![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What changes in lung volumes are seen in airway obstruction?
|
Increased TLC
Increased RV Increased FRC Increased ERV Decreased TV Decreased inspiratory capacity Decreased reserve volume |
|
|
What is summer hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
|
A unique form of hypersensitivity pneumonitis in which clinical symptoms appear in the summer and subside spontaneously in the mid-autumn.
Most prevalent HP in Japan Classically caused by Trichosporon cutaneum in moldy rugs. |
|
|
Describe the findings in ARDS.
|
Severe hypoxemia, respiratory failure, pulmonary infiltrates, small tidal volumes.
BAL: --TGFB, IL2, IL6 --surfactant proteins, von willebrand factor --PMNs, IL8, NFKB --proinflammatory (alveolar) macrophages |
|
|
What is Tranfusion Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)?
|
Transfusion of blood with antigranulocyte antibodies --> recipient becomes cyanotic, respiratory failure (mimics anaphylaxis)
Avoidance - no allo-antibodies in blood --no transfusion from multiparous women |
|
|
What is Toxic Organic Dust Syndrome?
|
(not HP)
Toxic alveolitis occurs in 12 hours with inhalation --> fevers, chills, myalgias, crackles Pulmonary mycotoxicosis - severe form of ARDS |
|
|
What causes Silo-unloaders Diease?
|
Oxides of nitrogen: NO, NO2, N2O2
Dangerous --> damage to respiratory epithelium --> dyspnea, death Oxides form with few days of crop storage (don't enter silos soon after filling it) |
|
|
What is Byssinosis?
|
(not HP)
Form of occupational asthma. Caused by exposure to cotton, flax, hemp or sisal. Bronchoconstriction (symptoms) occur early in the work week and then improve while away from the workplace, or later in the work week (tachyphylaxis with continued exposure). Risk - processing of raw cotton. |
|
|
What is Reactive Airways Dysfunction Syndrome (RADS)?
|
(non-immunologic lung disease)
~Irritant Induced Asthma Criteria: 1) No prior history of bronchoconstrictive lung disease 2) Onset with increased levels of exposure (i.e. World Trade Center cough) 3) Symptoms - abrupt onset 4) Symptoms - last at least 3 mo 5) Bronchial hyperreactivity present (PFTs show obstruction) 6) Symptoms suggest asthma 7) Other conditions excluded +methacholine Not associated with atopy, eosinophils, cigarretes/smoking, or increased WBCs on BAL |
|
|
What is Occupational Asthma?
|
Immunologic - IgE, has latency period (mo-yrs)
--immediate + late phase reactions --high molecular weight antigens (plant, animal, food) or low molecular weight + carrier (platinum, penicillin, epoxy) --> IgE Polyimmunogenic (IgE, IgG) from low molecular weight antigens (isocyanate, acid anhydride, plicatic acid [cedar]) NON-immunogenic - no latency period (i.e. RADS), may have isolated late phase. |
|
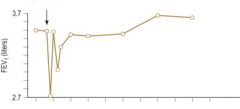
What causes this response?
|
Allergen challenge with early + late phase.
|
|
|
What causes humidifier HP?
|
May be caused by fungi or thermophilic bacteria.
Penicillium, Thermoactinomyces vulgaris, Bacillus cereus |
|
|
What is Malt Workers Lung?
|
Caused by barley spread on floor that is then flooded with water --> germination --> heated --> malt
Aspergillus clavatus, Aspergillus fumigatus |
|
|
What are the stages of HP?
|
Acute/Subacute - fever, myalgias, cough, decreased DLCO, restriction, rales
Chronic - +/- reversibility, decreased DLCO --> fibrosis |
|
|
What are the CT findings of HP?
|
alveolitis - ground glass opacities
end stage - honeycombing, irreversible |
|
|
What causes Avian Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (Bird Fanciers Lung)?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
Smoking exposure --> less intense immunologic (clinical?) responses |
|
|
What causes Hot Tub Lung?
|
Mycobacteria
|
|
|
What causes Bagassosis?
|
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis from sugar cane.
Thermoactinomyces sacchari/vulgaris |
|
|
What causes Machine Operator's Lung?
|
Pseudomonas flouorescens
|
|
|
What causes Farmer's Lung?
|
Thermophilic actinomycetes
Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula |
|
|
What causes Ventilation Pneumonitis?
|
Naegleria gruberi, Acanthamoeba (amoebae)
|
|
|
What happens with histone acetylation + deacetylation, and how does it related to asthma?
|
Acetylation - opens up DNA
--increased in asthma and COPD --increased IL8 - evidence of increased acetylation --> proinflammatory cytokines --> PMNs Deacetylation - closes up DNA --prednisone increased deactetylation in patient with asthma, but not COPD --theoplylline - increased deacetylation in COPD patients |
|
|
What are the ABPA diagnostic criteria?
|
In a patient with fleeting infiltrates...
Major criteria in asthma: --Asthma --Immediate cutaneous hyperreactivity to Aspergillus antigens (+SPT) --Central bronchiectasis --Elevated IgE (>1000) --Elevated A fumigatus-specific IgG and/or IgE --Eos >1000 ***if no bronchiectasis may have ABPA-S (seropositive) in CF: --deterioration --IgE >1200 --Immediate cutaneous hyperreactivity to Aspergillus antigens (+SPT) --Fixed pulmonary infiltrates on chest radiograph --Elevated A fumigatus-specific IgG and/or IgE |
|
|
What are the stages of ABPA?
|
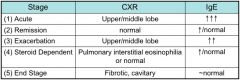
|
|
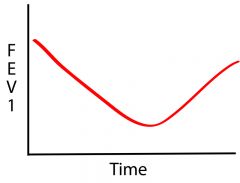
What causes this response?
|
Aspirin - caused by mediator release --> longer onset/duration
|
|
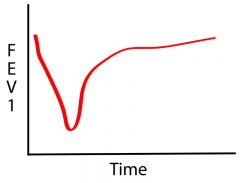
What causes this response?
|
Methacholine (non-selective challenge)
|
|
|
What happens in ABPA with steroid treatment?
|
Decreased IgE by 33% after 6 weeks of prednisone
|
|
|
What leads to genetic susceptibilty to ABPA?
|
HLA-DR2, HLA-DR5
|
|
|
Name diseases caused by Aspergillus fumigatus
|
1) ABPA
2) Allergic asthma 3) HP (malt workers lung) 4) Invasive aspergillus (immunocomprimised) 5) Aspergilloma 6) Chronic necrotizing pneumonia 7) Allergic fungal sinusitis (nasal polyps, peanut butter sputum) 8) Heat tolerance |
|
|
What are the components of the Asthma Predictive Index (API)?
|
Major Criteria (need 1):
--Parental asthma --Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis --Sensitization of aeroallergens Minor Criteria (need 2): --Sensitization to foods -->4% eosinphils --wheezing outside of colds |
|
|
What is Lofgren's Syndrome?
|
in women with Sarcoid:
Erythema nodosum HIlar adenopathy Polyarthritis |
|
|
What are the pro/con and examples of different methods of bronchoprovocation?
|
Non-selective:
--Increased sensitivity --Direct - methacholine (high NPV for asthma), histamine, PGD2, leukotrienes --Indirect - exercise, mannitol, hypertonic saline, cold air, eucapnic voluntary hyperventilation, adenosine monophosphate [AMP], propranolol Selective: --useful to confirm, but not rule out asthma (high specificity, low sensitivity) --Immunologic - allergen --Non-immunologic - ASA, NSAIDs |
|
|
What increases risk for asthma mortality?
|
1) history of sudden severe exacerbations
2) history of intubation/ICU 3) hospitalization in last month 4) 2 or more hospitalizations for asthma in the past year 5) >/= 3 ED visits in last year 6) >2 alb inhalers/month 7) Poor perception 8) Alternaria + cockroach sensitization 9) African American or Latino 10) Low social economic status 11) Illicit drug use 12) Inner city 13) Psych co-morbidity 14) Current use of or recent withdrawal from oral steroid ADAM33 - increased risk of bronchial hyperreactivity +remodeling |
|
|
Describe airway remodeling in asthma.
|
Contributes to accelerate lung function loss in asthma.
No data supports treatment to prevent remodeling. --> smooth muscle hypertrophy --angiogenesis --thickening of lamina reticularis (type 3 + 4 collagen) --Mucus plug - glandular hypertrophy under influence of IL9 --Epithelial damage |
|
|
What type of Occupational Asthma occurs with Platinum salts?
|
Platinum:
Immunologic Occupational Asthma - IgE specific for platinum Smoking is a risk factor for Occupational Asthma in this group |
|
|
What is the symptom progression for high molecular weight (HMW) vs low molecular weight (LMW) allergens?
|
Occupational Asthma
HMW Occupational Asthma is usually preceded by allergic rhinitis, LMW Occupational Asthma is not. |
|
|
When is Asthma not well controlled?
|
Albuterol >2/wk
Asthma symptoms >2/wk Night time symptoms 1-3/wk Some limitation FEV1 60-80% ACT<20 2-3 exacerbations/year = not well controlled >3 exacerbations/year = poor control |
|
|
What physiologic changes occur in the lung during pregnancy?
|
Minute ventilation increases --> respiratory alkalosis (normal pH in a pregnant asthmatic = bad)
Lung volumes: --increased TV --decreased RV --decreased FRC |
|
|
What medications can/cannot be used during pregnancy for asthma?
|
Category B medications:
--budesonide --chromones --omalizumab (!) --leukotriene modifiers (except Zileuton) NO decongestants Exacerbations - most common in wks 24-36 |
|
|
What are some major causes of indoor air pollution?
|
Biomass burning (tobacco, wood stoves, fireplace, gas stove) --> increased nitric oxide (NO)
Cleaning products --> volatile organic compounds (VOCs) --increased benzene from dry cleaning --> increased risk of asthma O3 cannot enter building, EXCEPT some electrostatic air purifiers give it off |
|
|
What is the Air Quality Index (AQI)?
|

Based on 5 pollutants:
Particulate matter 2.5um-10um CO SO2 O3 NO2 (not Lead) |
|
|
What are the effects of Diesel Exhaust Particles?
|
Allergens cling to diesel exhaust particles (DEP)
--act as adjuvant in healthy people --> increased inflammatory cells, increased neutrophils, increase IL6, IL13, IL8, VCAM, ICAM In mild asthma --increased methacholine response, increased airway resistance, increased IL6, increased IL10 |
|
|
What 6 pollutants have set standards?
|
1) Ground-level ozone (O3) - leads to asthma exacerbations, 24-36 hrs after exposure, increased neutrophils; peak on warm sunny nights (VOCs + UV light --> O3)
2) Particle pollution (particulate matter) 2.5 um - 10 um 3) Carbon monoxide (CO) - mobile sources 4) Sulfur dioxide (SO2) - bronchoconstriction, onset = 2 min, tachyphylaxis, nasal breathing = protective; point sources 5) Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - airway inflammation, increased response to allergen, increased late phase to allergen, point sources |
|
|
How do you use exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO)?
|
>20 ppb = asthma
Good NPV for asthma - normal FeNO , no asthma or well controlled Good measure of adherence False positive + (high FeNO): viral URI, AR, increased nitrate diet False negative - (low FeNO): CF, smoking, pulmonary hypertension, EtOH, recent spirometry maneuvers |
|
|
When should controller medications for asthma be started in children <4 years old?
|
1) 4 wheezing episodes in last year with + asthma predictive index (API)
2) Need symptom treatment more than 2 days/wk for >4 wks 3) Oral steroids x2 in last 6 mo 4) During seasons of previously documented risk |
|
|
What are some Asthma susceptibility genes?
|
ADAM33 - metalloproteinase - increased risk of bronchial hyperreactivity + remodeling
CD14 - coreceptor with TLR4 for LPS; polymorphism of soluble CD14 (sCD14) --> influences Th1/2 balance - increased asthma, decreased IgE (?) Chitinase - (chitin found in fungi and arthropods) - area of interest Chromosome 5q (B2-adrenegric receptor) - Arg-Arg - regular SABA use --> risk of death, no LABA influence |
|
|
What are the lower airway changes in Asthma and COPD?
|
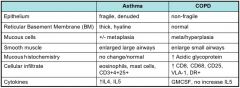
|
|
|
What are the causes of Eosinophilia?
|
I AM SAD HELP
G(I) - EGIDs Allergy Malignancy - Hodgkin's lymphoma Skin - atopic dermatitis, pemphigoid Arteritis - Churg Strauss Drugs Hematologic disorder - HES, mastocytosis Endocrine - Addison's disease Lung disease - ABPA, eosinophilic pneumonia Parasites + HIV |
|
|
What is a normal CD4/CD8 ratio in BAL, and what is it in some common disease states?
|
Normal CD4/8 = 2
Increased CD4/8 ratio: --asthma --sarcoid Decreased CD4/8 ratio (<1) --COPD --hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
|
|
What are Curschmann's spirals?
|
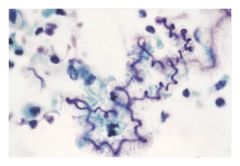
spiral shaped mucus plugs, associated with excess mucous plugs.
**Characteristic in asthmatic sputum |
|
|
What are Creola bodies?
|
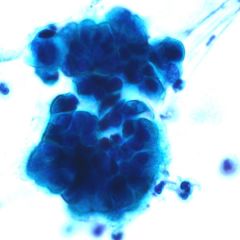
clusters of airway epithelia cells (ciliated columnar cells) sloughed from the bronchial mucosa of a patient with asthma.
**Characteristic in asthmatic sputum |
|
|
What are Charcot Leyden crystals?
|
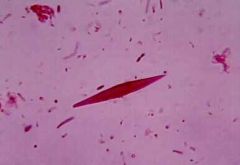
Charcot Leyden crystals made by eosinophils, colorless, needle shaped structures
**Characteristic in asthmatic sputum |
|
|
Name 3 characteristic findings in asthmatic sputum.
|
Charcot Leyden crystals
Curschmann's spirals Creola bodies |
|
|
How does treatment effect a specific allergen challenge?
|
if on immunotherapy (IT) --> blocks immediate + late phase + hyperreactivity that follows
Chromones - block immediate + late phase ICS - blocks late phase |
|
|
Methacholine Challenge
|
excellent NPV for asthma
Exercise induced bronchospasm cannot be excluded by negative test (need exercise challenge) False negative with elite athletes. + = PC20 <4 mg/ml borderline = PC20 between 4-16 mg/ml Blocked by: --theophylline --B agonist --anticholinergics (hold tiotroprium for 48 hrs) Not blocked by: --antihistamines --chromones --antileukotrienes + test w/o asthma: --AR --family history of atopy --asthmatic siblings --COPD --CF --viral URI --smokers --recent exposure to allergens |
|
|
Mannitol challenge
|
+ test = FEV1 decreased by 15% at cumulative dose <635 mg
On ICS --> negative test --> can check compliance Blocked by B2 agonist, chromones, LTRA, antihistamines Mannitol is associated with leukotriene and prostaglandin production Indirect challenge |
|
|
What is Exercise Induced Bronchospasm (EIB)?
|
EIB diagnosed by decreased FEV1 >/= 15% after exercise challenge
OR hx + bronchodilator response Cannot be excluded by negative methacholine/histamine challenge |
|
|
Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD)
|
Functional airway obstruction, stridor
Associated with psych, GERD, asthma, irritants FEF50/FIF50 = increased in VCD, decreased in asthma Treatment - pursed lip breathing (Speech), heliox, topical lidocaine, Botox to vocal cords Vocal cord anatomy: posterior cricoarytinoids abducts lateral cricoarytenoids adducts |
|
|
What happens with Trimellitic anhydride (TMA)?
|
Occupational asthma/disease
TMA - used in plastics, resins, coatings Low molecular weight sensitizers - needs a carrier TMA flu - late respiratory systemic syndrome, pulmonary disease, anemia |
|
|
What is Plicatic acid?
|
Sensitizers for occupational asthma in Western red cedar mill workers
Activates complement |
|
|
What is Diisocyanate?
|
Occupational asthma
found in spray paints, adhesives, body, insulation Can be an immunologic or non-immunologic sensitizers |
|
|
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
|
history of exposure + precipitating abs (confirms only exposure)
improves with cessation of exposure PFTs - restrictive, decreased TLC, decreased FVC, decreased DLCO CXR - recurrent/fleeting infiltrates mid/upper lungs BAL or biopsy (for diagnosis) - poorly formed non-caseating granulomas near bronchioles (T cell) Increased CD8 --> decreased CD4/8 ratio (compared with sarcoid which has increased CD4 + increased CD4/8 ratio) |
|
|
Sarcoidosis
|
Systemic inflammatory disease that can affect any organ.
CXR/CT Stages --Stage 1: bihilar lymphadenopathy --Stage 2: bihilar lymphadenopathy and reticulonodular infiltrates --Stage 3: bilateral pulmonary infiltrates --Stage 4: fibrocystic sarcoidosis typically with upward hilar retraction, cystic & bullous changes BAL - CD4/8 ratio --> 8:1 (normal 2:1) Labs: increased ACE, ESR, Ca2+, IgG Lofgren's syndrome - erythema nodosom, hilar adenopathy, polyateritis, which affects women with sarcoid |

