![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sagittal |
Divides body into left and right sections |
|
|
Frontal/Coronal |
Divides anterior from posterior |
|
|
Transverse |
Divides superior from inferior |
|
|
Cephalad |
Towards the head |
|
|
Dorsal Body Cavity contains... |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Ventral Body Cavity contains... |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
Tissues are |
groups of cells with similar appearance and functions |
|
|
What are the four types of tissue? |
Epithelial, muscle, nerve, connective |
|
|
What is the main function of epithelium? |
Covering and lining |
|
|
What are three distinct functions of epithelium? |
Filtration, secretion, diffusion |
|
|
Are epithelial tissues vascular or avascular? |
Avascular |
|
|
Do epithelial tissues regenerate? |
Yes - think skin |
|
|
What are the two classifications of epithelium? |
Simple - 1 layer thick Stratified - More than 1 layer thick |
|
|
What are the three shapes of epithelium? |
Squamous Cuboidal Columnar |
|
|
What is the main function of simple squamous epithelium? |
Diffusion and secretion |
|
|
Where is simple squamous epithelium found? |
Alveoli and capillaries |
|
|
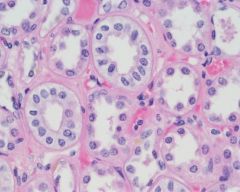
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
What is the main function of simple cuboidal epithelium? |
Secretion and Absorption |
|
|
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium found? |
Kidney tubules, ducts, secretory portions of small glands, surface of ovaries |
|
|
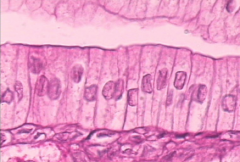
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium? |
Absorption, secretion of mucous, ciliated type propels |
|
|
Where is simple columnar epithelium found? |
The GI tract, gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands |
|
|
What is the function of pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium? |
Secretion and propulsion of mucous |
|
|
Where is pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium found? |
Male's sperm-carrying ducts, ducts of large glands, ciliated type found in trachea and upper respiratory tract |
|

|
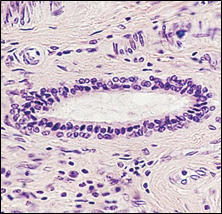
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
What is the main function of stratified squamous epithelium? |
Protection of underlying tissues from abrasion |
|
|
Where is stratified squamous epithelium found? |
Esophagus, mouth, vagina (non-keritinized), epidermis (keritinized) |
|
|
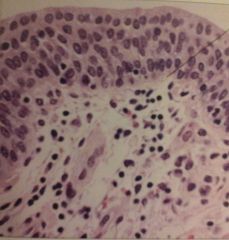
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
What is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium? |
Protection |
|
|
Where is stratified cuboidal epithelium found? |
Larger glands of body |
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
What is the main function of stratified columnar epithelium? |
Protection and secretion |
|
|
Where is stratified columnar epithelium found? |
Rare cells - found in male urethra and large ducts of some glands |
|

|
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
What is the main function of transitional epithelium? |
Stretching and distension |
|
|
Where is transitional epithelium found? |
The ureters, urinary bladder, and part of urethra |
|
|
What is the main function of connective tissue? |
Structure of the body - most abundant and widely distributed of the tissue types |
|
|
What are three distinct functions of connective tissue? |
Protection, support, connection of other tissues of the body |
|
|
What is the noncellular nonliving material between connective tissue cells called? |
The matrix |
|
|
Are connective tissues vascularized? |
Yes, highly |
|
|
What are the four classifications of connective tissue? |
Connective tissue proper Cartilage Bone Blood |
|
|
What is the extracellular matrix? |
Nonliving material between the cells |
|
|
Where does the extracellular matrix come from? |
It is produced by the cells and then extruded |
|
|
What is the function of the extracellular matrix? |
Primarily responsible for strength associated with connective tissue |
|
|
What are the two components of the extracellular matrix? |
Ground substance and fibers |
|
|
What is the ground substance in the extracellular matrix? |
Composed of interstitial fluid, cell adhesion proteins, and proteoglycans |
|
|
What is the function of the fibers in the extracellular matrix? |
Provision of support |
|
|
What types of fibers are found in the extracellular matrix? |
Collagen (white) fibers, elastic (yellow) fibers, reticular (fine collagen) fibers |
|
|
Which fibers are most abundant in the extracellular matrix? |
Collagen |
|
|
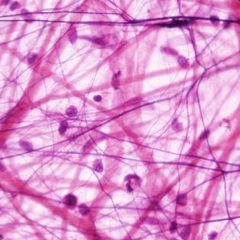
Areolar Connective Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of areolar connective tissue? |
Wrapping and cushioning of organs |
|
|
Where is areolar connective tissue found? |
Widely distributed under epithelia of the body - packages organs and surrounds capillaries |
|
|
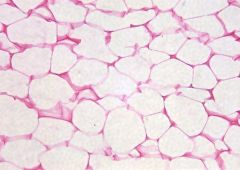
Adipose Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of adipose tissue? |
Reserve fuel, insulation, supports and protects organs |
|
|
Where is adipose tissue found? |
Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, in breasts |
|
|
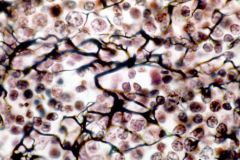
Reticular Connective Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of reticular connective tissue? |
Structure of tissues, supports other cell types |
|
|
Where is reticular connective tissue found? |
Lymph organs - lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen |
|
|
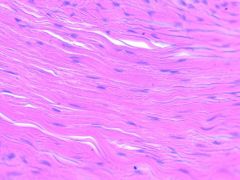
Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
|
|
What is the main function of dense regular connective tissue? |
Attaches muscle to bones, attaches bones to bones, withstands great pulling force |
|
|
Where is dense regular connective tissue found? |
Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |
|
|
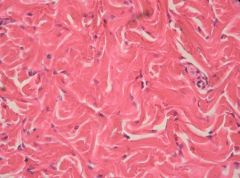
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of dense irregular connective tissue? |
Able to withstand tension exerted in many directions and provides structural strength |
|
|
Where is dense regular connective tissue found? |
Fibrous capsules of organs and joints, dermis of the skin, submucosa of GI tract |
|
|
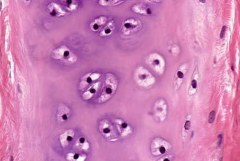
Hyaline Cartilage |
|
|
What is the function of hyaline cartilage? |
Support and reinforcement, resilient cushion |
|
|
Where is hyaline cartilage found? |
Ebryonic skeleton, ends of long bones, costal cartilage, cartilage of nose, trachea, and larynx |
|
|
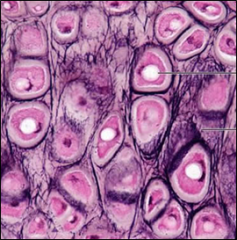
Elastic Cartilage |
|
|
What is the main function of elastic cartilage? |
Maintaining the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility |
|
|
Where is elastic cartilage found? |
External ear and epiglottis |
|
|
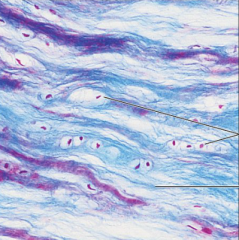
Fibrocartilage |
|
|
What is the function of fibrocartilage? |
Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock |
|
|
Where is fibrocartilage found? |
Intervertebral discs, pubis symphysis, knee joint |
|

|
Bone |
|
|
What is the function of bone? |
Support and protection, levers for muscles to act on, stores calcium and other minerals and fat |
|
|
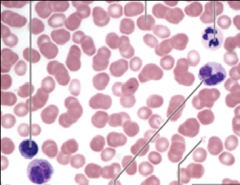
Blood |
|
|
What is the function of blood? |
Transport of gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances |
|

|
Skeletal Muscle Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of skeletal muscle tissue? |
Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression, voluntary control |
|
|
Where is skeletal muscle tissue found? |
Skeletal muscles, attached to bones or occasionally skin |
|

|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of cardiac muscle tissue? |
Propel blood into circulation, involuntary control |
|
|
Where is cardiac muscle tissue found? |
The walls of the heart |
|

|
Smooth Muscle Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of muscle tissue? |
Propels substances or objects along internal passageways - involuntary control |
|
|
Where is smooth muscle tissue found? |
Mostly in the walls of hollow organs |
|
|
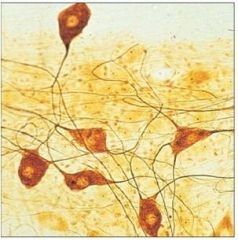
Nervous Tissue |
|
|
What is the function of nervous tissue? |
Transmission of electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors |
|
|
Where is nervous tissue found? |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
|
|
What effect will an isotonic solution have on a cell? |
Cells retain their normal size |
|
|
What effect will a hypertonic solution have on a cell? |
Cells lose water by osmosis and shrink in a hypertonic solution (crenate) |
|
|
What effect will a hypotonic solution have on a cell? |
Cells gain water by osmosis until they become bloated and burst (lyse) |

