![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When Using a Peripheral IV |
Follow up administered drugs w/ 20 ml bolus, and then elevate extremity 10-20 seconds. |
|
|
Intraosseous (IO) |
Definition: inside the bone marrow. Any drugs that can be delivered via IV can be delivered via IO. |
|
|
Endotracheal |
Definition: into the breathing tube. IV/IO more recommended. If endotracheal delivery is recommended, dilute drug to 10 ml volume w/ water/NS. |
|
|
Adrenosine |
First drug for MOST forms of SVT, especially those caused by "reentry." Can be considered for preparing for cardioversion. Will not treat poison/drug-related tachycardia or heart block. For IV push, place patient in Trendelenburg position, then administer 6ml dose over 1-3 seconds, followed by 20ml followup and elevation of extremity |
|
|
SVT |
SupraVentricular Tachycardia Any elevated heart rate not caused by stress, exercise, or fever. Can be symptomless, but symptoms include dizziness, shortness of breath, and chest pains. |
|
|
Amiodarone |
Extremely dangerous drug: prescribe only for these heart problems: 1. Recurrent VF 2. Recurrent hemodynamic unstable VT Usually prescribed by licensed physicians, familiar with the drug's affects. |
|
|
Aspirin |
Administer to all patients with ACS/chest pains. Works by preventing platelets from aggregating and arteries from constricting. Do not administer to anyone w/ sensitivity to aspirin, or patients w/ bad ulcers and/or asthma. Delivered as a 160-325 mg tablet. |
|
|
Atropine |
1st drug for symptomatic sinus bradycardia 2nd drug for bradycardic asystole (after epinepherine/vasopressin) Do not use when patient is suffering hypoxia or ischemia Bradycardia: 0.5 mg push every 3-5 minutes (max 3 doses) Asystole: 1 mg push every 3-5 minutes (max 3 mg) |
|
|
ACS |
Acute Coronary Syndrome. Caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Symptoms include chest pains, nausea, and shortness of breath. |
|
|
Symptomatic Bradycardia |
When symptoms of bradycardia begin to appear (<50 bpm) Symptoms include tiredness, shortness of breath, and physical weakness. |
|
|
Cardioversion |
Administered for all cases of serious tachycardia Electric shock delivered via defibrillation electrodes or handheld defibrillator paddles. Premedicate whenever possible (example: adenosine) Cannot treat poison-induced tachycardia |
|
|
Tachycardia |
Heart rate over 150 beats per minute |
|
|
Bradycardia |
Heart rate below 60 beats per minute |
|
|
Defibrillation |
First intervention for all cases of cardiac arrest Always combine w/ CPR |
|
|
Dopamine |
Second-line drug for symptomatic bradycardia (after atropine) Treats hypotension If treating hypotension, correct hypovolemia first before administration. NEVER mix with sodium bicarbonate. IV: rate is 2-20 micrograms/kg per minute. |
|
|
Hypotension |
Blood pressure below 70-100 mm Hg. |
|
|
Epinepherine |
Primary drug treatment for cardiac arrest. Can replace dopamine as 2nd line drug against bradycardia. Can treat severe hypotension should atropine fail or if hypotension accompanies cardiac arrest. IV: 1mg every 3-5 minutes during resuscitation Endotracheal: 2-2.5 mg in 10 ml water. |
|
|
Fibrinolytic Agents |
Can be used to treat AMI and ischemic stroke, though not tested enough to recommend regular use for cardiac arrest. Do not use if patient is bleeding, had recent surgery, or has uncontrollable hypertension. Avoid aspirin until 24 hours after administration of fibrinolytic agents. |
|
|
AMI |
Acute Myocardiac Infarction Medical term for "heart attack," when blood is blocked from reaching the heart. |
|
|
Lidocaine |
An alternative treatment to amiodarone for VT/VF cardiac failure. IV: initial dose of 1 to 1.5 mg/kg, followed by 0.5-0.75 mg every 5-10 minutes IF NECESSARY. Endotracheal: 2-4 mg/kg. |
|
|
Magnesium Sulfate |
Only recommended in cardiac arrest cases if torsades de points or suspected hypomagnesemia is present. (For Cardiac Arrest cases) IV: 1-2 g diluted in 10 ml of D5W IV/IO over 5-20 minutes. |
|
|
Torsades de Pointes |
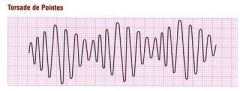
|
|
|
Morphine |
Painkiller: In this context, used for ACS-related chest pains. Also indicated by cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Use only if nitroglycerine fails. Countered by nalaxone. IV: 2-4 mg over 1-5 minutes every 5-30 minutes. |
|
|
Pulmonary Edema |
Condition when the lungs are filled with fluid. |
|
|
Nitroglycerine |
Initial response for suspected ischemic pains Also best for hypertensive emergencies with ACS Do not administer if patient has hypotension or either brady- or tachycardia, or if he's taken medicine for erectile dysfunction in the last 24 hrs. IV: Bolus of 12.5-25 ml. Begin at 10-20 micrograms/minute. Titrate to effect, 10 micrograms/minute until desired effect is reached. Tablets: 3 doses, one every 5-10 minutes. Spray: 3 doses, 1-2 sprays every 5 minutes. |
|
|
Oxygen |
Administer for any suspected cardiopulmonary emergencies, complaints of shortness of breath, and ACS patients. Delivered through a portable tank or device. |
|
|
Vasopressin |
An alternate choice to epinephrine for adult cardiac arrest patients. Not recommended for patients with coronary heart disease. IV: One 40 ml U IV/IO push; can replace either 1st or 2nd epinephrine dose. |

