![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is diascopy?
|
hold plate glass to lesion to determine if it blanches. This will assist determining if the lesion is vascularized
|
|
|
When should a patient have a complete head and neck examination?
|
Initial visit and every recall visit (6 months). If the patient is at high risk for something like oral cancer, then the complete exam should be done at every visit.
|
|
|
What is pallor?
|
Paleness
|
|
|
When should you make a progress note in the charts?
|
Each time a patient is seen or a conversation the the patient or health provider
|
|
|
What are different examination techniques?
|
1. Visual Inspection
2. Diascopy 3. Palpation 4. Probing 5. Percussion 6. Auscultation 7. Aspiration 8. Evaluation of Function |
|
|
What should you look for during your visual inspection?
|
1. Symmetry
2. Color 3. Consistency 4. Size, shape, swelling, deformity 5. Opening 6. Lesions 7. Superficial vascularity 8. Edema 9. Moistness of skin 10. Characteristics of hair/nails 11. Make sure you inspect whole neck (fold down the collar) |
|
|
What are you feeling for when palpating a structure like lymph nodes?
|
1. Texture
2. Dimension 3. Consistency 4. Temperature 5. Function |
|
|
What is rebound, when palpating for tenderness?
|
When you press on the area, it doesn't cause the patient any pain; when you remove the pressure they feel pain due to the tissue rebounding and impinging on nerves.
|
|
|
Why should you always aspirate before you inject local anesthetic?
|
To assure that you are not injecting into a blood vessel.
|
|
|
What are Rhonchi when auscultating for breathing sounds?
|
Deeper rumbling sounds
|
|
|
What are Rales when auscultating for breathing sounds?
|
Gargly sounds; crackles on inspiration.
|
|
|
What are wheezes when auscultating for breathing sounds?
|
Squeeky whistles, usually on inspiration. Asthma
|
|
|
T/F
Aspiration may include olfaction to detect odors that indicate metabolic/endocrine disease. |
True
|
|
|
What are vital signs?
|
1. Temperature
2. Respiration 3. Blood Pressure 4. Pulse |
|
|
What are the baseline indicators of health status?
|
1. Respiration
2. Blood Pressure 3. Pulse |
|
|
What is normal temperature range in healthy individuals?
|
98.6-99.4 F
|
|
|
What are some conditions that could increase body temperature?
|
1. Exercise
2. Infection 3. Ovulation 4. Inflammatory disorders 5. Hyperthyroidism (due to metabolism increase) |
|
|
What are some conditions that could decrease body temperature?
|
1. Anemia
2. Alcoholism 3. Chronic debilitating disease 4. Hypothyroidism |
|
|
What are the normal respiratory rates?****
|
16-20/min Adults
24-28/min children 44/min infants |
|
|
What is the term for increased rate and decreased depth of breathing?
|
Tachypnea
|
|
|
What is the term for increased rate and depth (hyperventilation)?
|
Hyperpnea
|
|
|
What is the term for hyperpnea with periods of apnea, typical of profound toxic states?
|
Cheyne-Stokes
|
|
|
What are the normal pulse rates?***
|
60-90 bpm adults
90-120 bpm children |
|
|
in patients over 50 which BP number is most important to be aware of?
|
Systolic BP
|
|
|
When you determine BP categorization, which component is used to determine the classification (sys/dias)?
|
By the most elevated value
|
|
|
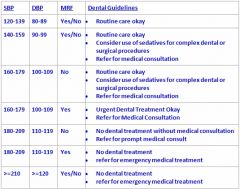
What is the range for Stage 1 Hypertension?
|
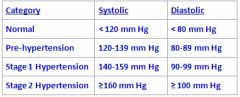
see above
|
|
|
What is the range for stage 2 hypertension?
|
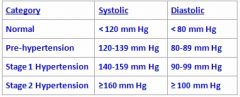
See Above
|
|
|
What category is an individual who has 129/90 BP?
|
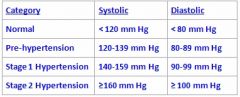
Stage 1 hypertension
Classified based upon diastolic BP |
|
|
What category does a patient fall into with a blood pressure of 138/88?
|
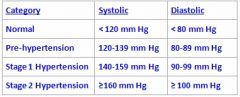
Pre-hypertensive
|
|
|
What category does a patient fall into who has a blood pressure of 140/100
|
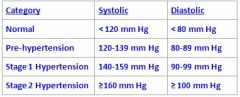
Stage 2 Hypertension
|
|
|
Up to what blood pressure range is routine dental care okay?
|
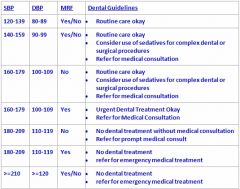
179/109 with NO MRF
(although 140/90 you should consider use of sedatives for complex dental procedures and refer for medical consultation) |
|
|
What is the blood pressure range and MRF for Urgent dental treatment only?
|
160-179/100-109 With MRF
|
|
|
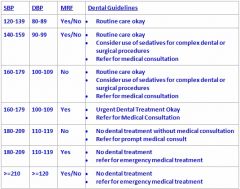
T/F
You may not treat any dental conditions without medical consultation with a BP of 180/110 and NO MRF |
True
|
|
|
May a patient with a BP of 160/110 be treated?
|
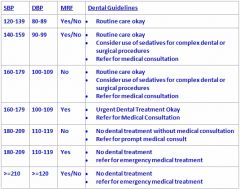
Not without a medical consultation if there are NO MRF, also refer for PROMPT medical treatment.
If patient has MRF then NO dental treatment and refer EMT. |
|
|
What is BP range for NO dental treatment and refer for EMT regardless of MRF?
|
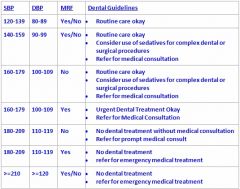
≥ 210/120
|
|
|
If someone has a BP of 143/99 and has MRF how should the patient be handled?
|
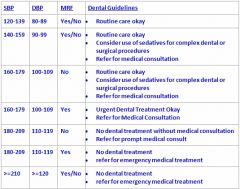
Routine care okay
Sedatives for big procedures Refer for medical consult |
|
|
What is the highest BP a patient may have for routine treatment?
|
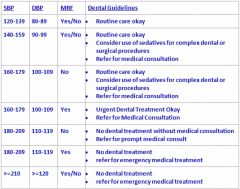
179/109 with no MRF
note: at this high sedatives for complex procedures and refer for medical consult |
|
|
What is the highest BP a patient can have in order to be treated WITHOUT a medical consult?
|
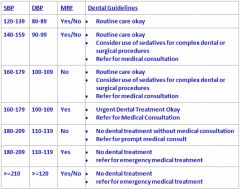
179/109 with MRF
note: this high is only for urgent dental treatment |
|
|
How high can a patients BP be before referring for medical consult or altering treatment?
|
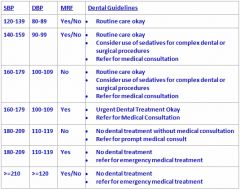
139/89 and it doesn't matter whether or not they have MRF
|
|
|
What is the difference between someone who has MRF or not with a BP of 180/110?
|
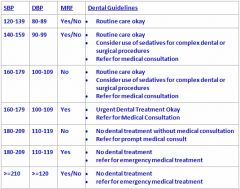
No MRF = no treatment w/o med consult & refer for Prompt med consult
Yes MRF = No treatment and refer to EMT |
|
|
How should we treat a patient who has a BP of 160/100 with no MRF?
|
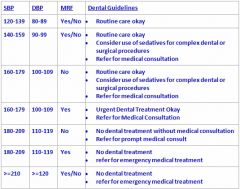
Routine care okay
sedatives for complex procedures refer for medical consult |

