![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is consumer surplus? |
The difference between the price that consumers are willing and able to pay for good or service and the market price. i.e. the difference between the total value consumers place on all units consumed and the price they pay in order to purchase that good or service. It represents a benefit (additional utility) to the consumer. |
|
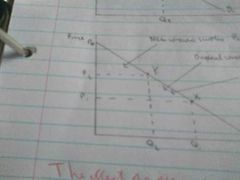
What area is original consumer surplus, new consumer surplus, and change in consumer surplus? |
Old consumer surplus: P0P1X New consumer surplus: P0P2Y Change in CS: P1P2XY (fall) |
|
|
The effect of a change in price on Consumer surplus will depend on... |
Size of the price change PED (if PED is inelastic, ∆P will lead to a relatively smaller change in CS). Ceteris Paribus |
|
|
What is producer surplus? |
The difference between the market price a firm receives and the price at which they would be prepared to supply. |
|

On this graph, where is original producer surplus, new producer surplus, and change in producer surplus? |
Old PS: PeX0 New PS: P1Y0 increase in PS: P1YXPe |
|
|
The size of a change in PS depends on... |
Size - if the increase in price is relitavely large then this means the increase in PS is also relitavely large. PES - if PES is more elastic then more firms will join the market/firms will expand output as they can make more profit. This means that there is a greater increase/decrease in PS. Ceteris Paribus - changes in other factors may affect size of shift in supply. |
|
|
What is the effect of an increase in demand on producer and consumer surplus? |
PS increases, CS increases. |
|
|
What is the effect of an increase in supply on consumer and producer surplus? |
CS increases, PS increases. |
|
|
What does a market do? |
Coordinates buyers and sellers (consumers and producers) to exchange goods and services. |
|
|
What does the interaction of demand and supply in a market determine? |
Equilibrium price and quantity. |
|
|
When will a market not achieve allocative efficiency? |
If market failure occurs. |
|
|
When is a market allocatively efficient? |
When consumer and producer surplus (social surplus/social welfare) is maximised. At the equilibrium point. |
|
|
If quantity demanded equals quantity supplied, a market is said to be... |
Allocatively efficient. |
|
|
Why is this so? |
Because resources are organised efficiently, and social surplus is maximised. |
|
|
What occurs in any situation but market equilibrium? |
Social welfare loss. |
|
|
In a free market economy, what do prices act to do? |
Signal information Ration/allocate scarce resources amongst competing uses (on basis of ability to pay) To provide an incentive via profit/utility maximisation. |
|
|
If their is excess demand in a market, how do prices help to achieve allocative efficiency? |
Prices rise. This leads to rationing (some consumers leave the market) and a contraction of Qd. In addition, signalling occurs due to the higher price, more producers enter the market to fulfil their incentive of profit maximisation. Supply extends. This leads to the market reaching equilibrium price. |
|
|
If their is excess supply in a market, how do prices help to achieve allocative efficiency? |
Price decreases. This leads to rationing, as some producers leave the market, so there is a contraction in Qs. Signalling by lower prices means more consumers enter the market in order to maximise their utility. Qd extends. A new equilibrium price is reached, with excess supply eliminated. |
|
|
In a free market system, what does the price mechanism do? |
Distribute goods and services to achieve allocative efficiency. |
|
|
When will social surplus be maximised? |
When demand = supply, at the equilibrium point. |
|
|
At equilibrium output, what is the price that consumers lay first good or service equal to? |
The additional cost to society of producing it. |
|
|
Even if firms break even in economic terms, do they still make some profit. |
Yes, because profit is a cost of production, so a certain level of profit is included in calculating total costs. |
|
|
How did Adam Smith describe the market system? |
"The invisible hand" guiding people's actions. |
|
|
In a free market system, what is assumed to be consumers motivation? |
To maximise utility |
|
|
In a free market system, what is assumed to be firms' motivation? |
To maximise profit. |
|
|
In a free market system, what is assumed to be the factors of producion's motivation? |
To maximise income. |
|
|
What is consumer sovereignty? |
When, in a market system, consumer preferences determine how resources are employed and what goods and services are produced. |
|
|
When does market failure occur? |
When The price mechanism leads to an inefficient allocation of goods and services. |
|
|
What do MSC and MSB mean? |
MSC: Marginal social cost. MSB: Mariano social benefit. |
|
|
What do MPB nd MPC mean? |
MPB: Marginal private benefit MPC: Marginal private cost |
|
|
When is the equilibrium price allocatively efficient? |
When supply = MSC and demand = MSB, so all costs and benefits are taken into account. |
|
|
Social costs = ? |
private costs + external costs |
|
|
Social benefits = ? |
Private benefits + external benefits |
|
|
What does private/internal mean? |
Incurred by consumers/firms directly involved in the economic transaction. |
|
|
What is an external cost/benefit? |
A cost/benefit incurred by third parties i.e. those not involved I the economic transaction. |
|
|
What are externalities? |
Cost/benefits for their parties not associated with the economic transaction/not reflected in market price. |
|
|
What are the 4 types of externality? |
Positive production externality. Negative production externality. Positive consumption externality. Negative consumption externality. |
|
|
What is the Y axis of a curve labelled when showing externalities? |
Price, cost, benefit. |
|
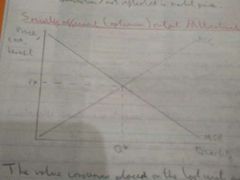
Why is this market allocatively efficient? |
Because supply = MSC and demand = MSB |
|
|
In an allocatively efficient market, what is the value consumers place on the last unit produced equal to? |
The full cost to society of producing the last unit. |
|
|
What needs to be taken into account for the market equilibrium to be equal to the allocatively efficient output? |
All costs and benefits. |
|
|
When MSB = MPC is the market allocatively efficient? |
No, it is only if MSB = MSC. |
|
|
If market quantity is greater than the social optimum, does this good have a negative or positive externality? Is it underproduced or overproduced? |
At outputs between the social optimum and market quantity, the cost to society is greater than the benefit. Therefore the good is overproduced and has negative externalities, resulting in a welfare loss. |
|
|
If market quantity is less that the social optimum, does this good have positive or negative externalities? Is it underproduced/consumed or overproduced/consumed? |
The cost to society is less than the befit at outputs from market quantity to the social optimum. This good is underproduced/consumed. This represents a welfare loss. This good has positive externalities. |
|
|
Draw a diagram showing a negative production externality. |
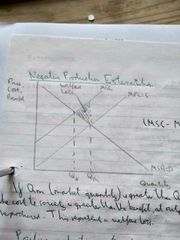
|
|
|
What does MEC (Marginal external cost) = ? |
MSC (marginal social cost) - MPC (marginal private cost) |
|
|
Draw a diagram showing welfare loss from a positive production externality. |

|
|
|
Draw a diagram showing the welfare loss from a negative consumption externality. |
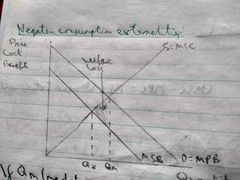
|
|
|
Draw a diagram showing the welfare loss from a positive consumption externality. |
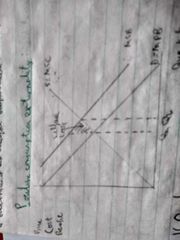
|
|
|
When does a welfare loss occur? |
When there is a divergence between Qm and Q*. |
|
|
What does the presence of externalities in a market mean? |
There will be a loss of social welfare in the market (allocative inefficiency). |
|
|
What is the effect of a negative production externality? |
The marginal social cost exceeds the marginal private cost. The good is overproduced. The market fails as it produces a level of output that is greater than the he socially optimum level and there is a welfare loss to society. |
|
|
What is the effect of a positive production externality? |
The marginal social cost is less than the marginal private cost. The good is underproduced. The market fails as it produces a level of output that is less than the he socially optimum level and there is a welfare loss to society. |
|
|
What is the effect of a negative consumption externality? |
The marginal social benefits are less than marginal private benefits. The good is over-consumed. The market fails as it produces an equilibrium level of output hat is greater than the socially optimum level of output and there is a welfare loss to society. |
|
|
What is the effect of a positive consumption externality? |
The marginal social benefit exceeds marginal private benefit. The good is under-consumed. The market fails as it produces an equilibrium level of output hat is less than the socially optimum level of output and there is a welfare loss to society. |

