![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
1define Sacroiliitis?
2What is SI associated with? 3Tx? |
1chronic inflammation of SI joints can lead to fibrosis & ossification within SI joint 2- HLA-B27, neg rheumatoid factor, Reiter's syndrome & ankylosing spodyliitis 3 most resolve with soft tissue rest and activity modification
|
|
1.end of spinal shock indicated by return of?
2. conus or cauda equina injuries may lead to permanent loss of 3.All trauma patients have what? |
1.the bulbocavernous reflex
2 the bulbocavernous reflex 3. cervical spine injury until proven otherwise |
|
|
what level is quadraplegia?
what level is paraplegia? |
quad C4--C6 no motor function UE
para T6-L1 no motor function LE |
|
17yo football player has injury 90 min ago. in ER; he is alert oriented, PE (+) tenderness pos midline C-spine; intact sensation in UE & LE. motor exam motion - arms & legs, but is unable to lift his legs/arms against gravity. His bulbocavernosus reflex is absent. The decision is made to initiate methylprednisolone. What is dosage and duration?
|
1-30 mg/kg bolus then 5.4 mg/kg/hr infus x 8 hrs; 2-30 mg/kg bolus then 5.4 mg/kg/hr infus x 24 hrs; 3-60 mg/kg bolus then 5.4 mg/kg/hr infus x 8 hrs
4-60 mg/kg bolus then 5.4 mg/kg/hr infus x 24 hrs 5-60 mg/kg bolus then 5.4 mg/kg/hr infus x 28 hrs::: 24-hr dose of MPSS when administered< 3 hrs of injury; 48-hr dose when administered 3> injury < 8 hrs p/injury.Ans2 |
|
describe ASIA (am spinal inj assoc)
define incomplete injury syndrome? |
5 categories, w/5 clinical synd=ASIA A- complete
ASIA E-nl; ASIA B- incomplete: Sensory but NO motor function is preserved below the neurological level, includes the sacral segments S4-S5 ASAI C- incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurological level, and > 1/2 of key muscles below the neurological level have a muscle grade < 3 strength;ASIA D - incomplete:= Motor function is preserved below the neurological level, and at least half of key muscles below the neurological level have a muscle grade of 3 or > strength. central cord S; Brown-Sequard S-same side no motor & contralat-pain temp 1-2 below; ant cord S; conus medullaris compression S; cauda equina compression S- |
|
All of the following are attributed to the loss of supraspinal control of the sympathetic nervous system that commonly occurs in pts w/ SCI @ T-6 or > EXCEPT, 1-Supine hypotension; 2-Orthostatic hypotension; 3-Spasticity; 4-Autonomic dysreflexia
5-Cardiac arrhythmias |
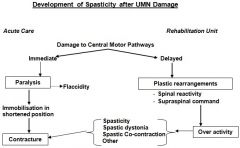
Spasticity is unrelated to the sympathetic system and usually occurs after the acute phase (SCI), when spinal shock has resolved. Hypotension (supine and orthostatic), cardiac arrythmias, autonomic dysreflexia (AD) = loss of supraspinal control of the sympathetic nervous system. AD = “an inc in systolic BP > 20% w/ a change in HR plus one signs (sweating, piloerection, facial flushing), or symptoms (headache, blurred vision, stuffy nose)” due to overdistended bladder or bowel impaction.
|
|

16 yo M s/p diving accident 6 mths ago that leads to a SCI. On PE = 5/5 deltoid & biceps strength. He has good brachioradialis muscle tone, 5/5 b/l wrist ext. 0/5 wrist flex and triceps strength. He has no anal sphincter tone, absent perianal sensation, absent LE sensation, and an intact bulbocavernosus reflex. He has no motor tone in his LE. define this pts neurologic deficit.
|
1-Incomp C5 SCI (ASIA A); 2-Comp C5 SCI (ASIA E)
3-Comp C6 SCI (ASIA A); 4-Comp C7 SCI (ASIA A) 5-Incomp C7 SCI (ASIA B)::: 3 steps ASIA classif= Step 1: Identify the neurologic level, lowest segment where motor & sensory is nl b/l. B/c this pt has nl function at C6 (brachioradialis and wrist extension), and no function at C7 (triceps and wrist flexion), his last nl functional level is C6. Therefore his neurologic level is C6. Step 2: Determine if injury is complete or incomplete. Complete injuries are defined as 1-no voluntary anal contraction (sacral sparing) AND2- 0/5 distal motor AND 3- 0/2 distal sensory scores (no perianal sensation) AND 4-intact bulbocavernosus reflex (patient not in spinal shock). Therefore, this patient has a complete injury. Step 3: complete injury, his ASIA impairment score is ASAI A.Ans3 |
|
|
ADLs (Activity of Daily Living) mnumonic
BATTED |
BATTED
B-athing A-mbulation T-oileting T-ransfers E-ating D-ressing |
|
C6 Quadriplegic,
|

1 movement head, neck, shoulders+arms and wrist
bend Elbows, extend wrist, rotate palms 2- perform self hygiene and feeding, propel a manual WC, transfers from bed to chair 3 ASAI wrist extensors |
|
C7 quad
|
1 movement head, neck, shoulders+arms and wrist
bend Elbows, extend wrist, rotate palms, loss of grasp; 2- EASIER to perform self hygiene and feeding, propel a manual WC, transfers from bed to chair 3 ASAI elbow extensors |
|
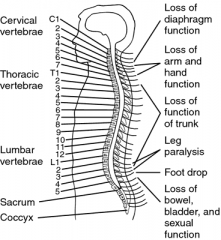
C5 quad
|

1-movement head, neck, shoulders- raise arm (deltoid); flexion of elbow (biceps); C6 externally rotates the arm(supinates)
2- self care capable, pt will be unable to move wrist or hand electric WC & drive car with adaptive equip 3- ASAI C5 think quad- flex at elbow |
|
ASAI findings w/ C8 & T1
|
C8 flex fingers
T1-abd fingers |
|
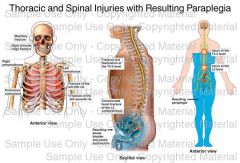
paraplegic defined at what level in spine?
|
T6- L1 paraplegic
|
|
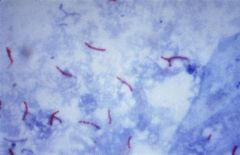
What stain used for Potts Dz what do Cx bacilli on?
Which ABX used to TX potts dz? |
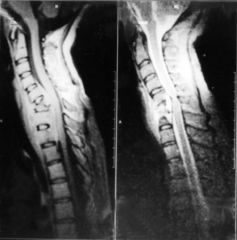
Ziehl-Neelsen stain displays the mycobacterium as "red snappers" against a blue background. Culture for acid-fast bacilli on Lowenstein-Jensen medium is diagnostic.
RIP + strepto ABx-, rifampin, Isoniazid pyrazinamide, and streptomycin is the first line of medical therapy. |
|
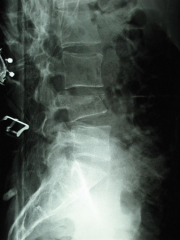
79 yo F s/p S &F & is hospitalized for LBP that prevents ambulating. denies sx of buttock or leg pain. PE she has point tenderness over the T12 vertebral body. Exam LE = nl, xrays Fig. An MRI no evidence of retropulsion or spinal cord compression. Which is true regarding this injury pattern?
|
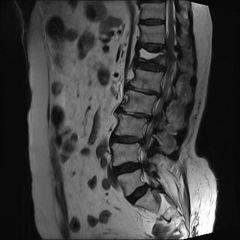
1-no assoc b/t this fx and future osteoporotic fragility fxs; 2-Prospective, randomized, 2x blinded studies have showed improv w/vertebroplasty;
3-2-yr mortality rates are > than those assoc w/ hip fxs; 4-This fx results in chronic LBP in the majority of pts regardless of tx; 5-Neurologic deterioration is a common complic w/ this injury pattern:::mortality rate of pts w/ vertebral fx > pts w/ hip fx when they are followed > 6 mths, observation, bracing, and medical management/bisphos < pain.Ans3 |

