![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
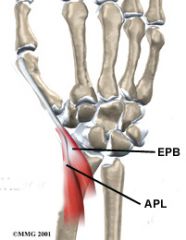
31yo F of a 2-mth-old infant c/o of radial sided wrist pn. Corticosteroid injections should be directed into what anatomic area? 1-1st CMC jnt; 2-Carpal tunnel
3-1st dorsal comprtmnt near the radial styloid; |
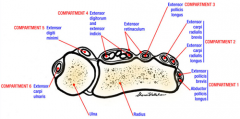
4-A1 pulley of thumb; 5-At the cross'g of the 1st & 2nd dorsal comprtmnts::: association b/w the postpartum & de Quervain’s tenosynovitis= pathologic process of the 1st dorsal (extensor) compartment (EPB & AbdPL).Ans3
|
|
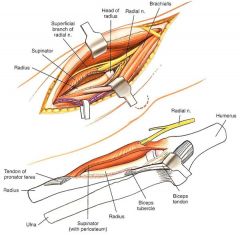
35yo F office worker c/o 6 mths of deep aching on her lateral dominant elbow which > w/ repetitive movements. The pn is located 4cm distl to the lat epicondyle. also c/o night pn. What is the most likely dx? 1-Lat epicondylitis;
|
2-Radial tunnel syndrm; 3-CTS; 4-Erb's palsy; 5-MS::: lat epicondylitis, focal point of tendernss is @ lat epicondyle @ the insertion of the ECRB. In contrast, RTS is 3-4 cm distal to lat epicondyle in the area of the mobile wad & radial tunnel.
|
|
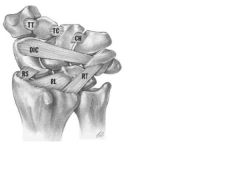
Instability of the lunotriquetral joint caused by rupture of which 3 lig?
|
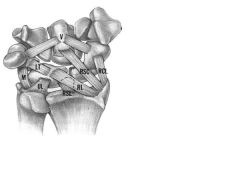
1-lunotriquetral ligament 2-dorsal radiocarpal ligament (aka radiotriquetral ligament) 3-LT ligament injury is less common than SL ligament injury
|
|
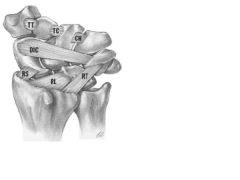
1 VISI Deformity, stands for ?
2-what is it a type of ? 3 caused by injury to which 3 ligments? |
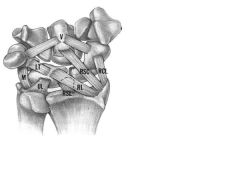
1 VISI Deformity=volar intercalated segment instability
2 a type of Carpal Instability Dissociative (CID) 3 caused by advanced injury with injury to lunotriquetral ligament dorsal radiotriquetral ligament volar radiolunate ligament |
|
|
1
|
1
|

