![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
154 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
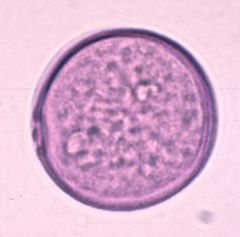
What is this pollen?
|
Grass
|
|
|
|
Describe a grass pollen.
|
Monoporate
Relatively Large (25-40 microns) Round Slightly granular Pore is surrounded by a thick annulus (ring) and may have a cap (operculum) |
|
|
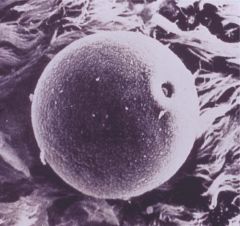
What is this pollen?
|
Grass
|
|
|
|
What are the northern grasses?
|
=Pooideae
Timothy, Orchard, Rye, Fescue, Bluegrass, Redtop, Sweet Vernal, Brome, Velvet, Canary |
|
|
|
What are the southern grasses?
|
=Chloridoideae
Bermuda, love grass. prarie grasses (salt, buffalo, grama) =Panicoideae Bahia (Brazil, Bermuda), Johnson (Mississippi), Corn, Sugarcane |
|
|
|
Are the northern grasses cross reactive?
|
Yes, Pooideae is very cross reactive. Timothy and sweet vernal may have unique antigens
|
|
|
|
What does Bermuda cross react with?
|
Bahia and Johnson
|
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Bermuda?
|
Cynodon dactylon
Allergen? |
Cyn d 1-14
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Timothy?
|
Phleum pretense
Allergen? |
Phl p 1-14
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Rye?
|
Lolium perenne
Allergen? |
Lol p 1-14
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Johnson?
|
Sorghum halepense
Allergen? |
Sor h 1-14
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Bluegrass?
|
Poa pratensis
Allergen? |
Poa p 1-14
|
|
|
What are the weed pollens?
|
Ragweed
Mugwort Pellitory |
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for Ragweed?
|
Ambrosia artemisiifolia
Allergen? |
Amb a 1-10
Profillin Cystatin |
|
|
What is the scientific name for Mugwort?
|
Artemisia vulgaris
Allergen? |
Art v 1-3
Profillin |
|
|
What is the scientific name for Pellitory?
|
Parietaria species
Allergen? |
Par o 1-2
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Amb a 1-10)
|
|
|
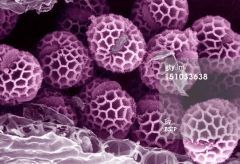
What is this pollen?
|
Mugwort (Artemesia vulgaris, Art v1-3/Profilin)
|
|
|
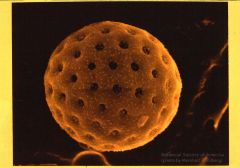
What is this pollen?
|
Pigweed (Amaranthus)
|
|
|
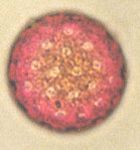
What is this pollen?
|
Lambsquarters (Chenopodium)
|
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Russian Thistle (Salsola)
|
|
|
|
What are characteristics of Ragweed pollen?
|
15-25 microns
Either Tricolporate or Tetracolporate Short Furrows Spiny exine 75-90% pollen captured between August and October |
|
|
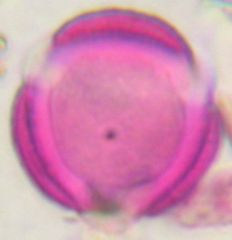
What is this pollen?
|
Sage
|
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Nettle (Urticaceae)
|
|
|
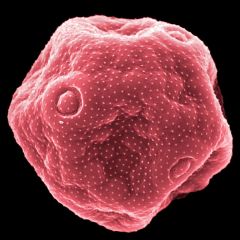
What is this pollen?
|
Plantain (Plantago)
|
|
|
|
What does Plantain Pollen look like?
|
20-40 microns
6-10 pores (periporate) Distinctive pore cap (operculum) that gives it a doughnut appearance |
|
|
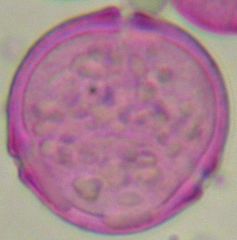
What is this pollen?
|
Dock or Sorrel (Rumex)
|
|
|
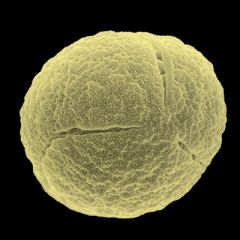
What is this pollen?
|
Dock or Sorrel (Rumex)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic of Dock or Sorrel pollen?
|
Round
20-30 microns Tricolporate Characteristic Starch inclusion granules Long furrows |
|
|
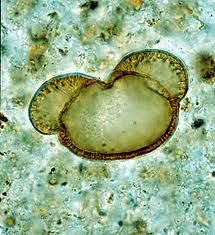
What is this pollen?
|
Pine (Pinaceae)
|
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Pine (Pinaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic about Pine allergen?
|
Large size 50-100 microns
Rarely implicated in allergy Mickey mouse ears are bladders |
|
|
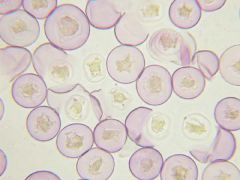
What is this pollen?
|
Mountain Cedar (Juniperus ashei)
|
|
|
|
What does Mountain Cedar Pollen look like?
|
Thick intine with stellate cytoplasmic contents and an exine, which can break off and look like Pac-Man.
|
|
|
|
What pollen pollinates mid winter in Texas?
|
Mountain Cedar (Juniperus ashei); causes "cedar fever"
|
|
|
|
When does Eastern Red Cedar pollenate?
|
Spring
Juniperus virginiana |
|
|
|
Which Cupressaceae cross react?
|
ALL
-cypress -Juniper -Cedar |
|
|
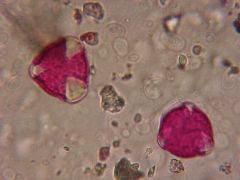
What is this pollen?
|
Oak (Fagaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic about oak pollen?
|
Triangular shaped
3 germinal furrows that appear as white pie slices |
|
|
|
What does oak cross react with?
|
Oak, Beech, Chestnut
ALSO.. - Birch - Betulaceae family members |
|
|
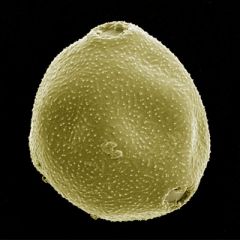
What is this pollen?
|
Birch (Betulaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic about the pollen of Birch (Betulaceae)?
|
Triporate, each with a oncus (collar)
May look like a lemon, if only 2 pores are visible Pores protrude (aspitdate) |
|
|
|
What foods cross react with Birch and cause oral allergy syndrome?
|
Apple, Apricot, Cherry, Kiwi, Nectarine, Pear, Plum,
Carrot, Celery, Coriander fennel, Parsley, Parsnip, Pepper, Potato Almond, Walnut, Hazelnut |
|
|
|
What family does Betulaceae cross react with?
|
Fagaceae
|
|
|
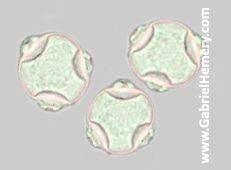
What is this pollen?
|
Birch (Betulaceae)
|
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Maple and Box Elder (Aceraceae)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic about Maple and Box Elder pollen?
|
Generally round like a beach ball
3 furrows Box elder is wind pollenated Maple is insect pollenated |
|
|
|
What is characteristic about Elm pollen?
|
5-7 oval shaped pores
May appeat pentagonal Outer surface appears wavy, undulating |
|
|
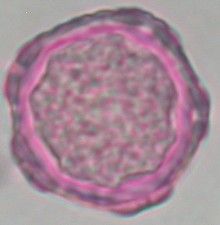
What is this pollen?
|
Elm (Ulmaceae)
|
|
|
|
What members are in the Oleaceae family?
|
Olive
Ash Privet Russian Olive |
|
|
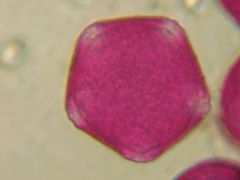
What is this pollen?
|
Ash (Oleaceae)
|
|
|
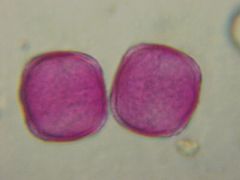
What is this pollen?
|
Ash (Oleaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is characterisitc about the Oleaceae (ash) pollen?
|
Four or Five sided- pentagonal or square
Exine net like pattern is coarse in olive and privet |
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Olive (Oleaceae)
|
|
|
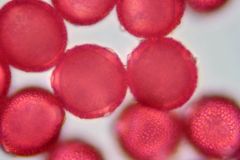
What is this pollen?
|
Privet (Oleaceae)
|
|
|
|
What trees are in the Salicaceae family?
|
Poplar
Willow Cottonwood |
|
|
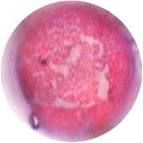
What is this pollen?
|
Cottonwood (Salicaceae)
|
|
|
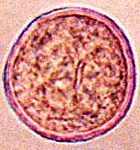
What is this pollen?
|
Poplar (Salicaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Poplar and Cottonwood pollen?
|
Round grains
Outer surface has a flaky appearance No furrows |
|
|
|
What drug is made from willow tree bark?
|
aspirin
|
|
|
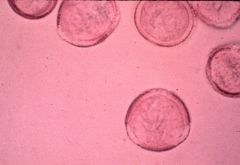
What is this pollen?
|
Sycamore tree (Platanaceae)
|
|
|
|
What does Sycamore (Platanaceae) pollen look like?
|
Round Grains
3 furrows Thin exine that is finely reticulate |
|
|
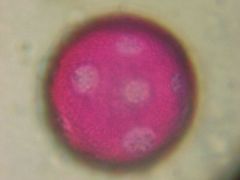
What is this pollen?
|
Sweetgum (Hamamelidaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Sweetgum (Hamamelidaceae) pollen?
|
SOCCERBALL
12-20 pores per grain South of the Mason Dixon Line in the US |
|
|
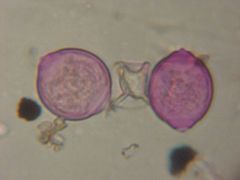
What is this pollen?
|
Mulberry (Moraceae)
|
|
|
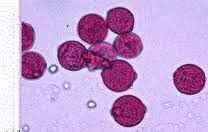
What is this pollen?
|
Mulberry (Moracaceae)
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Mulberry (Moracaceae) pollen?
|
Small 11-20 microns
Thin walled Diporate-- PINK LEMON Pores are slightly raised SHIELD shaped |
|
|
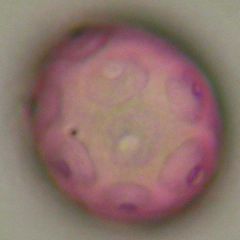
What is this pollen?
|
Walnut (Juglandaceae)
|
|
|
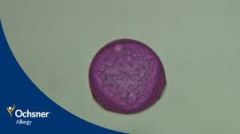
What is this pollen?
|
Pecan (Juglandaceae)
|
|
|
|
What members are in the Juglandaceae family?
|
Walnut
Hickory Pecan |
|
|
|
What is unique about the Juglandaceae family?
|
Walnut has 15 slightly raised pores
Hickory/Pecan are indistinguishable with 3 nonprotruding pores Hickory is limited to eastern US |
|
|

What is this pollen?
|
Acacia (leguminasae)
|
|
|
|
What are the members of the Leguminosae family?
|
Acacia
Mimosa Locust Mesquite |
|
|
|
What is unique about the Leguminosae family?
|
4 or 16 quadrangular grains in a group
Mesquite is in the SW US Acacia and Mimosa are ornamental trees in Tropical regions. |
|
|
|
What are the 5 major divisions in fungal taxonomy?
|
1. Zygomycota (mucor, Rhizopus)
2. Ascomycota (pleospora, leptosphaeria, Chaetominum) 3. Basidiomycota (mushroom) 4. Deuteromycetes (Alternaria, Cladosporium, Curvalaria, Helminthosporium, Epicoccum, Fusarium, Aspergillus, Penicillium) 5. Oomycota (water molds) |
|
|
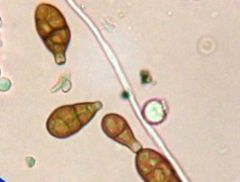
What is this pollen?
|
Alternaria
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Alternaria?
|
CLUB Shape
20-75 microns DRY DAY mold spore like decaying plants |
|
|
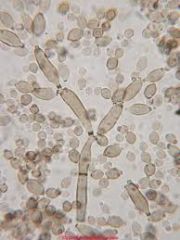
What is this pollen?
|
Cladosporium
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Cladosporium?
|
Simple CHAINS-- hotdog, cylindrical, spherical
DRY DAY spore +Indoors also 6-25 microns |
|
|
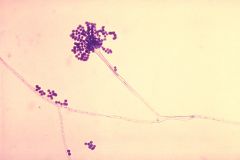
What is this pollen?
|
Aspergillus Fumigatus
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Aspergillus Fumigatus?
|
Indoor mold
may produce mycotoxins causes ABPA |
|
|

What is this?
|
Penicillium
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Penicillium?
|
Indoor mold
Looks like paintbrush Indistinguishable from aspergillus May produce mycotoxins Causes HP and Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis in cheese workers |
|
|
|
What are the dry day mold spores?
|
Alternaria
Cladosporium Helminthosporium Drechslera Bipolaris Exserohilum Epicoccum |
|
|
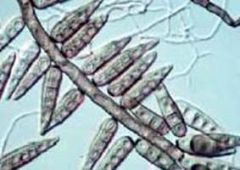
What is this?
|
Helminthsporium
|
|
|
|
What are the wet, rainy day spores?
|
Fusarium
Ascomycetes Basidomycetes Aureobasidum Zygomycetes Stachybotrys |
|
|
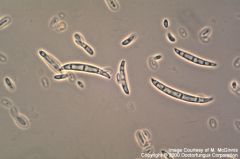
What is this?
|
Fusarium
|
|
|
|
What is unique about Fusarium spores?
|
3-7 transverse septa
spindle shaped with tapered ends 20-50 microns in length |
|
|
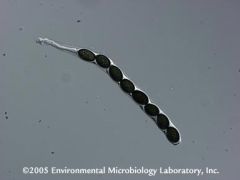
What are these spores?
|
Ascymycetes
---ascus or sac with 8 ascospores |
|
|
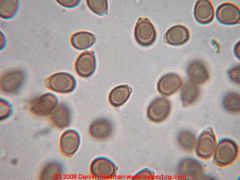
What are these spores?
|
Basidiomycetes
---Rainy day ---Common Mushrooms ---Always single celled ---2-8 microns |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of spore in Basidiomycota species (Mushrooms)?
|
Smut Spores
Rust Spores |
|
|
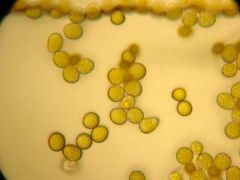
What are these spores?
|
Rust Spores
---Basidiomycota ---larger than Smut spores --- 20-30 microns --- oval to diamond in shape --- smooth or spiny wall |
|
|
|
What mold spore colonizes paper and lumber? Also found on damp surfaces in kitchens and bathrooms.
|
Aurobasidium
|
|
|
|
What mold grows well on ceiling tiles, walls, paint, paper, and food?
|
Phoma
|
|
|
|
What are the two Zygomycetes? Where are they found?
|
1. Mucor
2. Rhizopus --damp interiors, leaf litter, decaying vegetation |
|
|
|
What is another name for Black Mold?
|
Stachybotrys
|
|
|
|
Where do you find yeasts?
|
water, soil, plants, air
|
|
|
|
List 5 common indoor spores.
|
Aspergillus, Penicillium, Cladosporium, Rhizopus, Mucor
|
|
|
|
List 7 common outdoor molds.
|
Alternaria, Cladosporium, Epicoccum,Curvularia, Drechslera, Pithomyces, Botrytis, smut spores
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 rainy day mold spores?
|
Basidiospores, Ascospores, Fusarium
|
|
|
|
What spores are prevelent at night and in high humidity/
|
Ascospores
Basidiospores |
|
|
|
How can you control mold exposure?
|
keep relative humidity <50%
limit house plants avoid raking,mowing, mulching keep spoiled food out of fridge Disinfect bathroom Clean with bleach and soapy water |
|
|
|
What dust mite species are D. farinae and D. pteronyssinus included in?
|
Pyroglyphid species
-- most common offenders in the US |
|
|
|
What dust mite species is found in Florida, Puerto Rico, and Brazil?
|
Blomia tropicalis
|
|
|
|
What is the optimal temperatuer for dust mite growth? optimal relative humidity?
|
Temp: 65-80 F; 18-27 C
Humidity: >50% |
|
|
|
What are the 2 major dust mite allergens?
|
Der p1, Der f1
Der p2, Der f2 |
|
|
|
Which dust mite allergen is a tropomyosin and cross reacts with cockroach and shellfish?
|
Der p10
|
|
|
|
At what level of dust mites are predisposed individuals with atopy sensitized?
|
2-10 ug/g
|
|
|
|
What is the major cat allergen?
|
Fel d1
|
|
|
|
What level of Fel d1 predisposes susceptible people to sensitization? asthma?
|
Sensitization: >10 ug/g
Asthma: >20 ug/g |
|
|
|
What are the 5 major dog allergens? Which reacts with human PSA?
|
Can f1-5
Can f5 |
|
|
|
Which allergens are in the lipocalin family?
|
Can f1, Can f2, Can f4 (dog)
Rat n1 (rat); Mus m1 (mouse) Equ c1 (horse) Bos d2 and d5 (cow) beta lactoglobuin (cow's milk) Ory c1 (rabbit) Bla g1 (cockroach); NOT CAT!! |
|
|
|
What are the cockroach allergens and where do they come from?
|
Bla g1; Bla g2
---feces, saliva, debri |
|
|
|
What level of cockroach allergen is required for sensitization?
|
>10 ug/g
-- Large allergen |
|
|
|
Which allergens are carried on small particles and can remain in the air even when undisturbed?
|
Rat, mouse, cat
|
|
|
|
What is another name for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis
|
|
|
|
What is the scale that the US uses for Air Quality Index (AQI)?
|
Green: 0-50 (good)
Yellow: 51-100 (moderate) Orange: 101-150 (sensitive) Red:151-200 (unhealthy) Purple: 201-300 (very unhealthy) |
|
|
|
What pollutant is the precursor to photochemical smog?
|
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
--produced from fossil fuels, natural gas |
|
|
|
What is the major outdoor pollutant involved in asthma attacks?
|
Ozone
-- Keep <0.065 ppm |
|
|
|
What are the indoor pollutants?
|
tobacco smoke
endotoxin (animals, mold) Nitrogen dioxide (gas appliances) wood burning |
|
|
|
What are the Nonstandardized Units of Potency for allergen extracts?
|
Weight per Volume (w/v)
Protein Nitrogen Units/ml --PNU/ml |
|
|
|
Is there a bioequivalent relationship between w/v; PNU/ml; AU; BAU?
|
NO
|
|
|
|
What are the Standardized Units of Potency for allergen extracts?
|
Allergy Unit per ml (AU/ml)
Bioequivalent Allergy Unit per ml (BAU/ml) Major Allergen Content Venom protein content |
|
|
|
How are allergen extracts standardized by AU and BAU?
|
ID50EAL methol (by FDA)
---intradermal skin test endpoint titration in humans ---can also be determined by RAST or ELISA inhibition |
|
|
|
How are ragweed and cat extracts labeled?
|
by major allergen content in BAU
|
|
|
|
How are venom products standardized?
|
By venom protein content (hyaluronidase and phospholipase) in microgram per ml
--Individual species: 100ug/ml --Mixed vespid: 300 ug/ml |
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of standardized extracts?
|
Hymenoptera Venom (microgram of protein-- Hyal, phospho)
Dust mite (AU) Cat (BAU) Grass (BAU) Short Ragweed (major allergen- Amb a1) |
|
|
|
What forms are allergen extracts available in?
|
1. Aqueous
2. Glycerinated 3. Alum Precipitated 4. Lyophilized 5. Acetone Precipitated |
|
|
|
How are aqueous extracts prepared?
|
Raw source material is added to an extracting fluid and prepared in saline or buffer solution with less than 50% glycerin. 0.4% phenol is added to prevent bacterial growth.
|
|
|
|
How are glycerinated extracts prepared?
|
Raw source material is extracted into 50% glycerin. 50% glycerin inhibits microbial growth and is more stable than aqueous allergen. 0.4% phenol prevents microbial growth.
|
|
|
|
How are alum precipitated extracts prepared?
|
Allergic proteins are precipitated with aluminum hydroxide (alum), forming a complex--slower release. Not used in SPT, only IT. Can give larger doses in less frequent intervals. Less Systemics.
|
|
|
|
How are lyophilized extracts prepared?
|
Need to reconstitute powder. Recommended use Human Serum Albumin (HSA).
***Venoms use this*** |
|
|
|
How are Acetone- Precipitated extracts prepared?
|
Technique that make allergens more concentrated. Removed low molecular weight irritants. Takes about 50x as much raw materials. Used by Hollister Stier for cat, dog, cattle, horse, dust.
|
|
|
|
What factors cause allergen extracts to lose potency?
|
1. High Temperature-- 50% glycerin may protect at RT
2. Low Concentration- adhere to wall of vial 3. Large Vial Volume 4. Proteolytic Enzymes (cockroach, mold, dust mite) |
|
|
|
Do dust mite proteolytic enzymes affect pollens?
|
NO
|
|
|
|
What are the benefits of using 50% glycerin as a diluent?
|
maximizes allergen stability;
inhibits bacterial growth; inhibits proteolytic enzymes |
|
|
|
What are the benefits of using Human Serum Albumin as a dilutent?
|
Preservative effect
Minimizes binding of allergen to vial wall Protects from phenol denaturation |
|
|
|
What are the benefits of using phenol?
|
0.4% prevents microbial growth but it can break down allergenic proteins in extracts with 50% glycerin.
|
|
|
|
What are Thommen's postulates of Allergenicity (1931)?
|
1. Pollen must cause an allergic response (protein or glycoprotein)
2. Pollen must be wind pollenated (anemophilous) 3. Pollen must be produced in abundance, all over |
|
|
|
How big (microns) are the most significant aeroallergens?
|
10-60 microns
|
|
|
|
Define:
1) Anemophilous 2) Entomophilus 3) Amphophilous |
1) Anemophilous- wind pollenated
2) Entomophilus- insect pollenated 3) Amphophilous- insect and wind pollenated |
|
|
|
Define Pollination:
|
Transfer of pollen (~sperm) from the anter sac (~male) to the stigma (~female) of another plant
|
|
|
|
Define:
1) Monoecious 2) Dioecious |
1) Monoecious- plant species with male and female flowers on the same plant
2) Dioecious- species that have male and female flowers on different plants |
|
|
|
Describe a Durham Sampler.
1) Pros 2) Cons |

-Cover side with adhesive an let it sit outside for 24hrs
1)Pro= low cost, no power source 2) size dependent bias, don't know how much air its exposed too |
|
|
|
Describe a Settle Plate Pollen Sampler.
|
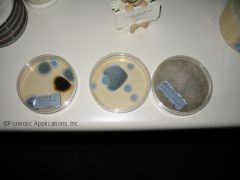
Particles settle onto agar medium and incubated prior to examining/counting molds
--indoor sampling |
|
|
|
Describe a Rotorod Sampler:
1) Pros? 2) Cons? |

Rod sweeps around and collects particles on greased slides. Divide #particles/volume air sampled
1) Pro= Not effected by wind direction 2) Con= can't get <10 micron spores |
|
|
|
Describe a Burkard Spore Trap.
1) Pro? 2) Con? |

Known amounts of air are sucked into sampling orifice. Tail keeps it oriented to the wind.
1) Pro= Collects <10 micron spores; consitent flow speed 2) more expensive |
|
|
|
Describe an Anderson Sieve Impinger Sampler.
|

Series of stages with up to 400 perforations; Air drawn in at 1 cubic foot/min; Particles pass through progressively smaller holes and are separated by size.
|
|
|
|
Describe an Allergenco Air Sampler.
|

Grab-type suction sampler collects samples on slides at programmed intervals.
|
|
|
|
Desribe a Liquid Impinger Sampling Device.
|

Draws air in and particles are suspended in liquid. Collect bioaerosols to examine immunochemically.
|
|
|
|
Describe a Cyclonic Collector.
|

Particles from dust collection are counted visually and may be cultured for fungi.
|
|
|
|
What 5 features are noted when describing pollen?
|
1. Size (microns)/ Shape
2. Surface Texture 3. Aperatures (pores, furrows) 4. Staining color 5. Exine (outer layer) or Intine (inner layer) |
|
|
|
What do you stain rod/slide surfaces with to define pollens collected?
|
Calberla's Solution
|
|
|
|
How do you count pollen?
|
Manually then conver to grains per cubic meter
|
|

