![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the difference between fear and anxiety |
Anxiety is fear of the future. Fear is the present threat |
Past & Present |
|
|
Contributions to Anxiety |
Social, behavioral, cognative, environmental |
|
|
|
11 Types of anxiety disorders |
Generalised Anxiety Disorder Panic Disorder Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Agoroaphobia Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Social Axiety Specific Phobia Acute Stress Disorder Subtance induced axiety disorder Anxiety NOS disorder Anxiety disorder due to a general medical condition |
|
|
|
Specific phobia |
Irrational fear of a specific object or situation that impairs daily functioning |
|
|
|
Social Anxiety |
The fear of being negatively percieved by others |
|
|
|
Generlised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) |
Intolerance of Uncertaintity Poor problem orientation Cognative avoidance Posative beliefs about worry |
|
|
|
What is emotional reasoning |
Emotional reasoning is aproaching a situation based on your emotional stare in the present |
|
|
|
Agoraphobia |
The fear of being in open spaces one cannot escape from/ are unsafe |
|
|
|
Obsession vs Compulsion |
Obsession is the thought process compulsion is the behavior designed to supress the thought I am likley to get robbed Locking all the doors |
|
|
|
Treatments of phobias |
Extention learning Exposure Therapy |
|
|
|
Mood Disorder |
A mood disorder is a maladaptive or abnormal mood |
|
|
|
2 Major Mood Disorder |
MANIA & DEPRESSION |
|
|
|
Major Depressive Episode |
Duration: At least two week of symptoms Major Symptoms are: Change in appetite/weight, change in sleeping patterns, Feelings of worthlesness, suicidal ideation |
|
|
|
MANIC EPISODE |
Duration: longer than week Symptoms: increased risk taking behaviour, delusions of granduer, elevated speech, decreased need for sleep |
|
|
|
MANIC VS HYPOMANIC |
Lasts at least four days |
|
|
|
What are the two types of mood |
Depressive & Manic |
|
|
|
Prevelence in the sexes |
Females are twice as likley to suffer from mood disorder |
|
|
|
Recurrent Major Depressive Disorder |
Two or more episodes, no history of manic episodes. |
|
|
|
Causal Factors of unipolar depressive disorder |
Biological eg. Chemistry/Heriditary Biological eg. Chemistry/HeriditaryPsychological eg. Trauma/Stress Biological eg. Chemistry/HeriditaryPsychological eg. Trauma/Stress Psychological eg. Trauma/Stress |
|
|
|
Bipolar Depression |
Depression coupled with Manic/Hypermanic episodes |
|
|
|
Cyclothymic Disorder |
Less sever form of Bipolar disorder can progress into either Bipolar 1 or Bipolar 2 |
|
|
|
Bipolar 1 |
Includes at least one manic episode |
|
|
|
Bipolar 2 |
Includes hypomanic episodes but is less sever than full manic episode |
|
|
|
Manic vs Depressive |
Depressive episodes are three times more likely than manic episodes |
|
|
|
Age of onset |
Young adult around 18-22 |
|
|
|
Mood Variation |
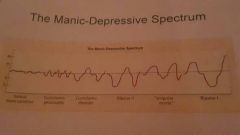
|
|
|
|
Hysteria |
Origanally thought to be pent up sexual energy in women |
|
|
|
Somatic Symptom Disorder |
Menifestation of physical/medical symtptomology without any medical reason |
|
|
|
Dissociative Disorder |
A break from normal functioning resulting in disruption of concoisness/identity/memory/perception |
|
|
|
Symptoms of dissociative disorders |
Periods of Amnesia Depersonalisation Time lapses Mood swings Unexplained changes in handwriting |
|
|
|
Dissociative Memory Loss |
Episodic & Autobiographical memories Selective memory loss |
|
|
|
Schitzophrenia |
Psychosis - a significant loss of contact with reality |
|
|
|
Who What When? Schitzophrenia |
All types of individuals Diverse symptoms Usually late adolescent onset |
|
|
|
DSM5 Criterion |
2 x delusions; hallucinations; Disorganised speech; disorganised or catatonic behavior; negative symptoms (deminished emotional expression) Impaired day to day function Continuos disturbance Schitzoaffective disorder Depressive or bipolar |
|
|
|
What are delusions |
Erroneous beliefs Fixed and firmly held despite evidence to the contrary Disturbance in the content of thought |
|
|
|
Hallucinations |
Sensory experience Seems real but occurs in absence of any external perceptual stimulas Can occur in any sensory modality |
|
|
|
Disorganized speech |
Failure to make sense Usualy conforms to semantics and syntax Disturbance in form (not content) of thought |
|
|
|
Disorganized Behavior |
Impairment of goal directed activity Occurs in daily functioning Catatonia Catatonia Stupor |
|
|
|
Other Psychotic Disorders |
Schizoaffective disorder Schizophreniform disorder Delusional disorder Brief psychotic disorder Shared psychotic disorder |
|
|
|
Risk Factors |
Genetic factors - first degree relatives of people with schizophrenia are ten times more likley to have the disorder |
|
|
|
More Risk Factors |
Prenatal exposure can put a person at risk - pre natal infections, Rhesus incompatibility, early nutritional deficiency. |
|
|
|
Biology |
Brain areas in schizophrenia is abnormal Deceased brain volume Enlarged ventricles Frontal lobe dysfunction Reduced volume of thalamus Abnormalities in tenporal lobe |
|
|
|
More Biology |
Dopamine and Glutamate transmitters Cytoarchitecture - Overall organization may be comprimised |
|
|
|
Neurocognition |
Defecits in attentional and working memory Eye tracking dysfunction |
|
|
|
Stress Model |

|
|
|
|
Schizoaffective Disorder |
Uninterupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode. Delusions or halucinations for 2 or more weeks in the absence of a major mood episode over lifetime Symptoms for major mood episode are present for the majority of the illness Not attirbutable to the effects of substance |
|
|
|
Prevelence of Schizoaffective Disorder |
About a third as common as schizophrenia |
|
|
|
Treatment types |
Pharmacological Psychosocial therapy |
|
|
|
Eating disorders |
Anerexia navosa Bulemia Navosa |
|
|
|
Common factors in eating disorder |
Intense fear of being obese Intense desire to loose weight |
|
|
|
Anorexia Nervosa |
Restriction of energy intake below what is healthy for that person Obsession with being skinny Disturbance in the way a persons views thier weight |
|
|
|
Bullemia Nervosa |
Recurrent episodes of binge eating accompanied by purging or fasting |
|
|
|
Two types of Bulemia Nervosa |
Purging - vomoting, taking laxatives, taking duiretics Non purging - fasting or extreme excorsice |
|
|
|
Ago of onset and prevelance for eating disorders |
Anerexia nervosa is more common in 15-19 year olds Bullemia more likley in 20-24 year olds Females are 3 times more likley to be diagnosed than males |
|
|
|
Medical complications of eating disorders |
Heart arythmia Renal failure Kidney Damage |
|
|
|
Other complications and outcomes of eating disorders |
Suicide attempts high in anorexia Bullemia more likley to have succsessful treatment than anorexia |
|
|
|
Comorbidity with Eating disorders |
Clinical eating disorder |
|
|
|
What us the definition of substance abuce? |
The excessive use of substance that ipacts on daily functioning |
|
|
|
Indicators of substance abuse |
Can cause legal problems Hazardouse situations Missing deadlines |
|
|
|
Considerations of substance abuce |
Who, what, why, how, when |
|
|
|
What are psycoactive drugs? |
Substances that effect the central nervouse system |
|
|
|
Differnce between Potancy and Toxicity |
Potancy = how much of the drug Toxicicity = capacity for damage |
|
|
|
Two types of acute toxicity |
Behaviorual Physiological |
|
|
|
Three processes of substance abuse |
Drug tolerance Physical dependance Psychological dependance |
|
|
|
What is Alcohohol Use Disorder |
The depdance on alcocohol that causes interference with daily functioning |
|
|
|
Ocurrances of alcohol abuse |
Violent or innapropriate behavior |
|
|
|
What pathological gamblicol |
Gambling that intereferea with daily functioning |
|
|
|
4 imoortant cognative emotional factors gambling |
Rewad and punishment Higher salience leading to craving Impulsivity Impaired decision making |
|
|
|
Childhood and Adolescent disorders |
Dislexia, ODD,ADHD,autism |
|
|
|
Developmental psychopathology |
The study of illnesses that can effect the mind during development |
|
|
|
Psychological challanges in children |
Less self understanding Lack of identity |
|
|
|
What is the most common type of disorder in children |
Intellectual |
|
|
|
What is ADHD |
Attention Defecit Hyperactivity Disorder. Inability tonfocus and contain impulsive behaviour |
|
|
|
Treatment options for ADHD |
Medications Behavioral therapy Family therapy |
|
|
|
What Oppositional Defience Disorder |
Persistant defience of the rules Persistant direct opposition to authority figure |
|
|
|
Three subtypes of ODD |
Irritible mood Defient behavior Vindictive |
|
|
|
4 causes of ODD |
Family patterns Peer relationships Biological factors Pathology |
|
|
|
Treatment types for Odd abd Conduct disorder |
Behavioral Therapy |
|
|
|
Class of Nuerdevelopment disorder |
Pervasive |
|
|
|
What is Autism spectrum disorder |
Defecit of speech Self stimulation Social defecits |
|
|
|
Causes of ASD |
Precise cayse unknown |
|
|
|
Treatment |
Behavioral |
|
|
|
Nuerological Characteristic with adhd and autism |
Frontal lobe Executive functioning |
|
|
|
Types of learning disorder |
Dislexia |
|
|
|
What is dyslexia |
Word recognition and reading comprehension |
|
|
|
Possible cause of dyslexia |
Central nervouse syndrome |
|
|
|
What is an intellectual disability |
Defecit in : Comprehension;reasoning;planning;abstract |
|
|
|
Causal factors of intellectual disability |
Biological |
|
|
|
Organic retardation syndromes |
Down syndrome |
|
|
|
Neurocognative Disorders |
Disorders with the brain |
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs of brain damage |
Loss of memory Speech impairment |
|
|
|
Difference between diffuse and focal brain damage |
Diffuse: spread out Focal: concentrated in one area |
|
|
|
4 states of waking |
Wakefulness Delerium Stupor Coma |
|
|
|
Treatment and outcome of delerium |
Medications Evironmental manipulation Family support |
|
|
|
Treatment and outcome of delerium |
Medications Evironmental manipulation Family support |
|
|
|
Major Nuerocognative disorders |
Dimentia Alzehmers Parkinsons Huntingings Brain Damage |
|
|
|
Major characteristics of Neurogcognatibe disorders |
Cognative decline |
|
|
|
Parkinsons |
Incontrollable tremors Loss dopamine |
|
|
|
Alzheimers |
Decaying grey matter Memory loss Dissasociation Social withdrawal Uncharistic behavior Cognative decline |
|
|
|
Three potential outcomes of head injury |
Amnesia retro grade or anterograde Personality change |
|
|
|
The Big Five of personality |
O = Open to experience C= Conscientiousness E = Extroversion A= Agreeable N= Nueroticism |
|
|
|
Cluster A personality disorders Odd and Eccentric |
Paraniod personilty disorder Schitzoid personailty disorder Schitzotypal personality disorder |
|
|
|
Cluster B personailty disorders Dramatic Emotional Erratic |
Borderline personility disorder Antisocial personailty disorder Histrionic personality disorder |
|

