![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Typical wastewater treatment list steps |
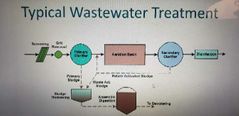
|
|
|
|
What is removed in screen |
Rags, paper, plastic, rocks and other debris |
|
|
|
What is grit |
inorganics. Grit can be parts of the pipe that are wearing off like concrete. Also includes eggshells, bone chips, seeds, coffee grounds |
|
|
|
What type of solids does biological treatment remove? |
Dissolved solids |
|
|
|
What is BOD |
The amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to break down organic matter in Wastewater |
|
|
|
Typical incoming BOD amount |
Typically around 200 mg per liter. Depends on industry excetera |
|
|
|
Why do Wastewater Plant typically reduce BOD to |
Single digits |
|
|
|
What is TSS |
The measurement of particulate matter in the wastewater |
|
|
|
Typical TSS in incoming was3 |
Same as bod around 200 mg per liter |
|
|
|
What is the bod removal process |

|
In the presence of |
|
|
Organic matter is converted to |
Carbon dioxide Ammonia New microorganisms |
Three things |
|
|
What is b o d – explained |
B o d is the amount of oxygen demand during the process of breaking down waste in the water |
|
|
|
What two things happen in a clarifier |
Microorganisms settled to the floor of the clarifier Clear liquid flows over the Weirs |
|
|
|
What is typical b o d and TSS leaving the plant |
Typically single digits |
|
|
|
In activated sludge process the sludge is returned back to the |
Aeration basin |
|
|
|
In activated sludge the microorganisms that settle our return back to the aeration basin 2 approximately how many times greater than the incoming stream? |
30 X the amount of microorganisms that were in the waste stream coming into the plant |
|
|
|
Wastewater plants can typically degrade the organic material how many more times faster then without treatment |
30 x |
|
|
|
This is not a balance of solids in and solids out because |
Microorganisms are growing and multiplying. Absorbing organic matter and growing new cells. |
|
|
|
Why is it called mixed liquor |
It's a mixture of the Raw Feed coming in and the return sludge from the clarifier |
|
|
|
Too high of solids concentration in aeration Basin will what? |
Prevent solids from settling |
|
|
|
What is the typical concentration of mixed liquor in aeration basin |
Typically between 2000 and 4000 mg per liter |
|
|
|
What is the typical dissolved oxygen leaving the aeration basin |
2 mg per liter |
|
|
|
Why don't you want the do too high in an aeration basin. 2 things |

|
|
|
|
What's the problem with filamentous bacteria |
Won't settle in clarifier |
|
|
|
What do filamentous bacteria look like and why is that a problem |
Look like tree branches are feathers. Just like a feather dropped in the water. Doesn't want to settle like a Rock would |
|
|
|
What is the problem with too low of dissolved oxygen in aeration basin |
Insufficient bod removal because microorganisms don't have enough oxygen Oders because it's now an aerobic |
|
|
|
What is HRT |
Hydraulic retention time |
|
|
|
What is HRT in aeration basin |
I think 24 hours. Verify |
|
|
|
What is SRT |
Solids retention time. Possibly sludge retention time. Verify |
|
|
|
If the SRT is shorter than the reproductive cycle of the microorganisms... |
The microorganisms will it be out of the system before they reproduce and we won't have the concentration we need for the job |
|
|
|
What is F/M ratio |
Ratio of influent bod/ day to mass of microorganisms. Like the amount of food you eat everyday / your weight |
|
|
|
What is the normal F/M ratio |
0.2 to 0.5 |
|
|
|
What happens if the food to mass ratio is too high |
Microorganisms can't handle all of the food Insufficient bod removal Bulking - poor settling Like fat bugs have eaten too much and Float to the top. Don't want to settle. Actually changes their specific gravity. Don't really get fat |
|
|
|
What's the problem with too low food to microorganism ratio |
Favors filamentous microorganisms – poor settling |
|
|
|
Types of activated sludge systems |
Diffused air aeration Mechanical surface aeration. Oxidation ditch is the most common type of mechanical surface aeration |
|

