![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anion gap |
Sodium - (Cl and HCO3) Normal is 8 to 15 |
|
|
Main site of renal bicarbonate reabsorption? |
Proximal tubule |
|
|
Main site of renal hydrogen secretion? |
Collecting duct intercalated cell H-K ATPase and H ATPase |
|
|
Main buffers to H+ |
Ammonium Phosphate |
|
|
Causes of a lower anion gap |
Low albumin. Correct .25 x alb g/L Myeloma |
|
|
Urine anion gap |
Na + K - Cl Unmeasured cation ammonium |
|
|
What is cause of negative urine anion gap? |
GI losses Proximal RTA (type 2) |
|
|
What is cause of positive urine anion gap? |
Renal tubular acidosis: Type 1 distal or Type 4 |
|
|
What is urine osmolar gap |
Use in normal anion gap metabolic acidosis where urine anion gap unreliable (Urine pH>6.5 or Na <20)
=Calculated Uosm - measured Uosm
Calculated: 2 (Na+K) + urea + glucose If >40 indicates intact ammonium excretion in acidosis |
|
|
Explain the 3 types of RTA |
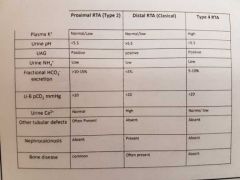
Type 1 distal Decreased H+ secretion. K+ excreted instead so hypoK Urine pH>5.5 (Serum most acidotic) Renal calculi (hypercalciuria) Causes include sjogrens, amphoteracin, PPi
Type 2 proximal Failure of HCO3 reabsorption Urine pH <5.5 (serum acidosis milder) Often assoc with generalised prox tubule disorder Fanconi syndrome
Type 4 affects aldosterone Aldo deficiency or resistance Less Na reabsorption so lumen less negative. Can't secrete H+. Hyperkalaemia Urine pH can <5.5 Commonest cause diabetic nephropathy, NSAIDs, ACE/ARB. |
|
|
RTA with urine pH>5.5? |
Distal type 1 Maybe type 4 but they can get it <5.5 |
|
|
RTA with hypokalaemia? |
Distal type 1 |
|
|
RTA with hyperkalaemia? |
Type 4 |
|
|
Confirmatory tests in RTA |
Type 1 ammonium chloride - fails to acidify urine Type 2 fractional excretion of bicarb >25% |
|
|
Treatments of RTA |
Type 2 lots of bicarb Type 4 restrict dietary sodium. Fruse. |
|
|
Raised anion gap metabolic acidosis |
Methanol Uraemia DKA Paraldehyde Isoniazid Lactic acidosis Ethanol/ Ethylene glycol Rhabdo/ Renal failure Salicylates Also carbon monoxide, aminoglycosides |
|
|
Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis |
Hyperalimentation Acetazolamide Renal tubular acidosis Diarrhoea Uretero-pelvic shunt Post-hypocapnia Spironolactone |

