![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Spontaneous Abortion
|
Termination of pregnancy prior to 20 weeks Gestation.
Usually occurs 1-3 weeks after embryonic or fetal demise. Approximately 12% of all pregnancy end in SAB, 75% occuring before 16th weeks. Etiology includes: endocrine factors, failure of corpus luteum cyst, myllerian duct anomalies, interruption of embryonic development, and specific chromosomal causes. |
|
|
Complete Abortion
|
All products of conception expelled
|
|
|
Sonographic findings for Complete Abortions.
|
-empty UT normal endometrium
-may have fluid within endo. -UT may remain enlarged for up to 2 weeks -trophoblastic wave form patterns may stay for up to 3 days |
|
|
Incomplete Abortion
|
Contained products of conception
|
|
|
Sonographic findings for Incomplete Abortion
|
-trophoblastic wave form patterns remains for up to 5 days past events.
-thickened or irregular endometrial cavity - may have fluid within endometrial cavity |
|
|
Missed Abortion
|
Embryo without cardiac activity
|
|
|
Clinical Symptoms for Missed Abortion
|
-loss of pregnancy symptoms
-brownish vaginal discharge without flank pain -hcg levels less than expected dates -decrease in uterine size |
|
|
Inevitable Abortion
|
Abortion in progress
|
|
|
Sonographic findings for Inevitable Abortion
|
-anechoic cresent surrounding GS
-downward movement of GS during exam -GS low in uterus or CX -dilated cervix |
|
|
Threatened Abortion
|
Pregnancy that is in jeopardy but pregnancy continues.
Can not diagnosis sonographically. Patient present with vaginal bleeding or cramping and a closed CX. |
|
|
Aembryonic Pregnancy
|
Gestation in which the embryo did not developed or stop developing early and can be visualized.
Also known as a blighted ovum. |
|
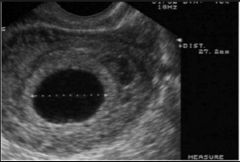
Sonographic Findings for an Aembryonic Pregnancy
|
-sac enlarges slightly on serial scans
- no identifiable embryo in a GS 25mm or larger. |
|
|
Septic Abortion
|
An abortion that was performed with non sterile instruments or from infection from retained products of conception.
|
|
|
Sonographic findings for Septic Abortion
|
-may have shaddowing due to gas bubbles within endometrial cavity.
-Enlarged UT with heterogeneous content |
|
|
Ectopic Pregnancy
|
Pregnancy that occur at any site other than the endometrial cavity.
The most common site for ectopic pregnancy is the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The incident of ectopic pregnancy has increased with an increase in PID, tubal constructive surgery, and assited fertility programs. |
|
|
Adnexal Ectopic
|
May occur at any site within the fallopian tubes or ovaries.
Most common site is ampulla of the Fallopian tube. May also occur in the isthmus, interstitial, or fimbrial portion of the fallopian tube. Ovarian ectopics are very rare. |
|
|
Uterine Ectopic
|
Fertilized ovum implants at any site within the uterus except endometrium.
May impant in cornua, uterine scar or CX. Most dangerous location is cornua pregnancy due to the high risk of hemorrhage. |
|
|
Sonographic findings of a cornual/interstitial ectopic
|
For identificatio of an ectopic pregnancy there is less than 5mm of myometrium surrounding any side of the gestational sac.
|
|
|
Cervical Ectopic
|
Rare occurence.
Risk factors include previous uterine curettage. Carry high mortality and mobidity rates due to risk of hemorrhage. |
|
|
What is used to treat Ectopic Pregnancy?
|
Methotrexate
If treatment with Methotrexate is unsuccessful than cervical artery embolism or complete hysterectomy may be necessary. |
|
|
Abdominal Ectopic
|
When fertilized ovum implants into the peritoneal cavity.
Abdominal ectopic pregnancy may progess further into gestation before it is recognized. |
|
|
Sonographic Findings for Abdominal Ectopic
|
-empty UT separate from developing fetus
-poor placenta visualization -unusual fetal presentatiin -oligohydramnios -absence of myometrium surrounding pregnancy |
|
|
Heterotopic Pregnacy
|
Coexisting extra and intrauterine pregnancy.
Most common with patient who has undergone zygote or gamete transfer. |
|
|
Clinical Symptoms of Ectopic pregnancy
|
-amenorrhea
-positive pregnancy test -vaginal bleeding or spotting -adnexal pain/tenderness -shoulder pain -pelvic pain |
|
|
Sonographic findings for Ectopic Pregnancy
|
-adnexal mass
-empty UT - free fluid in pericolic gutters, cul-de-sac, adnexea, morrisons pouch Misidentification of a corpus luteum cyst for an ectopic pregnancy when depending on the ring of fire. Absence of a doppler signal can not be used to exclude ectopic pregnancy. |
|
|
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
|
A spectrum of pathological condition resulting from abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic tissue.
GTD can occur during or after implantation of a fertilized ovum. Can occur months to a year after any type of pregnancy. |
|
|
Paternal Genomes
|
Controls the proliferation of trophblastic tissue and the growth of the embryo.
Excessive paternal material from duplicated chromosomes , lack of chromosomes in ovum, or an ovum being fertilized my 2 sperms may be the cause of GTD. |
|
|
Clinical Finding in GTD
|
-Enlarged UT
-Absence of fetal heart tone -Theca luteum cyst -hyperthyroidism -hyperemesis gravidium -vaginal bleeding or passage of tissue -markedly elevated HCG levels -early on set of pre-clampsia |
|
|
Complete Hydatiform Mole
|
Most common type of GTD
Chorionic villis are hydropic with no identifiable embryonic or fetal tissue |
|
|
Sonographic Findings for Complete Hydatiform Mole
|
-Enlarged UT filled with echogenic mass
-endometrial cavity is filled with echogenic material that appears homogenous in the 1st teimester and cystic in the 2nd -ovarian theca lutein cyst - hypervascular, low resistance flow pattern with doppler |
|
|
Partial Mole
|
Pregnancy most commonly has one set of maternal chromosomes and two sets of paternal chromosomes resulting in a triploid karyotype .
Has both hydropic and normal choronic villis. Fetal and embryonic tissue is frequently identified. |
|
|
Sonographic Findings for Partial Mole
|
-deformed Gs
-growth restricted fetus with triploid karyotype such as syndactly and hydrocephalus -enlarged placenta with multiple cystic areas |
|
|
Mole with Coexisting Normal Fetus
|
Two conception occurs.
One developed normally the other into GTD. This is a rare occurence |
|
|
Sonographic findings for Mole with Coexisting Normal Fetus
|
-similar to partial mole, but normal placenta and membrances.
fetus usually has a normal karyotype |
|
|
Persistent Trophblastic Neoplasia
|
Most commonly follows GTD
Can uncommonly follow, normal term pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, ectopic pregnancy. Clinically suspected when HCG levels do not decline after evacuation of pregnancy. Patient my present clinically with persistence heavy vaginal bleeding. |
|
|
Invasive Mole
|
Also known as chrioadenoma destruens.
Penetrates the myometrium and adjacent structures and may cause uterine rupture. It is a malignant non-metastic gestational trophoblastic disease. |
|
|
Choriocarcinoma
|
Is very rare.
Vascular invasion, hemorrhage, necrosis of the myometrium are common occurences. It is an malignant metastatic trophoblastic disease that may metastasize to lung, liver, bone, skin, GI tract. |

