![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
2 Types of Reproduction
|
Asexual - s/ gametes (eggs and sperm)
Sexual - c/ gametes |
|
|
|
d/ GAMETE
|
a mature male or female germ cell usually possessing a haploid chromosome set and capable of initiating formation of a new diploid individual by fusion with a gamete of the opposite sex -- called also sex cell
|
|
|
|
d/ HAPLOID
|
having the gametic number of chromosomes or half the number characteristic of somatic cells
|
|
|
|
d/ DIPLOID
|
having the basic gametic chromosome number doubled
|
|
|
|
d/ SPERMATOGENESIS
|
meiosis that occurs in the testes
|
|
|
|
d/ OOGENESIS
|
meiosis that occurs in the ovaries
|
|
|
|
capsule outside the testes
|
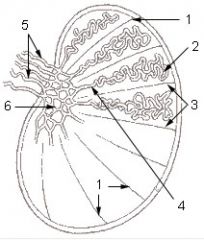
d/ TUNICA ALBUGINAE
|
|
|
|
d/ the LOBULES of the testes
|
sections (like a grapefruit) of the testes
|
|
|
|
how many LOBULES are there?
|
250 or so each testes
|
|
|
|
d/ SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE
|
30' long tube inside lobule where spermatogenesis occur
|
|
|
|
d/ SPERMATOGENSIS
|
male version of gametogensis (by meiosis), male spermatogonia develop into mature spermatozoa
|
|
|
|
d/ INTERSTITIAL CELLS and ANDROGENS of seminerferous tubules?
|
surround tubules and secrete hormones called Androgens
|
|
|
|
d/ ANDROGENS
|
male sex hormones
|
|
|
|
d/ TESTOSTERONE
|
the main androgen responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics
|
|
|
|
d/ SCROTUM
|
outside the body cavity that contain the testes
|
|
|
|
What is the most site for male Cancer?
|
Prostrate gland
|
|
|
|
Does PROSTRATE GLAND normally grow in size your entire life?
|
yes
|
|
|
|
What is the problem assoc with prostrate growth?
|
Squeezing urethra thus making urinating difficult
|
|
|
|
Would Dr treat prostrate enlargment in 50-60's and in 80-90's?
|
50-60 yes 80-90 no
|
|
|
|
Fx of PROSTATE GLAND
|
i1 - Secretes 50% of seminal fluid 2 - Makes semen alkaline
|
|
|
|
What is the benefit of the semen being alkaline?
|
Alkaline fluid makes semen more motile
|
|
|
|
How many columns of erectile spongy tissue are in Penis?
|
3
|
|
|
|
d/ PASSIVE HYPEREMIA
|
|
|
|
|
d/ PARASYMPATHETIC NS affect during errection?
|
during sexual excitement
|
|
|
|
1 mL of seminal fluid contains how many sperm cells
|
120 million
|
|
|
|
how much seminal fluid per ejaculation?
|
1-5 ml
|
|
|
|
How much sperm in seminal fluid to be considered sterile?
|
LEss than 20 million
|
|
|
|
Menstraul Cycle is also called the __________?
|
Estracycle
|
|
|
|
d/ MENSTRUAL/ESTRACYCLE?
|
28 day cycle that involves regular
|
|
|
|
d/ 2 Layers of the uterus
|
stratum basilum and stratum functionalis
|
|
|
|
Which layer of the emdometrium does the fertilized egg bury itself?
|
Stratus Functionalis
|
|
|
|
d/ OVULATION
|
release of egg by the ovary
|
|
|
|
d/ MENSTRUATION
|
ireleae of ticked endometrial layer
|
|
|
|
What hormone is responsible for Menses?
|
Reduction in Progesterone level is responsible for Menses onset
|
|
|
|
d/ MENARCHY
|
1st period cycle at puberty
|
|
|
|
What hormones are responsible for the onset of Menarchy?
|
FSH and LH
|
|
|
|
d/ MENOPAUSE
|
iAt approx 45-50 yrs menstrual cycle ceases. This is due to lack of ovarian secretion called estrogen
|
|
|
|
MENSTRUAL CYCLE occurs in the ____________
|
while the OVARIAN CYCLE occurs in the ovaries
|
|
|
|
d/ OOCYTE
|
an egg before maturation
|
|
|
|
How many OOCytes does a baby girl have?
|
1000's
|
|
|
|
d/ FSH fx
|
In both males and females
|
|
|
|
d/ LUTEINIZING HORMONE
|
This 'LH surge' triggers ovulation hereby not only releasing the egg
|
|
|
|
d/ Day 1 of the Menstrual Cycle
|
little activity except FSH increases
|
|
|
|
d/ Day 1-5 of Menstrual Cycle
|
1 - Stratum Functioalis is lost 2 - FSH reaches peak 3 - primary follicle become 20 secondary follicles 4 - Estrogen increases (fr follicles)
|
|
|
|
d/ Day 6-13 pre-ovulatory phase
|
1 - one Graafian follicle will surviv 2 - Edometrium thickens due to estrogen 3 - FSH declines 4 - LH increases and peaks on day 12-13
|
|
|
|
d/ Day 14 Ovulation
|
Follicle releases egg an becomes Corpus luteum (yellow body) and secretes Progesterone (for 10 days)
|
|
|
|
Fx of PROGESTERONE
|
1 - maintain endometrium (no menstruation) 2 - Inhibit FSH (so wont start a new follicles)
|
|
|
|
d/ what Hormone is used for birth control
|
Progesterone b/c it stops menstruation
|
|
|
|
d/ day 14-24 if no fertiliation occurs
|
i1 - Corpus Luteum atrophies in 10 days (day 24) 2 - on day 24 Progesterone stops thf menstruation starts and FSH is secreted again
|
|
|
|
d/ day 19-24 if fertiliation does occur
|
1 - Implantation would occur 5-7 days after ovulation 2 - HCG (fr Chorion layer of blastocyte) fx to maintain Corpus Luteum for 3 months 3 - p/ 3m Placenta secretes Progesterone and Estrogen The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ fx of Ovaries
|
1 - produce ova 2 - produce Estrogen and Progesterone The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ fx of ESTROGEN
|
to stimulate and maintain secondary sex charectoristics and responsible for the onset of the menstrual cycle The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
What parts consist of the OVIDUCT
|
Fallopian tube and uterus The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
|
fallopian tube pregnancy The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
fx of the FALLOPIAN TUBE
|
to transport the egg (zygote or blastocyte) day 10 embryo forms The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
Where is the FUNDUS and CERVIX of the UTERUS
|
top portion is the FUNDUS (thickest) and the bottom portion is the CERVIX (thinnest) The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ MYOMETRIUM of the Uterus
|
Muscular portion The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ ENDOMETRIUM of the uterus
|
Mucous membrane The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ HYSTERECTOMY
|
removal of the uterus The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
Fx of the VAGINA
|
1 - recieves penis 2 - duct for removal of thickened layer 3 - birth canal The correct answer is: None Of The Above
|
None
|
|
|
d/ parts of the VULVA 1. Dummy Answer
|
Mons Veneris
|
|
|
|
Second dummy question
|
Second dummy answer
|
|
|
|
Third dummy question
|
Third dummy answer
|
|

