![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Schleiden and Schwann
|
___ and ____ proposed the cell theory that cells are the basic units of life.
|
|
|
1. Enclose the internal contents of cell.
2. Replicate genetic information. 3. Synthesize cellular components. 4. Generate, store, and utilize energy-rich compounds (metabolism) |
What are the functions essential to all cells?
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cell
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type that is simple, without membrane-bound internal structures
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cell
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type that is larger, more complex, and have several internal membrane-bound structures including the nucleus.
|
|
|
Diplococci
|
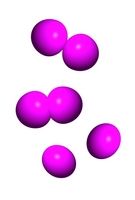
What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Streptococci
|

What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Cocci
Tetrads |
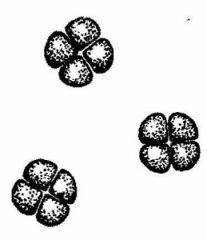
What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Cocci
Sarcinae |

What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Staphylococci
|

What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Diplobacilli
|

What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Streptobacilli
|
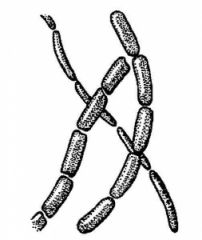
What is the shape and arrangement?
|
|
|
Vibrio
|
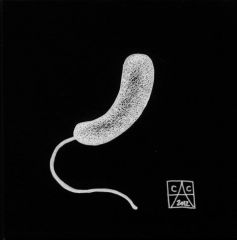
What is the shape?
|
|
|
Spirillum
|

What is the shape?
|
|
|
Spirochete
|
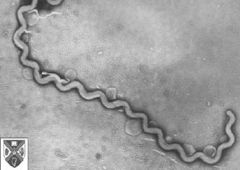
What is the shape?
|
|
|
Pleomorphic
|
_________ means many forms
|
|
|
monomorphic
|
________ means one form
|
|
|
Monotrichous
|
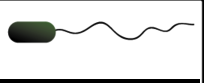
What is the location of the flagella?
|
|
|
Lophotrichous
|
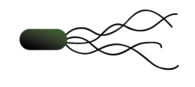
What is the location of the flagella?
|
|
|
Amphitrichous
|

What is the location of the flagella?
|
|
|
Peritrichous
|
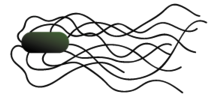
What is the location of the flagella?
|
|
|
Endospore
|
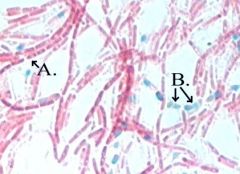
This special stain procedure is used to visualize __________
|
|
|
Acid Fast stain
Gram stain |
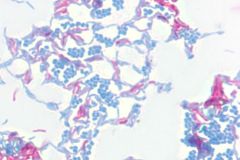
Differential stains for cell wall type are ___ and ____
|
|
|
Capsule
|
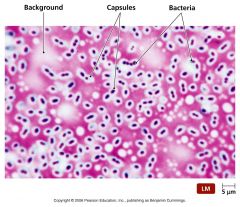
This special stain procedure is used to visualize the ____
|
|
|
Slime layer
|
Type of glycocalyx that is loosely attached and unorganized is a ______
|
|
|
Capsule
|
Type of glycocalyx that is firmly attached and organized is a _______
|
|
|
polysaccharides, polypeptides or both
|
What are most capsules are composed of?
|
|
|
1. Protects pathogens from phagocytosis
2. Aids in attachment to surfaces 3. Provides nutrients 4. Protects the cell from dehydration and loss of nutrients |
What are the functions of the bacterial capsule?
|
|
|
1.Strengthens cell surface
2.Attachment 3.Cell to cell recognition |
What are the 3 functions of the eukaryotic glycocalyx?
|
|
|
filament
hook basal body |
Name the three parts of a bacterial flagellum
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with no sheath around flagella.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with single filament flagella made of the globular protein flagellin.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with an flagella that rotates.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with fimbriae.
|
|
|
Chemotaxis
|
Bacteria move toward food sources and away from harmful materials using _____
|
|
|
Phototaxis
|
Movement stimulated by light is ________
|
|
|
Aerotaxis
|
Movement stimulated by oxygen is _____
|
|
|
Magnetotaxis
|
Movement toward or away from the earths poles is______
|
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with a flagella that is a bundle of microtubules made of the protein tubulin
|
|
|
Eukaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type that has flagella and cilia that move in a whip-like motion to push or pull the cells.
|
|
|
Eukaryote
Prokaryote- axial filament of a spirochete |
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with a flagella that is covered by a sheath
|
|
|
9 pairs surrounding 1 pair
|
What is the arrangement of the bundle of microtubules of cilia and flagella?
|
|
|
Axial Filaments
|
What are bundles of fibrils twisted around the spirochete and covered by a sheath?
|
|
|
Halophiles
|
What type of bacteria do not need a strong cell wall?
|
|
|
Fimbriae
|
____ are protein appendages of attachment in bacteria
|
|
|
Adhesins
|
____ are proteins at the fimbriae site of attachment which adhere to host cell receptors.
|
|
|
Pili
|
____ are protein appendages for the transfer of DNA during conjugation.
|
|
|
Pilin
|
The protein found in fimbriae and pili is _______
|
|
|
1) Prevents rupture from osmotic pressure
2) Maintains shape Anchors flagella |
What are the 2 functions of the cell wall?
|
|
|
Gram positive
|
Cell wall structure composed of multiple layers of peptidoglycan with teichoic acid is _____
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with simple plasma membranes that lack sterols.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with a long, double-stranded, circular DNA molecule.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with DNA that is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
|
|
|
1) Regulates the movement of cations
2) Regulates the activity of autolysins 3) Storage of phosphate Antigenic specificity |
List the 3 functions of teichoic acid
|
|
|
Gram negative
|
Cell wall structure composed of a single layer of peptidoglycan with several other additional layers. These include lipoprotein, lipopolysaccharide, and phospholipid is ______
|
|
|
Lipid A component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
|
What is the chemical composition of endotoxin?
|
|
|
1) Evade phagocytosis and complement
2) Barrier to some antibiotics, detergents, enzymes (lysozyme) and dyes (methylene blue) and heavy metals |
List the functions of outer membrane
|
|
|
Acid fast
|
Cell wall structure composed of teichoic acid and mycolic acid (waxy lipid) is _____
|
|
|
Archaea
|
_______ are prokaryotes that have no peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
|
|
|
Mycoplasma
|
______ are bacteria that lacks a cell wall but has sterols in the plasma membrane for strength
|
|
|
Animals
Protozoans |
__ and ____ are organisms with cells that lack cell walls
|
|
|
Fungi
|
_______ are organisms with chitin cell walls
|
|
|
Algae
Plants |
___ and ____ are organisms that have cell walls composed of primarily cellulose
|
|
|
prokaryotic cytoplasmic membrane
|
The _________ is a bilayer membrane composed of protein and phospholipids.
|
|
|
1) site of enzymes of energy generation
2) controls the exit and entrance of molecules by the mechanisms of diffusion and active transport |
List the functions of the prokaryotic plasma membrane
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cytoplasmic membrane
|
The _______ has phospholipid bilayer has sterols and sugars attached to the lipids and proteins.(glycolipids and glycoproteins)
|
|
|
1) forms a series of membranes called the endoplasmic reticulum. Other internal membranes surround structures such as lysosomes and the Golgi.
2) controls the exit and entrance of molecules by the mechanisms of diffusion and active transport. |
List the functions of the eukaryotic plasma membrane
|
|
|
Cytosol
|
______ is the viscous, semi-transparent medium. 80% water
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
_____ is the region of the cell internal to the plasma membrane but exclusive of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with only one or several identical chromosomes present per cell.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type without histones.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with 70S ribosomes only.
|
|
|
Plasmids
|
_______ are small DNA molecules that code for nonessential information and replicate independently of the chromosome.
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type that may have plasmids.
|
|
|
Eukaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type in which genetic information is contained in multiple linear chromosomes, each of which carries different information.
|
|
|
Eukaryote
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with histones associated with DNA.
|
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type with 80S ribosomes in cytosol.
|
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type that DNA contains introns and exons which require modification of the mRNA after transcription.
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
_______ are structures on which proteins are synthesized
|
|
|
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts |
Where are 70S ribosomes found in eukaryotes?
|
|
|
ribosomal protein
ribosomal RNA |
What are ribosomes composed of?
|
|
|
Metachromatic granules
|
Granule where phosphate is stored as volutin is a _______
|
|
|
Polysaccharide granules
|
_______ are granules that contain stores of glycogen or starch
|
|
|
Lipid inclusion
|
_______ are inclusions that contain stores of lipid
|
|
|
Sulfur granules
|
______ are granules that contain stores sulfur
|
|
|
Carboxysomes
|
________ are storage centers for the enzyme carboxylase used by photosynthetic organisms
|
|
|
Gas vacuole
|
_______ is a vacuole that stores air for buoyancy
|
|
|
Magnetosomes
|
______ is a storage center for iron oxide
|
|
|
endospore
|
A _______ is a unique cell type that develops from actively multiplying cells (vegetative cells) when they face starvation and dehydration.
|
|
|
Sporulation
|
Endospore formation is called _______
|
|
|
Germination
|
Formation of the vegetative cell from an endospore is called _______
|
|
|
Bacillus and Clostridium
|
What are the two endospore-producing bacteria that cause disease in animals and humans?
|
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
_________ (prokaryote/eukaryote) is a cell type in which energy is generated by mitochondria and chloroplasts.
|
|
|
Endosymbiotic Theory
|
What is the theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free-living bacteria?
|
|
|
Bacillus
palisades |
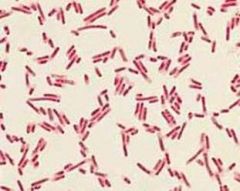
What is the shape and arrangement?
|

