upright person, blood perfusion increases __________ from:
a. apex to base of lung b. base to apex of lung |
increases linearly
from apex to base |
|
|
In what portion of the lung are flows greatest in the upright position.
|
greatest in the base
very low rates in the apex |
|
|
Where is pleural pressure most negative?
|
the apex of the lung
*this keeps alveoli distended |
|
|
Are dependent alveoli more or less distended
|
less distended and therefore more compliant
|
|
|
is most "tidal breath" distributed to the non-dependent or dependent alveoli
|
dependent
|
|
|
Lung Zones (think tic-tac-toe)
Zone 1 Zone 2 Zone 3 |
1= "PA">Pa>Pv
2= Pa>"PA">Pv 3= Pa>Pv>"PA" |
|
|
The tendency of the top of the lung to collapse inward creates a relatively ___________pressure at the apex, and the tendency of the bottom of the lung to spread outward creates a relatively ______pressure at the base
|
negative
positive |
|
|
Pleural pressure increases by _____cm H2O per centimeter of lung dependency
|
0.25cm H2O
|
|
|
What is a life threatening complication of DLT placement?
|
Vocal cord paralysis
|
|
|
What effect does hypoxemia have on the pulmonary arteries (except for the proximal pulmonary arteries)?
|
vasoconstriction
|
|
|
Onset and resolution of HPV occur very fast/slow following changes in tissue Po2?
|
Fast
|
|
|
HPV is triggered by ________ hypoxemia?
a. arterial b. alveolar |
b. alveolar
|
|
|
HPV decreases the blood flow to the nondependent lung by?
a. 20% b. 30% c. 50% d. 60% |
c. 50%
|
|
|
Name the symptoms of Mediastinal Mass
|
Sweats
Syncope Orthopnea Hoarseness Inability to lie flat Chest pain or fullness Superior vena cava Obstruction Cough(especially when supine) |
|
|
What can reveal whether the supine position of a patient with Mediastinal Mass will exacerbate obstruction intraoperatively?
|
Comparison of flow rates obtained with the patient in the upright and supine positions
|
|
|
The following tests may further delineate the size and effects of a mediastinal mass?
A. Computed tomography B. Transesophageal echocardiography C. Abdominal radiograph D. MRI |
A, B, D.
|
|
|
Flow-volume loops DO/DO NOT demonstrate a high correlation to the degree or severity of airway compression.
|
Caution: They DO NOT.
|
|
|
What type of gas mixture can improve airflow during partial obstruction? and why?
|
Helium-O2
The use of low-density gas decreases turbulence past a stenotic area, improving flow and decreasing the work of breathing. |
|
|
What is Mediastinoscopy?
|
-Passing a scope into the mediastinum via an incision above the suprasternal notch.
|
|
|
What are complications of mediastinoscopy?
|
-pneumothorax
-Hemorrhage -Arrhythmias -Bronchospasm Laceration of the esophagus Chylothorax secondary to laceration of the thoracic duct. |
|
|
What is Superior Vena Cava syndrome?
|
-A venous engorgement of the upper body caused by compression of the superior vene cava by a mass.
|
|
|
Compression of great vessels by Mediastinal Mass can lead to the following:
A. Chylothorax B. Sudden hypoxemia C. Hypotension D. Cardiac Arrest |
B, C, D.
|
|
|
What type of gas mixture can improve airflow during partial obstruction? and how?
|
-Helium-O2 mixture
-The use of low-density gas decreases turbulence past a stenotic area, improving flow and decreasing the work of breathing. |
|
|
True or False:
Pain after an open thoracotomy is generally more easily managed than after thoracoscopy. |
False-the reverse is the case(because the incision in thoracoscopy is smaller, and spreading of the ribs is avoided).
|
|
|
True or False:
Patients for thoracic procedure are generally at risk for cardiopulmonary morbidity. |
True.
|
|
|
What are Bullae?
|
-Air-filled spaces of lung tissue resulting from the destruction of alveolar tissues and consolidation of alveoli into large pockets.
|
|
|
During general anesthesia for bullous disease, to reduce the risk of rupture of bullae, what type of ventilation is desirable?
|
Spontaneous ventilation
|
|
|
What type of gas should be avoided in bullous disease because it rapidly enlarges the air-filled spaces?
|
Nitrous oxide
|
|
|
Absolute Indications for seperation of the two lungs (Double-Lumen Tube Intubation) or OLV:
A. Isolation of one lung from the other to avoid spillage or contamination B. One lung doesn't like the other C. Control the distribution of ventilation D. Unilateral bronchopulmonary lavage |
C. Control the distribution of ventilation
D. Unilateral bronchopulmonary lavage |
|
|
Relative Indications for seperation of the two lungs (Double-Lumen Tube Intubation) or OLV:
A. Surgical exposure - high priority B. Surgical exposure - medium (lower) priority C. Postcardiopulmonary bypass pulmonary edema/hemorrhage after removal of totally occluding unilateral chronic pulmonary emboli D. Severe hypoxemia related to unilateral lung disease |
A. Surgical exposure - high priority
B. Surgical exposure - medium (lower) priority C. Postcardiopulmonary bypass pulmonary edema/hemorrhage after removal of totally occluding unilateral chronic pulmonary emboli D. Severe hypoxemia related to unilateral lung disease |
|
|
What type of double-Lumen Tubes to intubate left bronchus?
|
Carlens with carinal hook OR
Robertshaw with no carinal hook |
|
|
What type of double-Lumen Tubes to intubate right bronchus?
|
White with carinal hook OR
Robertshaw with no carinal hook |
|
|
How do you determine tube size for right and left double lumen tube?
|
Determined by measurements of tracheal width from chest radiograph
|
|
|
Which lung separation devices are placed using fiberoptic bronchoscopy?
|
Left-sided DLT, Fogarty occlusion catheter, & Univent blockers
Right sided DLT & WEB blockers with guided technique |
|
|
Which lung separation devices use a standard ETT at least 6mm in diameter?
|
Fogarty occlusion catheter and Univent blockers
|
|
|
Which lung separation devices use a standard ETT at least 8mm in diameter?
|
WEB blockers
|
|
|
Which lung seperation devices is indicated for Majority of elective left or right thoracic surgical procedures?
|
Left-sided DLT
|
|
|
Which lung seperation devices is indicated for distorted left bronchus anatomy; left pneumonectomy?
|
Right-sided DLT
|
|
|
Which lung seperation devices is indicated for critically ill patient, small bronchus, difficult airway, nasotracheal intubation?
|
Fogarty occlusion catheter
|
|
|
Which lung seperation devices is indicated for selective lobar blockade, difficult airway requiring lung separation?
|
Univent blockers
|
|
|
Which lung seperation devices is indicated for critically ill patients, selective lobar blockade, difficult airway, nasotracheal intubation requiring lung seperation?
|
WEB blockers
|

