![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Complications of Laparoscopy include visceral injury. This is usuallly caused from insertion of the ________ or _________.
|
Needle or Trocar
|
|
|
Bladder and stomach decompression __________the incidence of visceral injury from laparscopy.
a. increase b. decrease |
b. decrease
|
|
|
Complications of laproscopy include which of the following:
a. pneumothorax b. subcutaneous emphysema c. visceral injury d. gas embolism e. all of the above |
E. all are complications
|
|
|
True or false: Subcutaneous emphysema is a result of intraperitoneal insufflation.
|
F. It is a result of extraperitoneal insufflation. It usually resolves itself.
|
|
|
Statement: Extraperitoneal insufflation involves inflating the extraperitoneal space with a balloon and then keeping the space inflated with CO2. This is used for some hernia surgeries and you may have lower abdomen and lower extremity sub-q emphysema
|
.
|
|
|
Patient response to pneumoperitoneum depends on which factors (choose all that apply)
a. pressure generated by the gas b. presence of pre-existing cardiopulm. disease c. intravascular volume status d. duration of procedure e. all apply |
e. all apply
|
|
|
Pneumoperitonum produces systemic effects caused by
DIRECT PRESSURE, NEUROHUMORAL RESPONSES, AND ABSORBED CO2. |
.
|
|
|
You may likely see what type of response from pneumoperitoneum?
a. vagal b.neurohumoral c. initial sympathetic followed by vagal response d. all of the above may happen |
d. all are possible
|
|
|
True or False:
Hemodynamically with pneumoperitoneum you may see a decrease in CVP in the rage of 14-20 torr insufflation pressure. |
False:
You will likely see an increase in CVP in the rage of 14-20 torr and a decrease in CVP above 20 torr of insufflation pressure. |
|
|
The elevation in CVP seen with pneumoperitoneum in the range of 14-20 torr insufflation pressure is caused by what factors.(choose 3)
a. compression of abdominal venous beds b. decreased intrathoracic pressure with decreased filling c. increased intrathoracic pressure with increased filling d. reverse trendelenburg position e. trendelenburg position. |
a, c,e
|
|
|
A decrease in CVP seen with pneumoperitoneum above the range of 20 torr insufflation pressure is caused by what 2 factors?
a. vena cava compression b. trendelenburg position c. reverse trendelenburg position |
a, c
|
|
|
With pneumoperitoneum you will likely see a _________ in SVR of up to 65 % in healthy patients.
a. increase b. decrease |
A. increase due to compression of vessels and neurohumoral response.
|
|
|
Neurohumoral response to pneumoperitoneum usually resolves in ______ minutes after release of pressure.
a. 10 b.20 c.30 d.40 |
c 30 minutes
|
|
|
With pneumoperitoneum you will likely see an _______ in MAP.
a. increase b decrease |
a. increase due to the sympathetic discharge
|
|

What is this? What are normal pressures?
|
CO2 insufflator:
-maintains a steady state of pressure in the abdomen - 10-15 mmHg (1mmHg roughly equals 1 torr) |
|
|
This needle has a blunt tipped inner stylet with a sharp outer needle
|
Veress needle
|
|
|
At what angle is the veress needle inserted?
a. 30-40 b. 20-35 c. 45-90 d. 10-15 |
45-90 degree angle
|
|
|
What can you use to elevate the abdominal wall during the insertion of a veress needle.
a. suction b. hands c. shop vac d. clamps |
hands and clamps
|
|
|
Which direction should you aim your needle during insertion of the veress insufflation needle.
|
Aim caudal
|
|
|
What methods are used to verify correct placement of the veress needle.
a. hanging drop technique b. hiss test (negative press. air flow) c. reach around technique d. williams jerk technique |
a & b
|
|
|
This needle has a blunt tipped inner stylet with a sharp outer needle
|
Veress needle
|
|
|
At what angle is the veress needle inserted?
a. 30-40 b. 20-35 c. 45-90 d. 10-15 |
45-90 degree angle
|
|
|
What can you use to elevate the abdominal wall during the insertion of a veress needle.
a. suction b. hands c. shop vac d. clamps |
hands and clamps
|
|
|
Which direction should you aim your needle during insertion of the veress insufflation needle.
|
Aim caudal
|
|
|
What methods are used to verify correct placement of the veress needle.
a. hanging drop technique b. hiss test (negative press. air flow) c. reach around technique d. williams jerk technique |
a & b
|
|
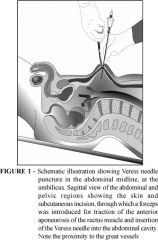
|
picture
|
|
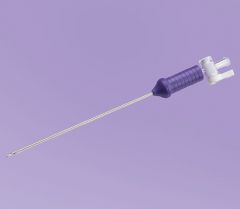
What is this? What is it used for?
|
Veress needle
Insufflation with CO2 |
|
|
In the supine position, the diaphragm is displaced which direction?
|
cephalad ( toward head)
|
|
|
For the supine position, the lungs zones are distributed how?
|
to more zone 3
( decreases dead space) |
|
|
In the lateral decub position, lung zones shift how?
|
more zone 1
|
|
|
How does the lateral position affect VQ?
|
creates a mismatch, ( decrease in vol in dependent lung and increased perfusion)
|
|
|
Which of the following would you see in a Laparoscopy pt that has absorbed CO2 from the pneumoperitoneum?
A. a decrease in myocardial contractility B. Higher arrythmia threshhold C. vasoconstriction D. decreased SVR |
A, D
|
|
|
hypercapnia can cause:
A. peripheral vasodilation B. increased cerebral blood flow C. pulmonary vasodilation |
A, B.
Actually causes pulm vasoconstriction |
|
|
3 causes of oliguria in a laparoscopy pt?
|
compression of kidneys by pneumoperitoneum
compression of IVC increased level of ADH |
|
|
What will the kidney do to attempt to increase blood flow to kidney in presence of pneumoperitoneum?
|
increase levels of aldosterone, vasopressin and renin
|
|
|
Insufflation needle is called what?
|
Veress needle
|
|
|
Veress needle:
>_____ tipped inner stylet with _____ outer needle >Inserted at an angle of ______ degrees >Elevated __________ _____ with hand or clamps >Aim ____ (______ bifurcation is at level of umbilicus) >Verify placement with "_____ ____" technique or "____" test (_______ pressure air flow) |
>Blunt tipped inner stylet with sharp outer needle
>Inserted at an angle of 45-90 degrees >Elevated abdominal wall with hand or clamps >Aim caudal (aortic bifurcation is at level of umbilicus) >Verify placement with "hanging drop" technique or "hiss" test (negative pressure air flow) |
|
|
_____ needle is used to insert a port into the body for laparscopy.
|
trocar needle
|
|
|
T/F - After trocar needle is inserted it is then completely removed and insertion hole sewn up.
|
F - Port is left in place to facilitate insertion of cameras and instruments.
|
|
|
T/F - All laparscopic surgery is done through the trocar and veress insertion ports.
|
F- After trocar needle is inserted and port left in place, subsequent ports are visualized with laparscope being inserted into the body
|
|
|
The word Laparoscopy is coined from the Greek words "Laparo" which means------------------ and "Skopein" for------------------
|
-Flank
-To examine |
|
|
Define Laparoscopy
|
-Looking at abdominal contents using an endoscope
|
|
|
What decade did Laparoscopy gained traction and in what year was the first laparoscopic cholecystectomy done?
|
-1980's
-1987 |
|
|
Air within the peritoneal cavity is known as:
|
Pneumoperitoneum
|
|
|
In laparoscopic procedures, pneumoperitoneum is created using which two techniques and with which two instruments?
|
1. Open technique-using Hasson (1.5-3 cm incision)
2. Closed technique-using Veress needle. |
|
|
All the following are properties of a perfect gas EXCEPT:
1. Colorless 2. Nonphysiological inertness 3. Lack of flammability 4. Excretion via pulmonary route. |
2. Nonphysiological inertness (A perfect gas should HAVE physiological inertness)
|
|
|
The preferred or most common gas used in insuflation during laparoscopic procedures is:
|
CO2
|
|
|
Name other gases which can be used for insuflation and the reason why they are not commonly used.
|
Air-supports combustion and increased risk for emboli
N2O-supports combustion Helium-not very absorbable and can create emboli. |
|
|
All the following are advantages of CO2 EXCEPT: It
1. is inexpensive 2. does not support combustion 3. is not readily absorbed from the vascular system 4. is readily excreted via the pulmonary system. |
Except # 3
It is readily absorbed from the vascular system |
|
|
True or False:
The reason why CO2 is the commonly used gas for insuflation during laparoscopic procedures is because of its bright color when introduced into the abdomen. |
False (CO2 is a colorless gas and it is commonly used because of this and other properties).
|
|
|
Which ONE of the following is NOT assoc with pneumoperitoneum?
a. increased SVR b. increased MAP c. increased SV d. biphasic CO response (low then high) e. Tachycardia |
C is false. Get a 30% decrease in SV d/t reverse T-berg and vol status.
E is true but may see brady too d/t vagus n. compresson. |
|
|
T/F: Insufflation psi for a pneumoperitoneum should be >20torr
|
False. >20Torr associated with decreased CVP, CO.
|
|
|
Which two of the following contribute to increased SVR with pneumoperitoneum?
a. vessel compression b. neurohumoral response c. positioning d. stress response |
A and B
|
|
|
statement: during pneumoperitoneum....biphasic response of CO (card output)...first low d/t vessel compression, increases within 5-10min d/t neurohumoral factors.
|
.
|
|
|
Which one of the following is not a result of pneumoperitoneum related to pulm fxn?
a. increased PIP b. decreased compliance c. decreased vital capacity d. increased FRC |
D. FRC is decreased d/t pressure on the diaphragm.
|
|
|
Cephalad displacement of diaphragm with T-burg position can cause _____________ in 6% of patients.
|
Right mainstem intubation
|
|
|
In the T-burg position how much increase in minute ventilation is needed?
a. 10-15% b. 12-16% c. 15-20% d. 20-30% |
d. 20-30% increase in MV
|
|
|
In reverse T-burg position how much increase in minute ventilation is needed?
a. 10-15% b. 12-16% c. 15-20% d. 20-30% |
b. 12-16%
|
|
|
With pulmonary dysfunction, it is more effective to increase ________ rather than increase the _______ to control CO2 elimination (assuming PIP is normal)
|
increase tidal volume rather than increase the rate.
|
|
|
What effects in pulmonary function are seen in patients with cardiopulmonary disease?
|
-significant decrease in CO with increased filling pressures and afterload
|
|
|
A study by Sofran and Orlando found that patients with co-morbidities have significant effects of pulmonary dysfunction at ___ torr?
a. 10 b. 15 c. 20 d. 25 |
b. 15 torr
|
|
|
Absorption of CO2 will show an __________ in the paCO2 and ETCO2.
|
Increase
|
|
|
True/False
Absorption of CO2 is due to hyper metabolism or the pneumoperitoneum itself? |
False - its primarily due to absorption of CO2 at the peritoneal surface
|
|
|
Maximal absorption of CO2 can occur with intraabdominal pressure of _______ torr.
a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 |
b. 10 torr
|
|
|
Maximal absorption of PaCO2 reaches a plateau after approximately ________ minutes.
a. 25 b. 30 c. 35 d. 40 |
d. 40 minutes
|
|
|
CO2 absorption can cause significant (choose 2)
A. Hypercapnia B. Alkalosis C. Acidosis D. Hypocapnia |
A and C
|
|
|
List effects of Hypercapnia from CO2 absorption.
|
-Decreased myocardial contractility
- Lower arrythmia threshold(more PVC's) -Vascular dilation and a decrease in SVR are offset by mechanical compression and catecholamine release |
|
|
Mild hypercapnia (45-50 torr) is or is not clinically significant?
|
Is not
|
|
|
Hypercapnia above 50 torr will cause? (choose all that apply)
a. increased cerebral blood flow b. peripheral vasodilation c. pulmonary vasoconstriction d. cardiac dysrhythmias e. all of the above |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
If a patient has symptomatic low back pain what should you do when positioning?
|
Place the patient in stirrups while the patient is awake for position of comfort.
|
|
|
What are "Major Vascular" Injury Complications of Laparscopy:
A. Aorta B. IVC C. Renal D. Iliac or mesentaric E. SVC |
Major Vascular injuries:
A. Aorta B. IVC C. Renal D. Iliac or mesentaric |
|
|
T/F - Bleeding from vascular injury d/t Laparscopy cannot be retroperitoneal and therefore always seen in the visualized field.
|
F - Bleeding from vascular injury d/t Laparscopy CAN be retroperitoneal and therefore NOT always seen in the visualized field.
|
|
|
Typical CVC pressure: ___
Insufflation pressure in Laparscopy: ___ What can be caused by these differences in pressure? |
Typical CVC pressure: 6-8 mmHg
Insufflation pressure in Laparscopy: 10-15 mmHg Greater pressure of insufflation can tamponade bleeding of a venous injury until pneumoperitoneum is removed. |
|
|
Gas embolism can be ___ complication of laparscopy.
A. Very Rare B. Very Common |
A. Very Rare
|
|
|
Gas embolism is usually caused from:
A. Initial insufflation B. Veress needle placement into a vessel C. Trocor placement into a vessel |
A. Initial insufflation
B. Veress needle placement into a vessel C. Trocor placement into a vessel |
|
|
What is gas lock? How does it relate to complications of Laparscopy?
|
Complication of Gas Embolism from Laparscopy - Gas bubbles can lead to "Gas Lock" (prevent right ventricular outflow)
|
|
|
What complication from Laparscopy will cause the following signs and symptoms.
> Hypotension > Dysrhythmias > Hypoxia > Pulmonary Edema > "mill wheel" murmur |
Gas Embolism
|
|
|
Treatment for Gas Embolism:
A. Discontinue insufflation B. Increase insufflation pressure C. Administer 100% O2 D. Release pneumoperitoneum E. Place in left lateral decubitus position |
A. Discontinue insufflation
C. Administer 100% O2 D. Release pneumoperitoneum E. Place in left lateral decubitus position |

