![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acropolis |
-a citadel or fortified part of an ancient Greek city, typically built on a hill. -Akro means “ high” and polis means “ city” |
|
|
Apse |
Rounded extensions at each end of the buiding |
|
|
Archaic Smile |

conventional closed lipped smile (used by Greeks in the Archaic Period) |
|
|
Barrel Vault |
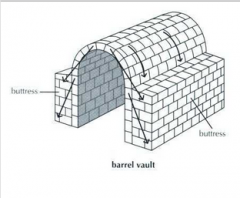
-Constructed in the same manner as the round arch -series of connected arches across a line -requires buttressing |
|
|
Buon Fresco |
Mural painted on wet plaster |
|
|
Caryatid |

Columns carved as people |
|
|
Codex |
-Sheets of paper bound together like a modern book -replaced the scroll in the early 1st century |
|
|
Contrapposto |
the convention of presenting standing figures with opposing alternations of tension and relaxation around a central axis |
|
|
Diptych/Triptych |
two/three carved panels hinged together |
|
|
Expressionism |
deliberate attempt to elicit a specific emotional response in the viewer |
|
|
Flying Buttress |

a gracefully arched, skeletal exterior support |
|
|
Fresco Secco |
Mural painted on dry plaster |
|
|
Groin Vault |
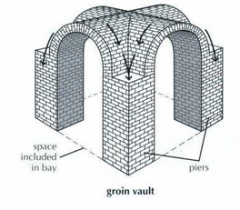
two barrel- vaulted spaces intersecting at the same level |
|
|
Iconoclasm |
-"image breaking" -the prohibition and destruction of works of visual art (usually because they are considered inappropriate in religious contexts) |
|
|
Illuminated Manuscripts |
Manuscripts decorated with gold and colors |
|
|
Kouros/Kore |
-free- standing figures -female statue of this type is called a kore, Greek for “ young woman,” and a male statue is called a kouros, Greek for “ young man” -nearly always nude -variously identified as gods, warriors, and victorious athletes |
|
|
Nave |
Large central area (of a church) |
|
|
Oculus |
a circular opening at the top of a dome |
|
|
Pointed Arch |
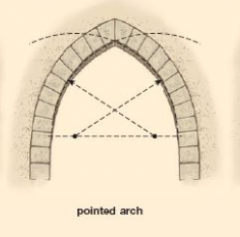
-introduced after the beginning of Islam -2 or 4 center points generating different circles that overlap for a very slightly pointed arch |
|
|
Red Figure/Black Figure |
apply slip ( a mixture of clay and water) to the surface of a pot and carefully manipulate the firing process in a kiln to control the amount of oxygen reaching the ceramics. |
|
|
Technique |
a way of carrying out a particular task |
|
|
Reliquary |
a container for holy relics |
|
|
Ribbed Vault |
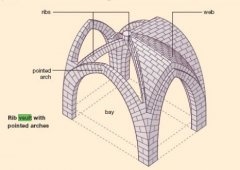
a form of groin vault, in which the diagonal ridges ( groins) rest on and are covered by curved moldings called ribs |
|
|
Stave Church |
named for the four huge timbers ( staves) that form their structural core |
|
|
Stele |
upright stone slab |
|
|
Tesserae |
small, regularly shaped pieces of colored stone and marble |
|
|
Transept |
a perpendicular hall crossing in front of the apse |
|
|
Basilica |
Large rectangular building with extensive interior space, adaptable for a variety of administrative governmental functions |
|
|
Cathedral |
A bishop’s church is a cathedral, a word derived from the Latin cathedra, which means “ chair” but took on the meaning of “ bishop’s throne.” |
|
|
Vellum |
thin sheets of cleaned, scraped, and trimmed sheepskin or calfskin |
|
|
What is the significance of Polykleitos' Spear Bearer? |
Polykleitos developed a set of rules for constructing what he considered the ideal human figure, which he set down in a treatise called “ The Canon." To illustrate his theory, he created Spear Bearer. |
|
|
Doric Column |
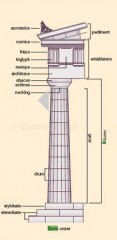
-shafts sit directly on the stylobate -no base -fluted |
|
|
Ionic Column |
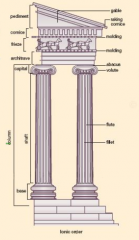
-more elongated than Doric -spiral scroll capitols |
|
|
Corinthian Column |
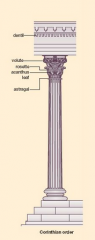
-elaborate capitols |
|
|
Geometric Period |
-900 and 700 BCE -ceramic vessels with linear motifs, such as spirals, diamonds, and cross- hatching -funerary vessels developed -geometric shapes used to represent human figures/animals/plants |
|
|
Orientalizing Period |
-700-600 BCE -more open compositions -began in Corinth |
|
|
Archaic Period |
-600-480 BCE -time of great new achievement -elaborate temples -kouros -archaic smile -black/red-figure |
|
|
Early Classical Period |
-480-450 BCE -contrapposto -bronze scuptures |
|
|
High Classical Period |
-450-400 BCE -pinnacle of artistic refinement -acropolis -parthenon -idealized proportions |
|
|
Late Classical Period |
-400-323 BCE -relaxed convntions -new canon -first depictions of fully nude women -goldsmithing & earrings |
|
|
Hellenistic Period |
-323-31/30 BCE -Corinthian order on exteriors -anti-classical style -expressionism |
|
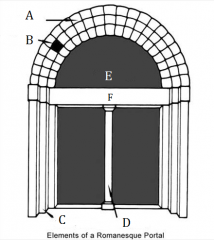
A |
Archivolt |
|
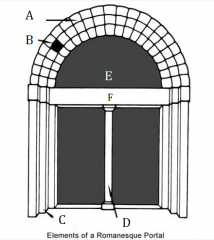
B |
Voussoirs |
|
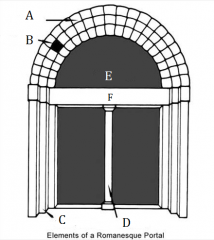
C |
Door Jambs |
|
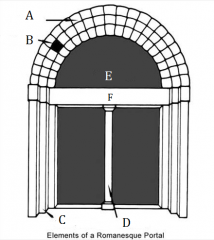
D |
Trumeau |
|
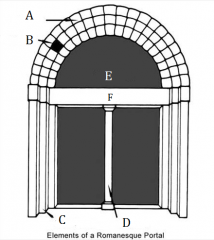
E |
Tympanum |
|
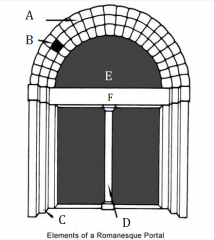
F |
Lintel |
|

A |
Cornice |
|

B |
Frieze |
|

C |
Architrave |
|

D |
Cella |
|

E |
Stylobate |
|

F |
Pediment |
|

G |
Entablature |
|

H |
Column |

