![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cost Behavior Analysis |
The study about how specific costs respond to changes in business activity |
|
|
Fixed and Variable Costs With Activity Level |
Variable- Changes with activity level Fixed-Stay the same regardless |
|
|
Relevant Range |
Range of activity which a company expects to operate during a year |
|
|
Mixed Costs |
Have variable and fixed costs |
|
|
Variable Costs |
With change |
|
|
Fixed Costs |
Always there |
|
|
Contribution Margin Per Unit |
Unit Selling Price/Unit Variable Costs |
|
|
Contribution Margin Ratio |
CM/Sales |
|
|
Breakeven analysis: Mathematical Equation |
Sales=Variable Costs +Fixed Costs+Net Income or Fixed Costs/contribution margin then Fixed/cmr
|
|
|
Contribution Margin Technique |
Fixed Costs/CM |
|
|
Break-even can be calculated from... |
Mathematical Equation Contribution Margin CVP graph |
|
|
CVP Graph |
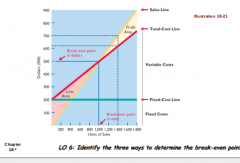
|
|
|
Target Net Income |
Indicates sales necessary for a certain income
Calculate using cost volume profit analysis:
E sales x e cm - fixed costs |
|
|
Margin of safety |
Actual Sales-Break-even sales |
|
|
Margin of safety ratio |
Formula:Actual Sales (in dollars)/Actual Expected Sales |
|
|
Weighted Average Contribution Margin |
Sum of weighted contribution margin of each product |
|
|
Sales Mix |
Relative percentage in which a company sells its products |
|
|
Operating Leverage |
Extent to which net income reacts to a given change in sales
CM/Net Income |
|
|
Cost Structure |
Variable vs fixed costs in a company |
|
|
Benefits of budgeting |
plan ahead definite objectives early warning system coordination of activities greater management awareness motivates personnel |
|
|
Budgeting Process |

|
|
|
Cash Budget |

|
|
|
Cash Receipts |
principle sources of revenue |
|
|
Cash Disbursements |
expected cash payments |
|
|
Financing Section |
Expected borrowing and repayments |
|
|
Service Companies budget |

|
|
|
Master Budget |
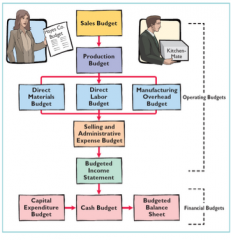
|
|
|
Differences between long term and short term budgeting |
Time Period involved Emphasis Detail Presented |
|
|
Sales Budget |
expected Sales * Selling Price |
|
|
Production Budget |

Note desired is percentage of next expected unit sales |
|
|
Direct Materials Budget |

Note same as last |
|
|
Direct Labor Budget |
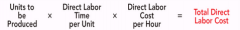
|
|
|
Weighted Contribution |
Take both number and x by percent it takes and add |

