![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are titrations (acid/base)?
|
Titrations can be used to determine an unknown concentration. A standard solution titrates the solution with the unknown concentration. Acid-base titrations use pH indicators to determine the endpoint of the reaction. An example is phenopthalein, which turns pink when the endpoint (or past the point) is reached.
|
|
|
What is a titration curve?
|
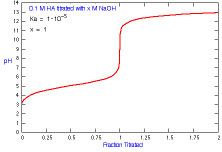
The titration curve is used to graph a titration. There are four basic points of a titration curve: pH of initial solution, pH before the reaction reaches the equivalence point, pH at equivalence point, and pH after equivalence point. The equivalence point is when the solution (usually an acid) is neutralized by what it is titrationg (usually a base). If it is a strong base and strong acid, the equivalence point is 7.00 at 25 degrees C.
|
|
|
What is Ksp?
|
The Ksp is a prediction of solubility of substances under specific conditions. Ksp is known as the solubility product constant. This value estimation is determined by the concentration of the anion or cation when the compound is dissolved. Ksp values are also used to predict solubility of solid salts or to determine if a solid will precipitate when the solutions of cation and anion are mixed.
|
|
|
What is the common ion effect?
|

This limits an acid inoization by adding of its conjugate base or limits a base ionization by adding its conjugate acid. According to le Chatelier's Principle when a stress is placed on a system in equilibrium, the system tries to reduce the stress. For example, the reaction NaCl <---> Na(+) + Cl(-), the addition of concentrated HCl adds H(+) and Cl(-). This increases the concentration of the Cl(-) and disturbs the equilibrium. The reaction will then shift to the left and cause some solid NaCl to come out of solution.
|
|
|
What is a buffer?
|
A buffer resists changes in pH when a strong acid or base is being added. There are two necesities: and acid that is able to react with added OH(-) ions and a base that can consume added H3O(+) ions, and the acid and base cannot react with each other. A buffer is typically prepared with a weak base and its conjugate acid, or a weak acid and its conjugate base. Henderson-Hasselbach quations is a way to find the pH of buffer solutions.
|
|
|
pH indicators
|
An acid-base indicator is usually made up of an organic compound that is usualy a weak acid or base. Common indicators are thymol blue (red to yellow), methyl red(orange to yellow), bromcresol purple(yellow to purple), and phenolphthalein(white to pink). Indictaors help deteremine the end points of acid-base titrations.
|
|
|
What are the different types of acids?
|
A Bronsted-Lowry acid dontes a proton. A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. Strong acids include HClO4, HI, HBr, HCl, H2SO4, and HNO3. Strong acids ionize completely in aqueous solutions. Weak acids do not dissociate completely. Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group.
|
|
|
What are the different types of bases?
|
A Bronsted-Lowry base are proton acceptors. A Lewis base is a electron pair donator. Strong bases are hydroxides of alkali metals and alkali earth metals: NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, and more.
|
|
|
What is Kb?
|
Kb is the quilibirum expression for a weak base. Strong bases have larger Kb values, and weaker bases have smaller values. The weaker the acid, the stronger the conjugate base, and a larger Kb value. The value is less than 1 for weak bases.
|
|
|
What is Ka and pKa?
|
Ka is the equilibrium constant for the ionization of an acid in a aqueous solution. pKa is = -log(Ka). Large values of K product-favored, and small vaules is reactant-favored. Stronger acids of large Ka values. Weaker acids, have stronger conjugate bases.
|
|
|
What are polyprotic acids and bases?
|
A polyprotic acid is able to donate two or more protons. They are also referred to as diprotic(2 protons), triprotic (3protons), etc. A polyprotic base accepts more than one proton. Examples includ SO4(2-), PO4(3-), CO3(2-), and C2O4(2-). Titrations of polyprotic acids (diprotic) experience two significant raises in pH.
|
|
|
Types of acid-base reactions
|
Strong acid and strong base net ionic equtions is always the hydronium ion and hydroxide ion giving water. The solution is neutral with pH = 7 at 25 degrees C. A weak acid and strong base form a basic solution, with the pH depending on the Kb value of the anion. A strong acid and weak base form a acidic solution with a pH depending on the Ka value of the cation. A weak acid and weak base produces a salt, the cation is the conjugate acid of the weak base and the anion is the conjugate base of the weak acid. The pH depeds on the Ka and Kb values.
|
|
|
Amphoteric
|
Amphoteric substances can act as acids or bases. One example is water: as a base H2O + HCl → H3O(+) + Cl(−), and as an acid H2O + NH3 → NH4(+) + OH(−). Some metal hydroxides can act as acids or bases. In strong acidic situations they are bases, and in strong basic situations they are acids. An example: in acid ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O, and in base ZnO + 2NaOH + H2O → Na2(2+)[Zn(OH)4](2-).
|
|
|
Equations
|
In buffers: [H30(+)] = [acid]/[conjugate base] x Ka.
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = pKa + log[cojugate base]/[acid] Titrations: [H30(+)] = [weak aicd remaining]/[conjugate base produced] x Ka or pH = pKa + log[cojugate base produced]/[weak acid remaining] At halfway point of titration of weak acid/strong base [H30(+)] = Ka and pH = pKa |
|
|
What are the effects of basic anion on salt solubility?
|
Any salt that has an anion that is the conjugate base of a weak acid, then it will dissolve in water at a greater extent than given Ksp. Also insoluble salts in which the anion is the conjugate base fo a weak acid dissolves in strong acids. Examples: acetate, carbonate, hydroxide, phosphate, and sulfide.
|
|
|
Reaction Quotient (Q) and Ksp
|
If Ksp = Q, then the solution is saturated at equilibrium.
If Ksp > Q, then the solution is not saturated at equilibrium. If Ksp < Q, then the solution is supersaturated and not at equilibrium. |

