![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is destructive testing? |
It refers to a range of tests that ultimately result in the destruction of a material or product |
|
|
What is meant by 'hardness' |
Hardness is the ability of a material to resist abrasive wear, indentation or deformation |
|
|
Brinnel test |
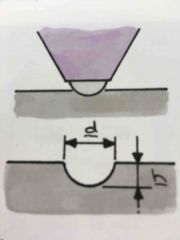
When a hardened steel ball is forced in to a materials surface to find its hardness.
Calculated using the diameter and depth of the indentation
|
|
|
Vickers test |
Process that uses a diamond pyramid to indent a material to test for hardness
Calculated using the surface area of the indent and the load |
|
|
What is tensile testing |
Tensile testing involves putting material under tension by stretching to provide information regarding tensile strength, elasticity and plastic properties such as malleability and ductility |
|
|
Impact tests |
Impact tests indicate the toughness of a material and its response to mechanical shock |
|
|
3 main methods of impact testing |
• The Izod test • The Charpy test • The Houndsfield test |
|
|
Example of a product that would be used for fatigue testing |
Plastic chairs |
|
|
What is global manufacturing |
It is when a product is designed in one part of the world and manufactured in another where it's cheaper |
|
|
9 P's of marketing mix |
- Product - Price - Place - Promotion - process - Physical evidence - Properties - Pleasure - People |
|
|
What is technology push |
Technology push is when research and development in new technology, drives the development of new products. |
|
|
What is market pull |
Market pull is when product ideas are produced in response to market forces. |
|
|
4 criteria's to patent a product |
• It must be new • It must involve an inventive step • It must be capable of industrially made • It must not be excluded |
|
|
What is the design right |
This is when designers can protect their designs they have created |
|
|
What are patents |
This is when an inventor or designer can protect their inventions from others who try to copy them |
|
|
Ecolabel |
It is a voluntary scheme where manufacturers are encourage to to label products that have a reduced impact on the environment over their life cycle |
|
|
What is the WEEE Directive |
• stands for waste electrical and electronic equipment directive
• Encourages manufacturers to develop electrical products that can be dismantled for reuse or recycling |
|
|
What is the green design |
An approach in design to reduce the impact on the environment |
|
|
What is ecodesign |
• An approach that goes further than the green design • Try to reduce the impact of a product through its entire life-cycle |
|
|
Possible ecodesign idea to make a 'green' tv |
- Combine TV and DVD player to reduce materials used - Remove standby features so it has to be switched off - Use low energy circuits - Use LCD display as it uses less power |
|
|
Environmental impact of cars |
- manufacturing processes and painting use lots of energy and produce large amounts of emissions - Petrol or diesel produces lots of CO2 - |
|
|
What are the main ways manufacturers ensure the safety of their employees |
- Training - Guarding on machines - Personal protective equipment - Extraction - COSHH |
|
|
Products that use nanotechnology |
• Vehicles • Clothing • Electrical consumer goods • Medical
|
|
|
4 stages of a product life cycle |
1. Introduction 2. Growth 3. Maturity 4. Decline |
|
|
What is planned obsolescence |
This is when companies deliberately design products to have short life cycle so that they can then produce better versions and keep sales high |
|
|
What is Quick Response Manufacturing (QRM) |
This is when products are made once an order has been placed
Example: Cars |
|
|
What is Electronic Point Of Sale (EPOS) |
This is when products are barcodes and scanned at checkout. This allows the system to know when stock is getting low and when re-stocking is needed |
|
|
What is Just In Time (JIT) production |
This is when manufacturers organise their suppliers to deliver materials just in time for their use.
This stops the need for lots of storage space |
|
|
What is telematics |
A system for tracking a product from customer order through to manufacture and dispatch |
|
|
What is Master Production Schedule (MPS) |
This is a scheduling system used to organise the work to be completed with a set time period |
|
|
Example of a product via batch production |
Cars |
|
|
Example of products that are mass produced |
- Shoes -Clothes - Household appliances |
|
|
Example of products via continuous production |
- Oil - Glass |
|
|
Benefits of using robots |
- Can do repetitive tasks that humans dislike - Carry out physically demanding jobs - Work in hazardous areas - Very accurate and precise - Work for long periods of time |
|
|
Drawbacks of using robots |
- Poor mobility and flexibility - High set up costs - Employment issues |

