![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Job Costing
|
Goods are produced "to order." Units of product are differentiated; that is you can tell the difference between them by looking at them.
EX: consulting assignments and custom-built homes |
|
|
Process Costing
|
Undifferentiated, mass-produced goods.
EX. computer disks or blank video tapes |
|
|
Hybrid System
|
Combination of job and process costing. In a hybrid system, a "basic unit" might be mass produced, but then customized based on a client's order.
|
|
|
Forms Used in Manufacturing
|
1. Materials Requisition
2. Job Cost Sheet 3. Labor Time Ticker 4. Production Cost Report 5. Materials Move Ticket |
|
|
Materials Requisition
|
Purpose- Requests material from the warehouse for production.
Originator- Production Recipient- Warehouse |
|
|
Job Cost Sheet
|
Purpose- Summarizes the material, labor, and overhead costs in a job costing system.
Originator- Production Recipient- Accounting |
|
|
Labor Time Ticket
|
Purpose- Accumulates labor data (time, pay rate, total labor cost)
Originator- Production Recipient- Accounting |
|
|
Production Cost Report
|
Purpose-Summarizes cost and quantity information in a process costing system.
Originator- Production Recipient- Accounting |
|
|
Materials Move Ticket
|
Purpose- Documents the movement of materials from the warehouse into production.
Originator- Warehouse Recipient- Production |
|
|
Conversion Process
|
The process of combining raw materials, labor, and overhead in the production of finished goods.
|
|
|
Financing Process
|
The process of acquiring external funding, most commonly through debt or equity.
|
|
|
Risk: Stolen Equipment
Control: ??? |
Control- Engraved Identification, Recorded serial numbers,
|
|
|
Risk: Malfunctioning Equipment
Control: ??? |
Control: Backup equipment, Regular periodic testing
|
|
|
Risk: Bad weather contributing to poor output
Control: ??? |
Control: Production insurance, Extra lighting for cloudy days
|
|
|
Risk: Software Malfunction
Control: ??? |
Control: Backup Software
|
|
|
Financing Process Transactions
|
Issuance of capital stock, purchase of treasury shares, issuance and repayment of long-term debt, and dividend distributions.
|
|
|
Human Resource Process
|
Associated with personel activities in an organization, from the time of hiring to the time of discharge via retirement, termination, or quitting.
|
|
|
Application Service Providers(ASP)
|
Organizations that provide services on an as-needed basis to their clients.
EX: Quickbooks |
|
|
ASP(webopedia.com) definition
|
Defines an application service provider as "a third party entity that manages and distributes software-based services and solutions to customers across a wide area network from a central data center. They are a way for companies to outsource some or almost all aspects of their information technology needs.
|
|
|
ASP Benefits
|
1. Less costly than purchasing software outright.
2. Offer organizations more flexibility than purchasing outright. Software is a long term commitment where ASP can be short term. 3. ASP model of doing business might make them more accountable to customer because at the end of subscription a vendor will fight to keep you subscribed. 4. Disaster recovery plans. Information system are offsite. |
|
|
ASP Costs
|
1. Long term costs, if an organization decides to stay with a software for a long time, purchasing maybe better in the long term.
2. Managers may be less comfortable with the idea that their data isn't actually in their "possession." |
|
|
Certificate
|
Endorsed authoritatively as having met certain requirements. essentially the process of publicly attesting that a specified quality or standard has been achieved or exceeded.
EX: Certified Public Accountant |
|
|
License
|
A legal document giving official permission to do something. non-voluntary process by which an agency of government regulates a profession. It grants permission to an individual to engage in an occupation if it finds that the applicant has attained the degree of competency required to ensure the public health, safety, and welfare will be reasonably protected.
|
|
|
Certified Management Accountant(CMA)
|
Sponsored by the Institute of Management Accountants. Four part online exam: (i)Business Analysis, (ii)Management accounting and reporting, (iii)strategic management, (iv)business applications. Becoming one is a three part process: education, examination, experience.
|
|
|
Certified Fraud Examiner(CFE)
|
Sponsored by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners. Four part online exam: (i)Criminology and ethics, (ii)Financial transactions, (iii)Fraud investigation, and (iv)Legal elements of fraud. Solely dedicated to fighting fraud. Becoming one is a three part process: education, examination, experience.
|
|
|
Certified Internal Auditor(CIA)
|
Sponsored by Institute of Internal Auditors, Four part, in person exam: (i)Internal audit activity's role in governance, risk, and control, (ii)conducting the internal audit engagement, (iii)business analysis and information technology, and (iv)business management skills.
|
|
|
Application Service Providers(ASP)
|
Organizations that provide services on an as-needed basis to their clients.
EX: Quickbooks |
|
|
ASP(webopedia.com) definition
|
Defines an application service provider as "a third party entity that manages and distributes software-based services and solutions to customers across a wide area network from a central data center. They are a way for companies to outsource some or almost all aspects of their information technology needs.
|
|
|
ASP Benefits
|
(i)Often less expensive than purchasing software outright
(ii)More flexibility (iii)Potential for making vendors more accountable (iv)Role in disaster recovery plans |
|
|
ASP Costs
|
(i)Monetary costs
(ii)Psychological and behavioral factors (e.g., mistrust and worry) (iii)Unique internal control issues |
|
|
Certificate
|
Endorsed authoritatively as having met certain requirements. essentially the process of publicly attesting that a specified quality or standard has been achieved or exceeded.
EX: Certified Public Accountant |
|
|
License
|
A legal document giving official permission to do something. non-voluntary process by which an agency of government regulates a profession. It grants permission to an individual to engage in an occupation if it finds that the applicant has attained the degree of competency required to ensure the public health, safety, and welfare will be reasonably protected.
|
|
|
Certified Public Accountant
|
Must pass the Uniform Certified Public Accountant Examination, which is set by American Institute of Certified Public Accountants,
|
|
|
Certified Management Accountant(CMA)
|
Sponsored by the Institute of Management Accountants. Four part online exam: (i)Business Analysis, (ii)Management accounting and reporting, (iii)strategic management, (iv)business applications. Becoming one is a three part process: education, examination, experience.
|
|
|
Certified Fraud Examiner(CFE)
|
Sponsored by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners. Four part online exam: (i)Criminology and ethics, (ii)Financial transactions, (iii)Fraud investigation, and (iv)Legal elements of fraud. Solely dedicated to fighting fraud. Becoming one is a three part process: education, examination, experience.
|
|
|
Certified Internal Auditor(CIA)
|
Sponsored by Institute of Internal Auditors, Four part, in person exam: (i)Internal audit activity's role in governance, risk, and control, (ii)conducting the internal audit engagement, (iii)business analysis and information technology, and (iv)business management skills.
|
|
|
Certified Information Systems Auditor(CISA)
|
Sponsored by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Seven-part, in-person exam: (i)IS audit process, (ii)Management, planning and organization of IS, (iii)Technical infrastructure and operational practices, (iv)Protection of information assets, (v)Disaster recovery and business continuity, (vi)Systems development life cycle,
(vii)Business process evaluation and risk management |
|
|
Career Planning Steps
|
(i)Determine your strengths, aptitudes and abilities, (ii)Create a career mission statement, (iii)Research related employment opportunities, (iv)Build your resume, (v)Practice your interviewing skills
|
|
|
Risks and Threats to Information Systems Part 1
|
1. Fraud
2. Service Interruptions and Delays 3. Intrusions 4. Information Manipulation |
|
|
Fraud(Risks and Threats Part 1)
|
Any illegal act for which knowledge of computer technology is used to commit the offense
|
|
|
Service Interruptions and Delays(Risks and Threats Part 1)
|
Delay in processing information
|
|
|
Intrusions (Risks and Threats Part 1)
|
Bypassing security controls or exploiting a lack of adequate controls
|
|
|
Information Manipulation (Risks and Threats Part 1)
|
Can occur at virtually any stage of information processing from input to output
|
|
|
Carter's Taxonomy
|
1. Target
2. Instrumentality 3. Incidental 4. Associated |
|
|
Target(Carter's Taxonomy)
|
Targets the system or its data
|
|
|
Instrumentality(Carter's Taxonomy)
|
Computer furthers a criminal end
|
|
|
Incidental(Carter's Taxonomy)
|
Computer is not required for the crime but is related to the criminal act
|
|
|
Associated(Carter's Taxonomy)
|
New versions of traditional crimes
|
|
|
Risks and Threats to Information Systems Part 2
|
1. Denial of Service Attacks
2. Error 3. Disclosure of Confidential Information 4. Information Theft |
|
|
Denial of Service Attacks(Risks and Threats 2)
|
Prevent computer systems and networks from functioning in accordance with their intended purpose
|
|
|
Error(Risks and Threats 2)
|
Can vary widely
|
|
|
Disclosure of Confidential Information(Risks and Threats 2)
|
Can have major impacts on an organization's financial health
|
|
|
Information Theft(Risks and Threats 2)
|
Targets the organization's most precious asset: information
|
|
|
Risks and Threats to Information Systems(Part 3)
|
1. Malicious Software
2. Web Defacements 3. Extortion |
|
|
Malicious Software(Risks and Threats Part 3)
|
Virus, Trojan horse, worms, logic bombs
|
|
|
Defacements(Risks and Threats Part 3)
|
Digital graffiti where intruders modify pages
|
|
|
Extortion(Risks and Threats Part 3)
|
Threat to either reveal information to the public or to launch a prolonged denial of service if demands are not met
|
|
|
Computer Criminals
|
1. Script Kiddies
2. Hacker 3. Cyber-Criminls 4. Organized Crime 5. Corporate Spies 6. Terrorist 7. Insiders |
|
|
Script Kiddies(Computer Criminals)
|
Young inexperienced hacker who uses tools and scripts written by others for the purpose of attacking systems
|
|
|
Hacker(Computer Criminals)
|
Someone who invades an information system for malicious purposes
|
|
|
Cyber-Criminls(Computer Criminals)
|
Hackers driven by financial gain
|
|
|
Organized Crime(Computer Criminals)
|
Spamming, phishing, extortion and all other profitable branches of computer crime
|
|
|
Corporate Spies(Computer Criminals)
|
Computer intrusion techniques to gather information
|
|
|
Terrorist(Computer Criminals)
|
Target the underlying computers and networks of a nation’s critical infrastructure
|
|
|
Insiders(Computer Criminals)
|
May be the largest threat to a company’s information systems and underlying computer infrastructure
|
|
|
Prevention and Detection Techniques
|
CIA triad and Internal controls
|
|
|
CIA Triad(Prevention and Detection Techniques)
|
Confidentiality
Data integrity Availability |
|
|
Internal Controls(Prevention and Detection Techniques)
|
(i)Physical: locks, security guards, badges, alarms
(ii)Technical: firewalls, intrusion detection, access controls, cryptography (iii)Administrative: security policy, training, reviews |
|
|
COBIT Framework(Part 1)
|
(i)Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology
(ii)Published by Information Systems Audit and Control Association (iii)Three points of view: -Business objectives -IT resources -IT processes |
|
|
COBIT Framework(Part 2) Four Domains of Knowledge
|
(i)Plan and organize
(ii)Acquire and implement (iii)Deliver and support (iv)Monitor and evaluate |
|
|
COBIT Framework(Part 3) 7 Information Criteria
|
(i)Effectiveness
(ii)Efficiency (iii)Confidentiality (iv)Integrity (v)Availability (vi)Compliance (vii)Reliability of information |
|
|
COBIT(Accountability Framework) Figure 14.3
|
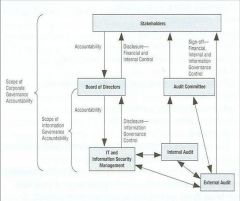
|
|
|
How organizations convert resources into salable products and services?
|
Resources:
Direct material- major components of the finished product Direct labor- salaries, wages and benefits of production personnel Factory overhead- everything else in the production operation |
|
|
Chiefly applicable to manufacturing, but can be applied to service and retail as well?
|
Systems:
Job order- goods are differentiated; produced “to order” Process- goods are homogeneous; produced in mass quantities Hybrid- characteristics of both systems; for example, a standard unit is customized |
|
|
Financing Process
|
-Transactions with stockholders and with long-term creditors
-Results seen most clearly in long-term debt and equity sections of balance sheet and financing cash flows on statement of cash flows |
|
|
Financing Process(Common Transactions) Part 1
|
1)Issuance of capital stock- Data needed: number of shares, par value per share, market value per share, stockholder identification data
2) Purchase of treasury shares- Data needed: number of shares, price per share, shareholder identification data |
|
|
Financing Process(Common Transactions) Part 2
|
3)Long-term debt transactions- (issuance and repayment)
Data needed: principal, coupon and market interest rates, term, number of interest payments per year, lender data 4) Dividend distributions- Data needed: dividend type (cash, stock, property), shareholder identification data, amount of dividend, dates (declaration, record, distribution) |
|
|
Human Resource Process
|
Activities associated with employees:
(i)Hiring (ii)Paying (iii)Coordinating benefits (iv)Evaluating performance (v)Terminating |
|
|
Payroll Forms(Part 1)
|
(i)Form W-4: establishes payroll withholding status
(ii)Form W-2: reports year-end tax information (iii)Payroll register: computations for a single pay period |
|
|
Payroll Forms(Part 2)
|
(i)Employee earnings record: computations for one employee across pay periods
(ii)Form 1099: independent contractor compensation (iii)Form 940: federal unemployment taxes (iv)Form 941: withholding transmittal |
|
|
Process Review(Part 1)
|
1.Human resources: concerned with people
2.Financing: concerned with money 3.Acquisition / payment: concerned with other resources (inventory, for example) |
|
|
Process Review(Part 2)
|
4.Conversion: manufacturing products / services using people, money and other assets
5.Sales / collection: selling products / services to clients and collecting payment |
|
|
Five Characteristics for Internet ASPs:
|
1.They own and operate a software application
2.They own, operate and maintain the servers that run the application 3. They also employ the people needed to maintain the application 4. They make the application available to customers everywhere via the Internet, either in a browser or through some sort of “thin client” 5. They bill for the application either on a per-use basis or on a monthly / annual fee basis |
|
|
ASP Examples
|
(i)Job applicant tracking
(ii)Stock trading (iii)Personal financial planning (iv)Tax preparation (v)General ledger software (vi)Enterprise resource planning systems (vii)Web hosting |
|
|
Cost-Benefit Analysis(Part 1)
|
1.Examine needs, consider constraints, and formulate objectives and targets
2.Define options in a way that enables the analyst to compare them fairly 3.Analyze incremental effects and gather data about costs and benefits 4.Express the cost and benefit data in a valid standard unit of measurement |
|
|
Cost-Benefit Analysis(Part 2)
|
5.See what the deterministic estimate of net present value (NPV) is
6.Conduct a sensitivity analysis to determine which variables appear to have the most influence on the NPV 7.Analyze risk by using what is known about the ranges and probabilities of the costs and benefits values and by simulating expected outcomes of the investment 8.Considering all of the quantitative analysis, as well as the qualitative analysis of factors that cannot be expressed in dollars, make a reasoned recommendation |
|
|
Risk and Controls
|
1.Liquidity risk: inability to pay the ASP
Control: establish a budget 2.Systems risk: ASP service interruption Control: daily backup of ASP data locally 3.Human error risk: mistakes in using the software Control: training 4. Legal and regulatory risk: computer hacking Control: firewalls and encryption 5. Business strategy risk: collecting too little information, irrelevant information Control: personnel involvement |

