![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Accounting |
An information and measurement system that identifies, records, and communicates relevant, reliable, and comparable information about an organization's business activities. |
|
|
Accounting equation |
The relation of assets, liabilities, and equity; Assets = Liabilities + Equity |
|
|
Assets |
Resources a company owns or controls, expected to yield future benefits. |
|
|
Audit |
Examination of whether financial statements are prepared using GAAP. It does not attest to absolute accuracy of statements. |
|
|
Auditors |
Examine financial statements to verify that they are prepared according to GAAP; must also verify the effectiveness of internal controls. |
|
|
Balance sheet |
Financial statement that describes a company's financial position at a point in time; shows types and amounts of assets, liabilities, and equity. |
|
|
Bookkeeping |
Also recordkeeping; the recording of transactions and events, either manually or electronically; 2nd step of accounting (1st is identifying, 3rd is communicating) |
|
|
Common stock |
Also capital stock; ownership units of a corporation; part of contributed capital, reflects inflows of resources such as cash and other net assets from stockholders in exchange for stock. |
|
|
Conceptual framework |
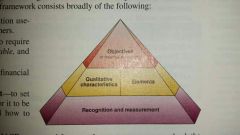
Guides standard-setting of accounting principles; consists of objectives, qualitative characteristics, elements, and recognition and measurement; FASB and IASB attempting to converge and enhance. |
|
|
Contributed capital |
Refers to amount that stockholders invest in a company; part of the equity portion of accounting equation. |
|
|
Corporation |
A business legally separate from its owner or owners; it is responsible for its own acts and debts. |
|
|
Cost-benefit constraint |
Constraint on financial reporting that prescribes that only information with benefits of disclosure greater than the costs of providing it need be disclosed. |
|
|
Dividends |
The outflow of resources such as cash and other assets to stockholders; reduces equity. |
|
|
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act |
1. Promote accountability and transparency in the financial system; 2. Put an end to the notion of "too big to fail"; 3. Protect the taxpayer by ending bailouts; 4. Protect consumers from abusive financial services. |
|
|
Equity |
The owner's claim on assets; is equal to assets minus liabilities; also called net assets or residual equity; consists of contributed capital plus retained earnings. |
|
|
Ethics |
Beliefs that distinguish right from wrong; accepted standards of good and bad behavior. |
|
|
Events |
Refer to happenings that affect the accounting equation and are reliably measured. |
|
|
Expanded accounting equation |
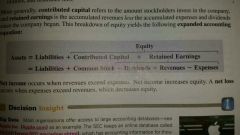
Accounting equation with equity broken into its parts; Assets = Liabilities + Common Stock - Dividends + Revenues - Expenses |
|
|
Expenses |
Decreases equity from costs of providing products and services to customers; one component of net income. |
|
|
External transactions |
Exchanges of value between two entities, which yield changes in the accounting equation. |

