![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Diaphysis vs proximal and distal epiphysis |
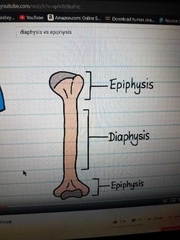
|
|
|
|
Spongy (cancelous) vs compact bone |
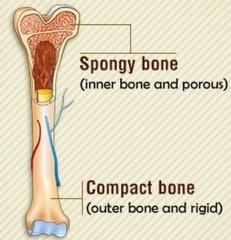
|
|
|
|
Medullary Cavity |
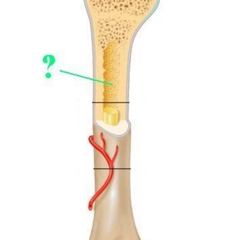
Contains the bone marrow. |
|
|
|
Epiphyseal Line |
Remnant of the epiphyseal plate, site of growth during childhood. |
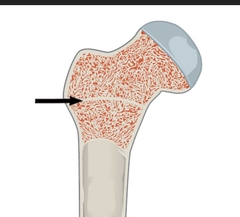
|
|
|
Nutrient Foramina |
Small holes where blood vessels enter the bone. |
|
|
|
Articular Cartilage |
Covers the portion of the bone found in the joint. |
|
|
|
Periosteum |
a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the joints of long bones. |
|
|
|
Endosteum |
a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the medullary cavity of long bones. |
|
|
|
Sesemoid Bones |
a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. |
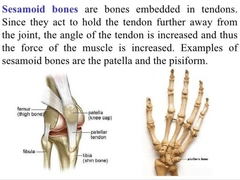
|
|
|
Holes in Bone (usually passageways for nerves or blood vessels) |
Meatus, foramen, canal, fissure |
|
|
|
Fossa |
A depression or basin in a bone. |
|
|
|
Process, Trochanter, Tubetosity, Tubercle |
Projections on bone, usually sites of muscle attachment |
|
|
|
Spine, line, crest |
Ridges on a bone |
|
|
|
Condyle |
Rounded articular surface. |
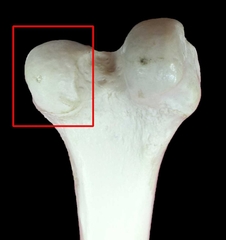
|
|
|
Lambdoid Structure (skull) |
a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. |
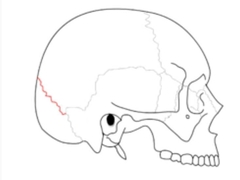
|
|
|
Sagittal structure (skull) |
a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. |
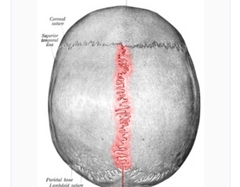
|
|
|
Coronal structure |
a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull. |
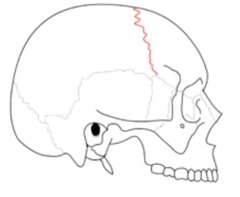
|
|
|
Fontanelle |
an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising any of the soft membranous gaps (sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. •Anterior frontanel is the biggest |
|
|
|
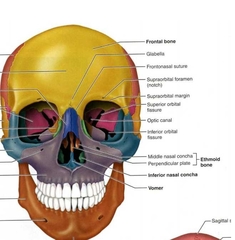
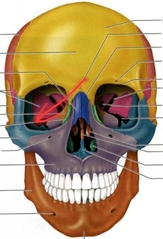
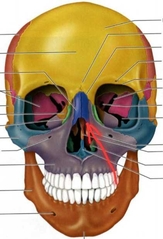
Paranasal Sinus |
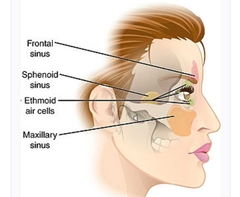
a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. |
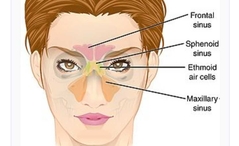
The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located |
|
|
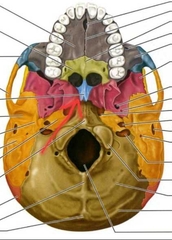
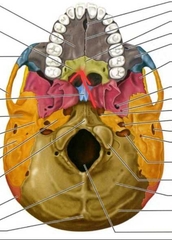
Jugular Foramen |
Passageway for jugular vein and several cranial nerves. |
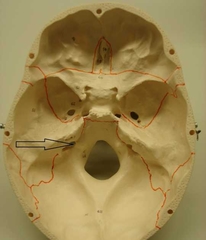
|
|
|
Zygomatic Arch |
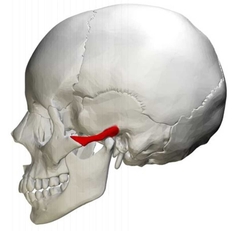
|
|
|
|
CN |
Cranial Nerves I-XII |
|
|
|
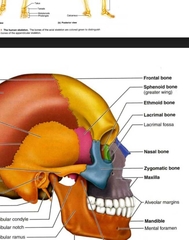
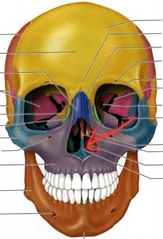
Frontal (Cranial Bones) |
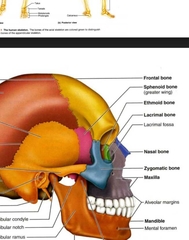
|
|
|
|
Parietal PAIRED (Cranial Bones) |
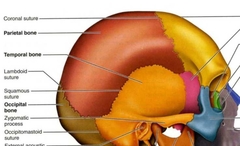
|
|
|
|
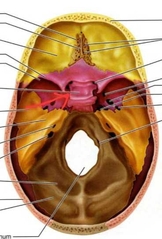
Occipital (Cranial Bones) |
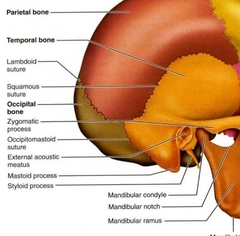
|
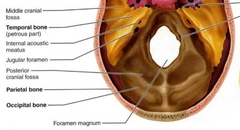
|
|
|
Occipital (Foramen Magnum) |
Spinal cord leaves the skull through this large hole. |
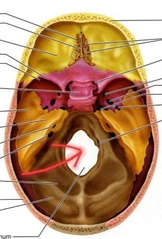
|
|
|
Occipital (Occipital Condyles) |
Articulation with atlas. [C1] |
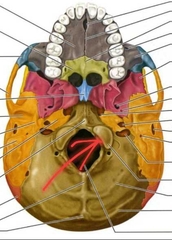
|
|
|
Temporal PAIRED (Cranial Bones) |
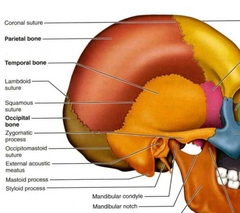
|
|
|
|
Temporal (External Acoustic Meatus) |
External ear canal, carries sound to ear. |
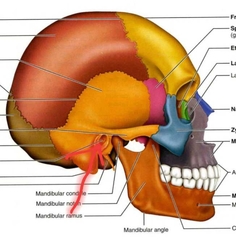
|
|
|
Temporal (Internal Acoustic Meatus) |
Within the cranium, passage for the facial and vestibulocochlear cranial nerves |
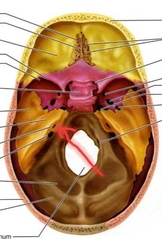
|
|
|
Temporal (mastoid process) |
Attachment site of muscles that move the head. |
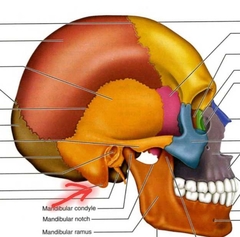
|
|
|
Temporal (Zygomatic Process) |
Posteroir part of the zygomatic arch. |

|
|
|
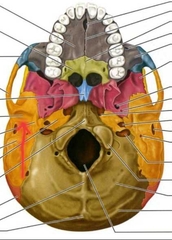
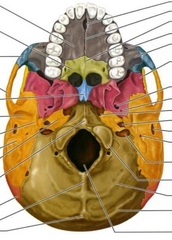
Temporal (Mandibular Fossa) |
Articulates with the mandibular condyle to form the TMJ) |
|
|
|
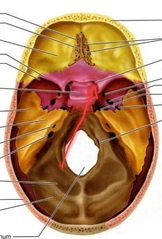
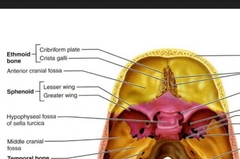
Sphenoid (Cranial Bone) |
|
|
|
|
Sphenoid (Hypophyseal Fossa) |
Part of the larger sella turcica. Contains the hypophysis (pituitary) gland. |
|
|
|
Sphenoid (Optic Canal) |
Passage for the optic nerve (CNII). |
|
|
|
Sphenoid (Superior Orbital Fissure) |
Passage for cranial nerves and blood vessels. |
|
|
|
Ethmoid |
|
|
|
|
Ethmoid (Crista Galli) |
Attachment point for meninges. Think rooster. |
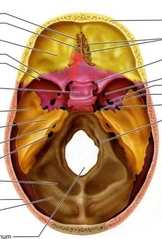
|
|
|
Ethoid (Olfactory Foramina) |
Passage for the olfactory nerve (CN I). Think holes. |
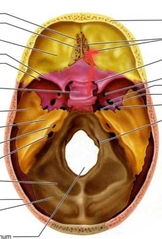
|
|
|
Ethoid (Perpendicular Plate) |
Superior part of bony nasal septum. |
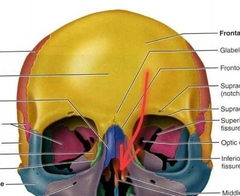
|
|
|
Ethoid (Middle Nasal Conchae (turbinates)) |
Increases surface area of nasal cavity, aiding in warming and moisturizing inhaled air. |
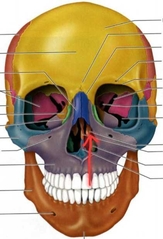
|
|
|
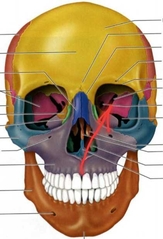
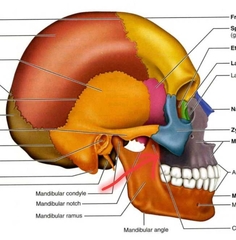
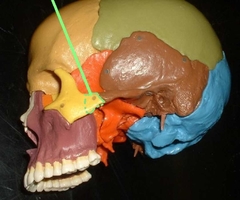
Zygomatic Bones (Zygoma) PAIRED (Facial Bones) |
|
|
|
|
Zygomatic Bones (Temporal Process) |
Anterior part of the zygomatic arch. |
|
|
|
Nasal PAIRED |
|
|
|
|
Lacrimal PAIRED |
|
|
|
|
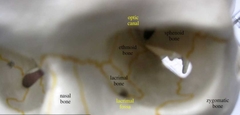
Vomer (Facial Bones) |
The inferior most portion of the bony nasal septum. |
|
|
|
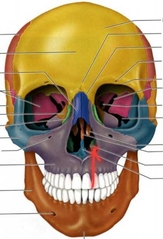
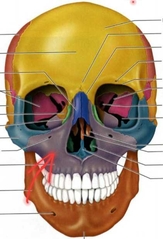
Inferior Nasal Concha PAIRED (Facial Bones) Not ethmoid |
|
|
|
|
Palatine PAIRED (Facial Bones) |
Forms posterior portion of hard plate. |
|
|
|
Maxilla PAIRED (Facial Bones) |
|
|
|
|
Maxilla PAIRED (Infraorbital Foramen) |
Contains nerves and blood vessels for Infraorbital region of face. |
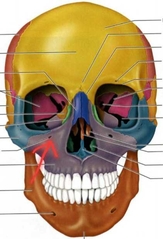
|
|
|
Maxilla & Mandible (Alveolar Process) |
Bony mass containing roots and teeth. |
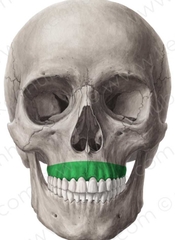
|
|
|
Maxilla & Mandible (Alveolar Margin) |
Edge of the alveolar process. This recedes with gum disease until eventually the teeth fall out as the roots are no longer supported. |
|
|
|
Maxilla (Palatine Process) |
Forms the anterior 2/3 of the hard plate. |
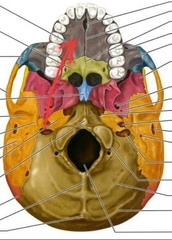
|
|
|
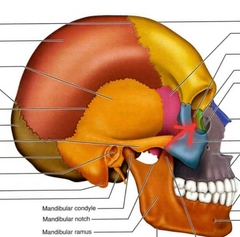
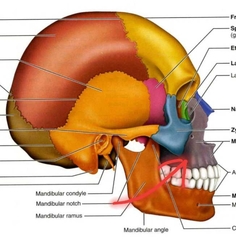
Mandible (Facial Bones) |
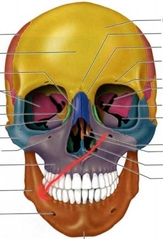
|
|
|
|
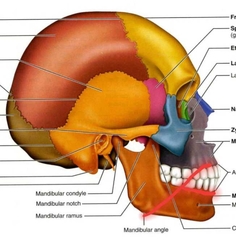
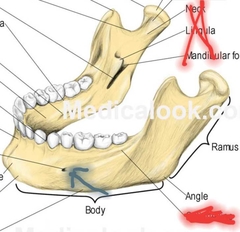
Mandible (Body, Angle, Ramus) |
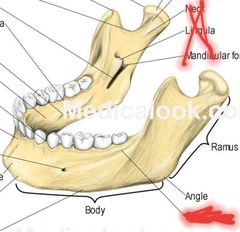
|
|
|
|
Madible (Coronoid Process) |
Attachment for muscles of mastification. |
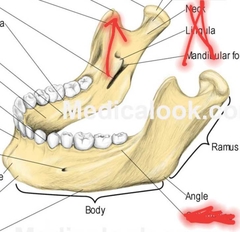
|
|
|
Mandible (mandibular condyle/condylar process) |
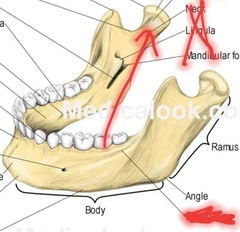
|
|
|
|
Mandible (mental foramen) |
Passage for blood vessels and nerves to mental region of face. |
|
|
|
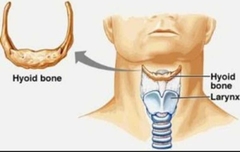
Hyoid Bone |
Not a skull bone or a vertebral bone. It is an integral part of the larynx structure and is held in position by ligaments and muscles. |
|
|
|
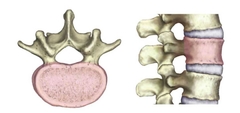
Vertebral Body |
Compression fractures are common with osteoporosis and associated with kyphosis, pinched spinal nerves, and loss of height. |
|
|
|
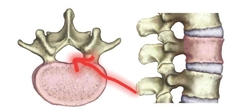
Vertebral Foramen = lamina + pedicle |
The spinal cord runs through themis large opening. Together, they make up the spinal cord. |
|
|
|
Vertebral Arch |
This surrounds the spinal cord, and the spinous and transverse processes project from it. |
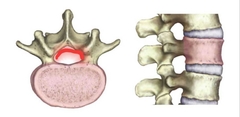
|
|
|
Traverse Process |
Many muscles of the neck and back originate and insert here. |
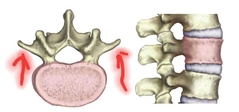
|
|
|
Spinous Process |
Many muscles of the neck and back origniate here. |
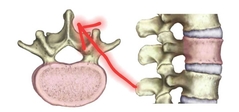
|
|
|
Superior and Inferior articular facets |
This is where each vertebra atriculates with the vertebra above and below it. |
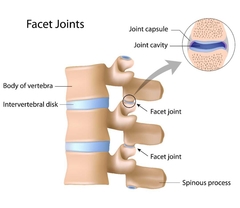
|
|
|
Intervertebral Formen |
The hole between adjustment vertebrae where spinal nerves exit the spinal cord. |
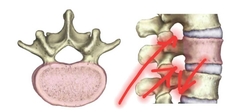
|
|
|
Cervicle Vertebrae c1-c7 |
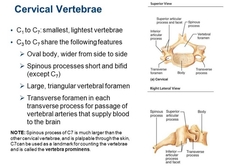
|
|
|
|
C1 & C2 Atlas and Axis |
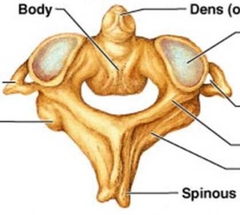
Axis |
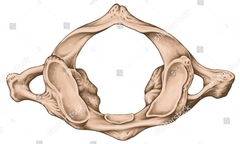
Atlas |
|
|
Odontoid Procress |
During embryonic development, the body of the atlas and axis become fused. |
|
|
|
C7 |
This spinal process is much larger than the others and is visible through the skin. This is used as a clinical landmark, and is called the vertebra prominens. |
|
|
|
Thoracic Vertebra |
(T1-T12) No traverse foramina |
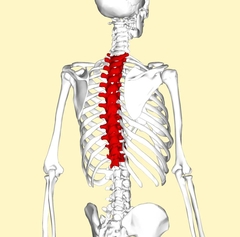
|
|
|
Lumbar Vertebrae |
L1-L5 Lcan be identified by their bodies and short spinous processes. |
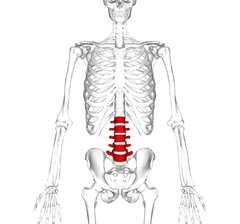
|
|
|
Sacrum S1-S5 |
Formed a fusion of 5 vertevrae during development. |
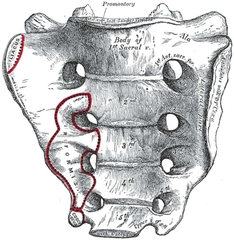
|
|
|
Sacral Canal |
Spinal nerves from the spinal cord run through this hole, which is continuous with the vertebral Foramen. The spinal cord ends at approximately L1 |
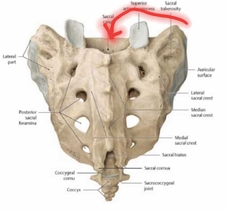
|
|
|
Sacral Foramina |
Spinal nerves exit/enter the sacral canal through thise wholes. |
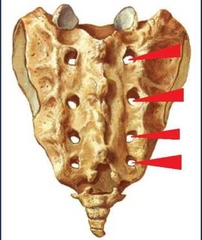
|
|
|
Coccyx |
Formed from the fusion of several samll vertebrae. It is the vestige of a tail. |
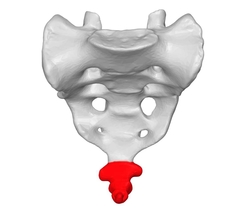
|
|
|
Manubrium |
Articulates with the sternal (midial) end of the clavicle. |
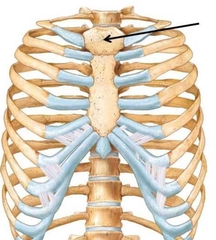
|
|
|
Jugular Notch |
Clinical Landmark |
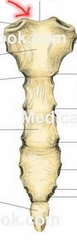
|
|
|
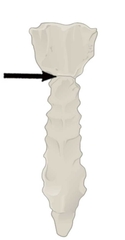
Sternal Angle |
Important clinical landmark |
|
|
|
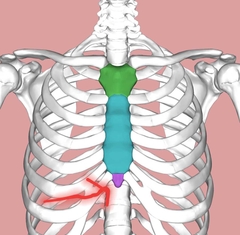
Xiphoid Process |
•Important clinical landmark. A strip of tendon called the linea alba runs from the siphoid process to the pubic sysmphysis of the pelvis and divides the rectus abdominus muscle. |
|
|
|
Features of ribs |
•1-7 are true ribs. •8-12 are false ribs because their costal cartilage does not articulate with the sternum directly. •11-12 are floating ribs because their anterior extremity does not attach to the sternum at all. |
|
|
|
Rib Notes |
•Each rib articulates with the vertebrae at two points: proximally with the vertebral body and laterally with the transverse process. •All rib articulations with the vertbrae are synovial joints, and all the sternocostal articulations except for the first rib are also synovial joints. Synovial joints are are the most common type of joint and will be discussed lated with tibiofemoral joint in detail. |
|
|
|
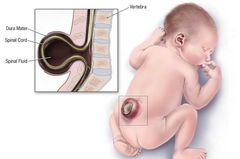
Spina bifida |
Spina bifida is a birth defect where there is incomplete closing of the backbone and membranes around the spinal cord. |
|
|
|
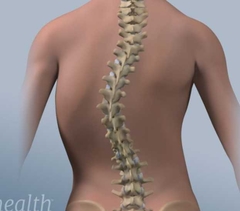
Scoliosis |
Scoliosis is a medical condition in which a person's spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually "S"- or "C"-shaped. |
|
|
|
Kyphosis |
an abnormally excessive convex kyphotic curvature of the spine as it occurs in the cervical, thoracic and sacral regions. Kyphosis can be called roundback or Kelso's hunchback. |
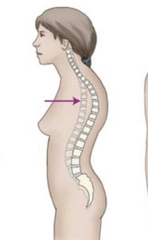
|
|
|
Lordosis |
the normal inward lordotic curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. |

|
|
|
Clavical |
Most common bone broken. •Sternal End (midial) •Acromial End (lateral) |
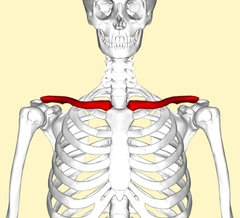
|
|
|
Scapula |
. |
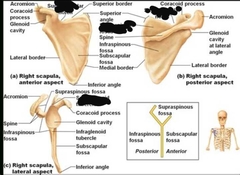
|
|
|
Bony fratures of upper arm (Humerus) |
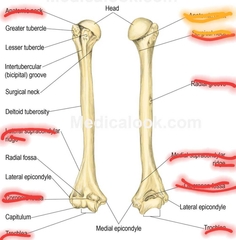
|
|
|
|
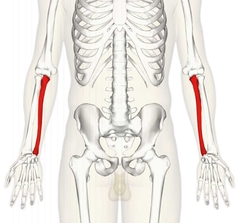
Ulna |
Olecranon- Elbow; insertion of triceps brachii Styloid Process- distal |
|
|
|
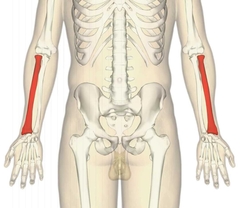
Radius |

•Styloid Process •radial tuberosity |
|
|
|
Carpals (8 bones) |
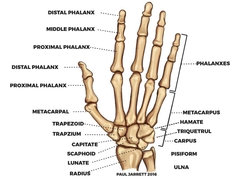
Memorize 14 phalanx (phalanges) 5 metacarpal |
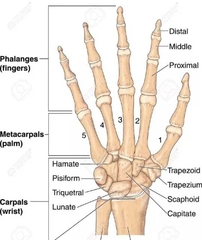
|
|
|
Coxal (Ilium) |
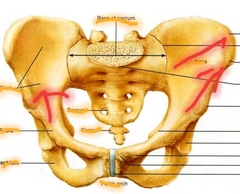
|
Iliac Crest Anterior superior iliac spine Greater sciatic notch |
|
|
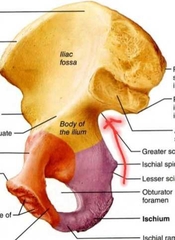
Coxal (Ischium) |
|
Ischial Tuberosity |
|
|
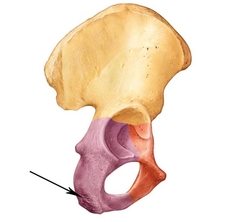
Coxal (Pubis) |
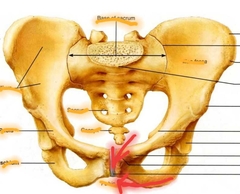
|
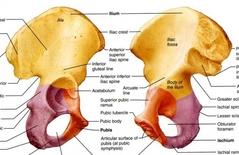
Pubic Symphysis Pubic Arch |
|
|
Femur |
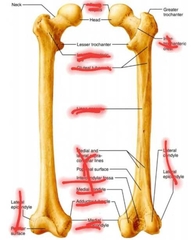
|
|
|
|
Patella (Sesamoid bone) |
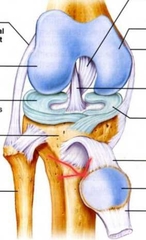
|
|
|
|
Tibia & Fibula |
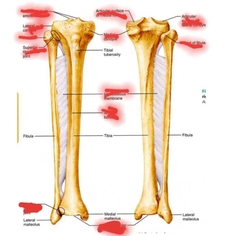
|
|
|
|
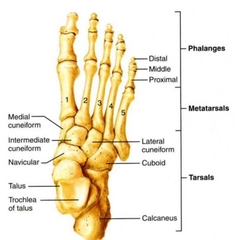
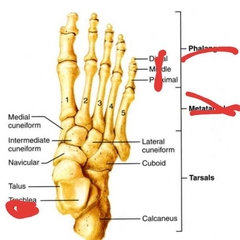
Tarsals |
|
|
|
|
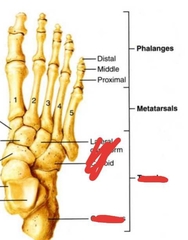
Metatarsals & Phalanges |
|
|
|
|
Synovial Joints |
Freely Movable joints |
|
|
|
Cartilaginous Joints |
Slightly movable |
|
|
|
Fibrous joints |
Immovable |
|
|
|
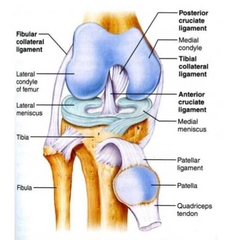
Tibiofemoral Joint |
|
|
|
|
Synovial Joint Structures |
•Joint Cavity/synovial cavity •Articular cartilage •synovial membrane •Fiberous Capsule |
|

