![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
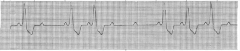
|
Block
2nd degree type 2 Brady |
|
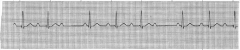
|
Block
2nd degree type1 Brady 52 |
|
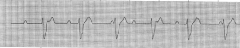
|
Block
3rd type 3 Brady |
|
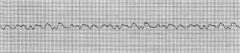
|
V-Fib (Fine)
|
|
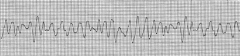
|
V-Fib (Coarse)
|
|
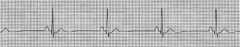
|
Sinus Brady
HR 39 |
|
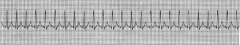
|
SVT
HR 212 |
|
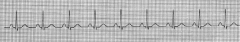
|
NS
|
|
|
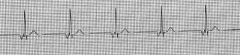
Inverted P wave (Juctional block)
HR 49 |
|
|
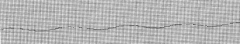
Asystole
Dead |
|
|
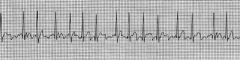
A-Fib (No P wave)
HR 134 |
|
|
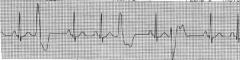
PVC (Polymorphic)
|
|
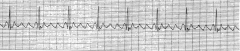
|
A-Flutter (Fast)
HR-75 |
|
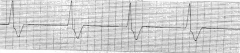
|
Brady (V-Escape) aka Junctional
|
|
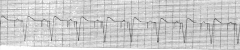
|
Paced
|
|
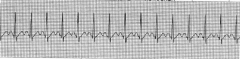
|
Sinus Tachy
|
|
|
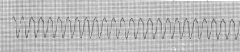
V-Tach
HR 150 |
|
|
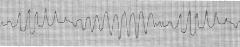
Torsades
|
|
|
How many compressions per min?
|
AT LEAST 100/min"
|
|
|
When no airway has been established what is the compressions/breath ratio.
|
30:2
|
|
|
When airway is established how many seconds between breaths?,
|
6-8 seconds
(7-10)/min) |
|
|
When airway is established and pt has pulse how many seconds between breaths.
|
5-6 seconds
(10-12)/min |
|
|
If scene is unsafe what does rescuer do?,
|
DO NOT go on scene (provider safety)
|
|
|
What do you do immediately following a shock?
|
Resume compressions
|
|
|
When a pt is suspected of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS aka heart attack), how much Aspirin do you provide?
|
160-325mg non EC chewable
|
|
|
When a pt is suspected of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS aka heart attack), when do you give nitroglycerin?,
|
When the pt BP is normal, HR is normal, no ED meds on board, and pt is not having a Right sided inferior wall MI determined by and ECG.
|
|
|
If a hospital is close but does not have the capabilities to treat ACS, what do you do?,
|
Divert do facility that is capable.
|
|
|
When shocking a peds pt do you use an attenuator?
|
No, too much electricity is better than not enough.
|
|
|
How long do you check the carotid pulse for?
|
No longer than 10 seconds.
|
|
|
What is the difinitive way to comfirm adequate compressions and correct placement of airway.,
|
Waveform capnography.
|
|
|
If initial CO2 read by the waveform capnography shows <10mmHg?
|
Pt is dead
|
|
|
If CO2 readings begin at 20 and continuously go down, what does that indicate?
|
Inneffective compressions. Switch people out
|
|
|
What does a surge of CO2 indicate.
|
ROSC
|
|
|
Shock joule dosing rule?
|
"Escalated dosing 200->300->360"
|
|
|
When to treat arrhythmia with medication?
|
Pt systolic is abov 90mmHg, pt not altered, pt is stable.
|
|
|
When to treat pt with electricity (shock)?
|
Pt is altered, BP below systolic 90mmHg, and unstable.
|
|
|
We ________ the dead?
|
Defibrillate
|
|
|
We ________ the living (who have a pulse).
|
cardiovert
|
|
|
What are the FAST arrythmias?
|
V-Tach
A-Flutter SVT Sinus Tachy Torsades |
|
|
What are the slow arrythmias?
|
Sinus Brady
Blocks V-Escape (no Pwave) |
|
|
What do we treat with Amioderone?
|
V-Tach & SVT. Amioderone slows heart activity.
|
|
|
What arrythmias are considered DEAD?
|
Torsades
PEA V-Tach V-Fib |
|
|
What are the Big Block Countdowns?
|
300 150 100 75 60
|
|
|
What do you do if your AED malfunctions?
|
Start compressions while trying to fix. You can shock in snow or on ICE.
|
|
|
When defribrillating, what should be removed from scene?
|
O2. Hands free pads are faster defribulators.
|
|
|
CPR person switch and analysis should be less than ____.
|
10 seconds
|
|
|
Suctioning?
|
Suction Pharynx, Only suction for 10 sec while withdrawing."
|
|
|
RAT/MERT/RRT do what?
|
respond to clinical deterioration.
|
|
|
When administering dopamine ___/____/___? And what arrythmia is it use for?
|
"2-10mcg/kg/min
ONLY USED IN BRADY (SLOW)" |
|
|
Adult capnography waveform readings are _____?
|
35-40mmHg
|
|
|
A spike from 10mmHg to 50mmHg capnography readings indicate?
|
correct advanced airway placement and return of perfusion.
|
|
|
_________ may restrict venous return.
|
Circumferetnial trach ties
|
|
|
Once ROSC (return of spontaneous circulation) has occurred, what is the priority?
|
ventillation and oxygenation.
|
|
|
Cricoid pressure.
|
"Cricoid pressure is no longer used.
|
|
|
Closed loop communication.
|
Repeating orders back to avoid errors.
|
|
|
What is the desired O2 range?
|
94-99%
|

