![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Resistance |
exercise |
|
|
Resistance __: overall program |
training |
|
|
General principles (5):
-specificity of ___ |
training |
|
|
General principles (5):
-____ principle |
SAID |
|
|
General principles (5):
Progressive |
overload |
|
|
General principles (5):
____ in training |
Variation |
|
|
General principles (5):
____ of training |
Prioritization |
|
|
-Identifying ___ variables that can be controlled to __ training outcomes is key to improved program design |
-specific
-predict |
|
|
Sound ___ must be made based on __ understanding of resistance training, the needs of the sport or activity, individual training responses, and testing data |
decisions
factual |
|
|
Planning and ___ the exercise prescription is vital for success |
changing |
|
|
Clients who are relatively ___ will see great gains initially |
deconditioned |
|
|
As training progresses, gains ____ |
decrease |
|
|
___ are linked to the clients genetic potential |
Gains |
|
|
Keep records of you clients ____ |
progress |
|
|
_____ training logs are a useful tool |
Individualized |
|
|
____ the clients progress periodically |
Reasses |
|
|
___ the program variables accordingly |
Modify |
|
|
Modifications for client variablitlity:
-Anatomical characteristics
-Needs
-Abilities
-Training adaptations |
Info |
|
|
Client feedback
___ ____: openly expressed, solicited by personal trainer |
expressed verbally |
|
|
Client feedback
_____ ___: physical signs of discomfort or pain, reduction in technique |
Expressed physically |
|
|
Client feedback
Of special concern is careful and proper progression, especially in ___ or those coming off __ or disease |
beginners
injury |
|
|
Client feedback
Too much exercise, too heavy of exercise, and or accentuated eccentric exercise can lead to an excessive amount of muscle tissue ___ or ___ |
damage
breakdown |
|
|
Client feedback
Symptoms of ___ ___ ___ ____ is a first sign that the individual has done too much too soon
-swelling, pain, and soreness are classical signs of muscle tissue damge |
delayed onset muscle soreness |
|
|
Client feedback
Explain muscle ___ the exercise is intended to target |
groups |
|
|
Client feedback
Watch for deterioration of __ - proper technique must always be a priority |
technique |
|
|
Client feedback
Likert-type chart of soreness:
1 = |
minor soreness |
|
|
Client feedback
3= |
Moderate soreness |
|
|
Client feedback
5: |
Extreme soreness |
|
|
Goals:
- ____
- Testable/measurable |
Obtainable |
|
|
Time frame:
- ___ |
Realistic |
|
|
____ : value judgemetn of gains versus training time. Leads to maintenance training program |
Capping |
|
|
Decisions such as ____ are part of the many types of decisions that must be made when monitoring the progress of resistance training programs |
Capping |
|
|
Program Design: ___ _____
-genetic limitations
-lack of underlying scientific principles
-Ultimately, for both men and women, it is a question of whether the resistance training program used can stimulate the desired changes in their body |
unrealistic goals |
|
|
Choice of resistance training ____ depends on clients:
-needs
-goals
experiences
limitations |
modalities |
|
|
___: Dynamic constant external resistance |
DCER |
|
|
- Lifting (_____) phase |
concentric |
|
|
-Lowering (____) phase |
eccentric |
|
|
Types of __ devices: dumbbells, barbells, kettle bells, weight machines, medicine balls |
DCER |
|
|
Examples of ___ ___ exercies:
-exercise stabilizing muscles
-operate in multiple dimensions
-almost unlimited range of motion
-easily adaptable to individual |
Free Form |
|
|
Static resistance devices:
Muscular action that does not change muscle length:
-Immovable ___
-___ muscle group against__ |
apparatus
weak, strong |
|
|
Strength gains less that ___ per week related to:
-Action number
-Action duration
-Action strength (maximal or submaximal)
-Training frequency |
5% |
|
|
___ devices control speed for maximum resistance:
-Friction
-Compressed air
-Pneumatics
-Hydraulics |
Isokinetic |
|
|
machines vs. free-weight exercises:
Machines at comparative disadvantage:
-Do not fit all ___
-Do not allow __ range of motion
-Negate __ muscles |
-proportions
-full
-stabilizing |
|
|
machines vs. free-weight exercises:
Machines at comparative disadvantage:
- Allow greater ___
-Are less ___
-Do not allow ___ training
-Do allow body movements that __ __ do not |
- independence
-intimidating
- power
-free weights |
|
|
Transfer Specificity:
Each resistance exercise will have __ amounts of transfer to other activites |
various |
|
|
Transfer Specificity:
No conditioning activity has __ transfer |
perfect |
|
|
Transfer Specificity:
OPtimal training program needs to ___ carryover to the target sport or activity |
maximize |
|
|
Energy sources:
- ATP metabolism
-Anaerobic metabolism
-Aerobic metabolsim |
info |
|
|
Most resistance training programs use several types of muscle actions:
-Isometric
-Dynamic concentric
-Dynamic eccentric
-Isokinetic |
info |
|
|
Enhance strength and function of tissue to:
-Resist __
-Recover ___
-Reduce extent of __ |
-Injury
-Faster
-Damage |
|
|
Prehabilitation:
-Prevent injury by training susceptible __ and ___
-Prevent reinjury |
joints
muscles |
|
|
Classic acute program variables:
-Choice of ___
-Order of ___
-Resistance and ___ used
- Number of ___ for each exercise
-Duration of __ period between sets and exercises |
-exercises
-exercises
-repetitions
-sets
- rest |
|
|
Choice of Exercises:
- Primary or ___
- ___ or single-joint
-Single joint or single __ group
-___ or unilateral |
-assistance
-multijoint
-muscle
-bilateral |
|
|
Order of exercises:
1. ___ muscle group before __ muscle group exercises |
Large, small |
|
|
Order of exercises:
2. ___ before ___ exercies |
Multijoint, single joint |
|
|
Order of exercises:
3. Alternating ____/___ exercises for total body sessions |
push/pull |
|
|
Order of exercises:
4. Alternating ___/___ body exercises for total body sessions |
upper/lower |
|
|
Order of exercises:
5. __/___ type lifts (e.g., Oympic lifts) and plyometric exercises before basic strength and single-joint exercises |
Explosive/power |
|
|
Order of exercises:
6. Exercises for priority weak areas before exercises for ___ areas |
strong |
|
|
Order of exercises:
7. Most ___ to least __ (particularly when performing several exercises consecutivel for the same muscle group) |
intense |
|
|
Resistance and repetitions used:
-Repetition ___ (RM)
-Absolute ___
-Percentage of __ RM |
-maximums
- resistance
- 1 |
|
|
Number of days per week of training (frequency:
- Depends on ___ outcome, training status, competitive season, and type of training sessions (full body or split routine) |
desired |
|
|
Number of days per week of training (frequency:
Health related: __ to __ days per week using a full body resisitance training program |
2, 3 |
|
|
Number of days per week of training (frequency:
Additional days may be needed for intermediate (__ to __ days per week) or advanced ( __ to __ days per week) |
4 to 5
4 to 6 |
|
|
Number of sets for each exercise:
Volume of exercise equation:
-long term progression
-maintenance |
sets x reps x resistance |
|
|
Number of sets for each exercise:
- __ set programs
- ___ set programs
|
Multiple
one |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Primary energy system (_____ needs to be replenished
-The duration of the rest period signifcantly influences the metabolic, hormonal, and cardiovascular responses to a short term bout of resistance exercise, as well as the performance of subsequent sets |
ATP |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
- __ versus __ rest |
long, short |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
- __ versus __ loading |
Heavy, moderate |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Effects of __ |
aging |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Rest periods can be characterized as:
-Very short rest periods- __ minute or shorter |
1 |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Rest periods can be characterized as:
-Short rest periods- __ to __ minutes |
1, 2 |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Rest periods can be characterized as:
-Moderate rest periods- __ to __ minutes |
2, 3 |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Rest periods can be characterized as:
Long rest periods- __ to __ minutes |
3, 4 |
|
|
Duration of rest period between sets and exercises:
Rest periods can be characterized as:
-Very long rest periods- _ minutes or longer |
5 |
|
|
Variation of acute program variables:
-Variation addresses ___ change in demands on neuromuscular system |
needed |
|
|
Variation of acute program variables:
- __ exercise can rest higher threshold motor units |
Light |
|
|
Variation of acute program variables:
- Motor recruitment follows the "___ principle" |
size |
|
|
Variation of acute program variables:
Different loads can result in __ amounts and types of muscle tissue being used |
varying |
|
|
Muscles can produce force while performing one of three different actions (1/3):
- When sufficient force is produced to overcome the external load and shorten the muscle, the actions is termed ____ muscle action or contraction. |
Concentric |
|
|
Muscles can produce force while performing one of three different actions (2/3):
-If the muscle produces force but there is no change in length of the muscle, the action is termed ___ |
isometric |
|
|
Muscles can produce force while performing one of three different actions (3/3):
-Production of force while the muscle is lengthening (i.e., resisting the movement) is termed ___ muscle action |
eccentric |
|
|
True repetition and range of movement:
-Muscle actions involving joint movement are dynamic:
- ___ phase
- ___ phase
-Importance of using entire range of motion |
Concentric
Eccentric |
|
|
- ____: systematic changes in prescribed volume and intensity during different phases of resistance training program
-Hypertrophy
-Strength/power
-Peaking
-Recovery |
Periodization |
|
|
Periodization of exercise:
Phases: (3) |
-macrocycle
-mesocycle
-microcycle
|
|
|
Traditional American Style Periodization schedule |
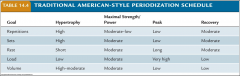
|
|
|
___ periodization: progressive increase in intensity originally evolved from training fro single peak events (eg, track and field, weightlifting)
-Steady linear increase in intensity
- Volume of the training program decreases gradually in concert with an increase in intensity.
|
Linear |
|
|
___ linear program:
-follows tenants of linear periodization for volume and strength but in the reverse order
-May be of benefit when muscular endurance is the primary program outcome |
Reverse |
|
|
_____ periodized programs:
- Also called daily undulating periodization (DUP)
-Maintains variation in training stimulus
-Variation in intensity and volume within each week
-Flexible and can accommodate to client schedules
|
Nonlinear |
|
|
___/___ nonlinear periodized programs
-Overall plan is developed for a 12-week mesocycle bu the actual day a given workout will be performed is based on the readiness to train
-Allows for only the most optimal workout that can be performed on a given day |
unplanned/flexible |

