![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of muscle
|
Voluntary-skeletal muscle fibers, striations-light and dark bands
Involuntary- smooth, myocytes relatively short Cardiac- myocytes, involuntary, striated |
|
|
Functions of muscles
|
movement
stability communication control body openings heat production |
|
|
Movement
|
place to place
move body contents |
|
|
stability
|
maintain posture
resist pull of gravity hold articulating bones in place |
|
|
communication
|
facial expressions
body language writing speech |
|
|
Universal characteristics of all muscle
|
ECCEE:
Excitability Conductivity Contractivity Extensibility Elasticity |
|
|
Action of muscle groups
|
PAFS:
Prime mover Antagonist Fixator Synorgist |
|
|
Intrinsic muscles
|
Entirely contained within a particular region. ie between metacarpal bones of hand
|
|
|
Extrinsic muscles
|
Acts upon a designated region but has its origin elsewhere.
ie. move of the fingers by muscles of the forearm |
|
|
Anatomy of a muscle
|
BIO:
Belly Insertion Origin |
|
|
Classification of muscles
|
CCFPP:
Circular Convergent Fusiform Parallel Pennate - uni, bi, multi |
|
|
Connective tissue and fascicles - mysiums and fascias
|
PEEDS:
Perimysium-thick tissue that wraps muscle fibers in bundles calls fassicles Endomysium-areolar tissue surrounds each muscle fiber Epimysium-surrounds muscle,extends beyond muscle to form tendons Deep fascia-seperates neighboring muscles Superficial fascia-seperates muscle from skin. |
|
|
Epimysium
|
surrounds entire muscle
DIDS: Direct attachment - collegen fibers w periosteum Indirect attachment - collegen fiber to tendon merges periosteum Deep fascia - between muscles Superficial fascia - between muscles and skin |
|
|
Myofilaments
|
TTE:
Thick filaments Thin filaments Elastic filaments |
|
|
Anatomy of muscle fiber
|
STSS:
Sarcolemma T-Tubules Sarcoplasm Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Neuromuscular Junction
|
Motor neuron
Neuromuscular junction Neurotransmitters Motor Units |
|
|
4 stages of contraction
|
Excitation
Excitation - contraction coupling Contraction Relaxation |
|
|
Calcium - essential component in...
|
nervous, muscular, blood clotting, exocytosis
|
|
|
Calcium is at the ...
|
start of everything & when they permeate a membrane it makes nerves, muscles and blood flow correctly
|
|
|
Ca & Phosphate homeostasis
|
Phosph -DNA, ATP & acid/base bal
Ca - nervous, muscular sys, blood clotting, exocytosis |
|
|
Hypocalcemia v Hypercalcemia
|
too low v too high
hypo - muscle spasm in hands and feet |
|
|
Phosphorus
85-90% stored in _____. 500-___g on human body. HP04 -2 - is ... H2PO4 - is... |
Bones
800g monohydrogen phosphate dihydrogen phosphate |
|
|
Calcitriol is activated by _____.
Acts like a _____. Stimulates the ______. Reduces the ______. Promotes ______ ______. |
Vit D.
hormone Small intestine urinary excretion of Ca and Ph. osteoclast activity - to get bone out for blood stream for nourishment of body. |
|
|
In what areas in our bodies do we find Ca and Phosphorus? How are each important?
|
found in hydroxyapitie & in bones.
Important for nerves, blood & our bodies to function correctly. |
|
|
How is Calcitriol formed?
|
7-dehydrocholesterol circulates thru the dermal capillaries where UV radiation converts it to Vit D.
Liver adds hydroxyl group converting it to calcidiol. Kidneys add another hydroxyl group converting to calcitriol. |
|
|
Vit d def (lack of cacitriol) causes _____ in children and _____ in adults.
these are ____ ____ diseases |
rickets
osteomalacia soft bone |
|
|
The hormone Calcitonin is secreted by __ cells in the _____ _____.
Important role in ________. Lowers concentration of ____ in blood and puts into forming bone. It _____ osteoclasts and _____ osteoblasts |
C, thyroid gland
children Calcium inhibits, stimulates |
|
|
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) -
____ blood Ca levels. Osteoblast _______. Osteoclast _______. |
raises
inhibitor stimulus |
|
|
PTH _____ Ca excretion and _____ phosphate excretion.
|
reduces, increases
|
|
|
PTH - stimulates ...
|
enzyme from kidneys that stimulates calcitriol synthesis.
|
|
|
Bone disorders:
osteoporitis rickets osteosarcoma |
bone loss from too much Ca loss
vit d def most common and most deadly |
|

|
cardiac muscle
|
|

|
intercalated discs
|
|
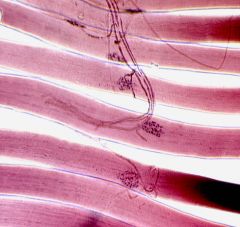
|
motor end unit
|
|

|
neuromuscular junction
|
|

|
smooth muscle
|
|

|
smooth muscle
|
|

|
striated muscle
|
|
|
circular
|
orbicularis oculi
|
|
|
convergent
|
pectorialis major
|
|
|
fusiform
|
biceps brachii
|
|
|
parallel
|
rectus abdominus
|
|
|
unipennate
|
palmer interosseous
|
|
|
bipennate
|
rectus femoris
|
|
|
multipennate
|
deltoid
|

